3 Common Types Of Building Foundations Brown Concrete And Backhoe

3 Common Types Of Building Foundations Brown Concrete And Backhoe 3 types of building foundations & their applications. 1. individual footings. in warm areas where the soil isn’t subject to regular freezing, individual footing foundations are common. this technique is frequently used when the weight of the building is supported by columns and features a square pad of concrete underneath the soil. Description: pier and beam foundations consist of a series of piers (columns) that support beams running across the structure. this type of foundation elevates the building and provides a crawl space underneath. advantages: provides access to plumbing and electrical systems.

3 Common Types Of Building Foundations Brown Concrete And Backhoe A building’s foundation is a critical structural component that transfers loads from the building into the underlying soil or bedrock. as civil engineers, understanding the principles behind foundation design and the various types of foundations is key for any construction project. in this in depth guide, we’ll explore what building. 1. mat (raft) foundation. consisting of a single large continuous rectangular or circular slab under a building, the mat (or raft) foundation carries and distributes an entire load of a structure. raft foundations can support a number of columns and walls at once and spread the load out under the entire footprint of the building. This foundation type can be used to help stabilize a building in loose soil. most common foundation types for commercial buildings. commercial buildings may use one of the following foundation types: pile, slab on grade, mat, spot footing, caisson, and t shaped. when dealing with loose soil conditions, commercial buildings may rely on a pile. These types of foundations are commonly used for residential buildings, light commercial buildings, and smaller structures. in contrast, deep foundations (usually piles) are used when the soil is weak or unstable, and the building's weight needs to be supported by deeper, stronger soils or rocks.
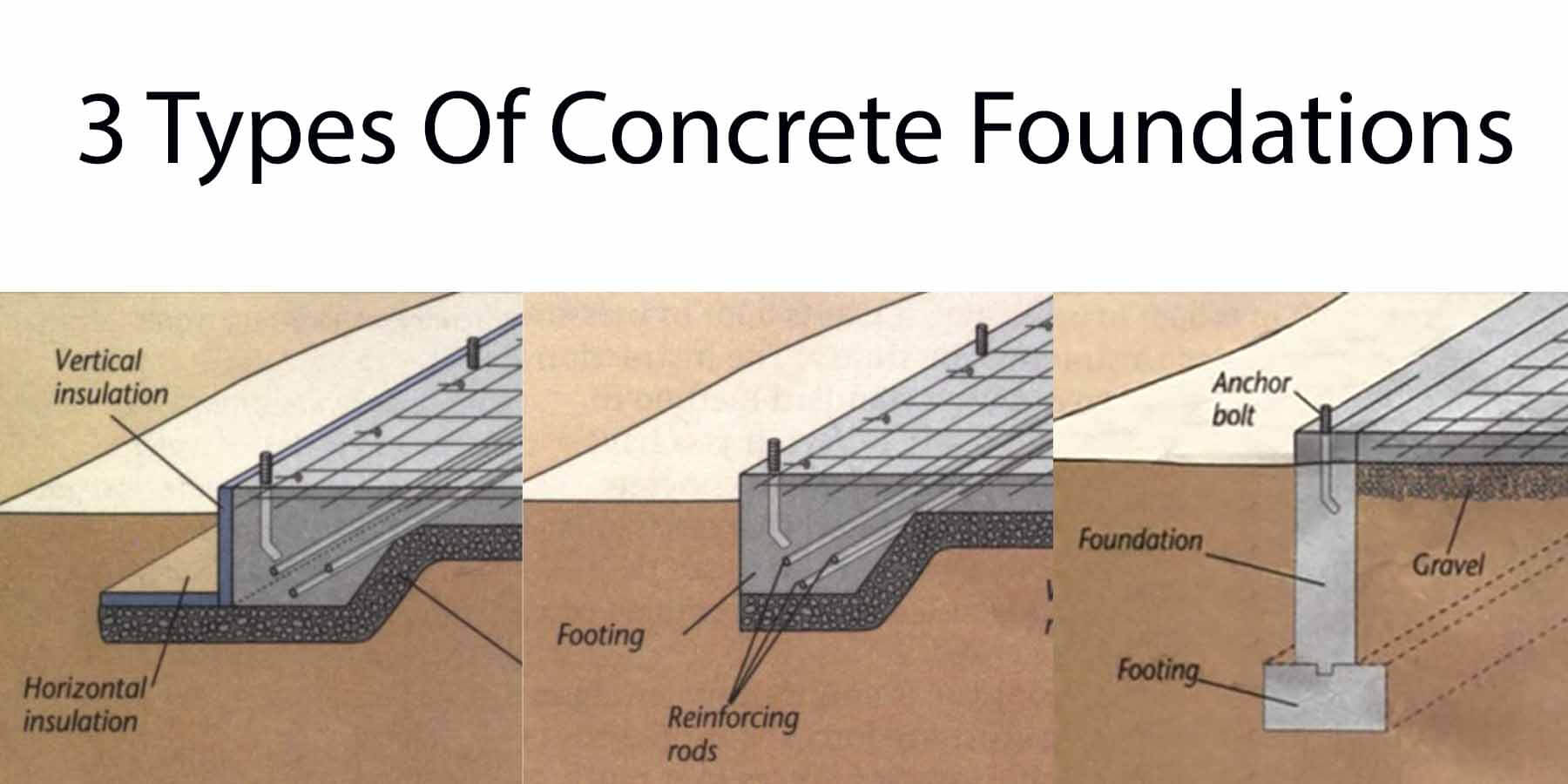
3 Types Of Concrete Foundations Engineering Discoveries This foundation type can be used to help stabilize a building in loose soil. most common foundation types for commercial buildings. commercial buildings may use one of the following foundation types: pile, slab on grade, mat, spot footing, caisson, and t shaped. when dealing with loose soil conditions, commercial buildings may rely on a pile. These types of foundations are commonly used for residential buildings, light commercial buildings, and smaller structures. in contrast, deep foundations (usually piles) are used when the soil is weak or unstable, and the building's weight needs to be supported by deeper, stronger soils or rocks. For the sake of keeping this article organized, we’ll discuss the three types of foundations you’re most likely to encounter in this market, starting with the least expensive, concrete slab foundation. 1. concrete slab foundation. a concrete slab is one of the most common types of house foundations, requiring the least amount of lot prep to. Strip foundations. strip foundations are the cheapest and most common. in the method, each strip foundation supports a load bearing wall (or row of columns). trenches for the strips are dug out by digger to match the plan of the building’s load bearing walls, then a relatively shallow slab of concrete is poured into the bottom of each trench.
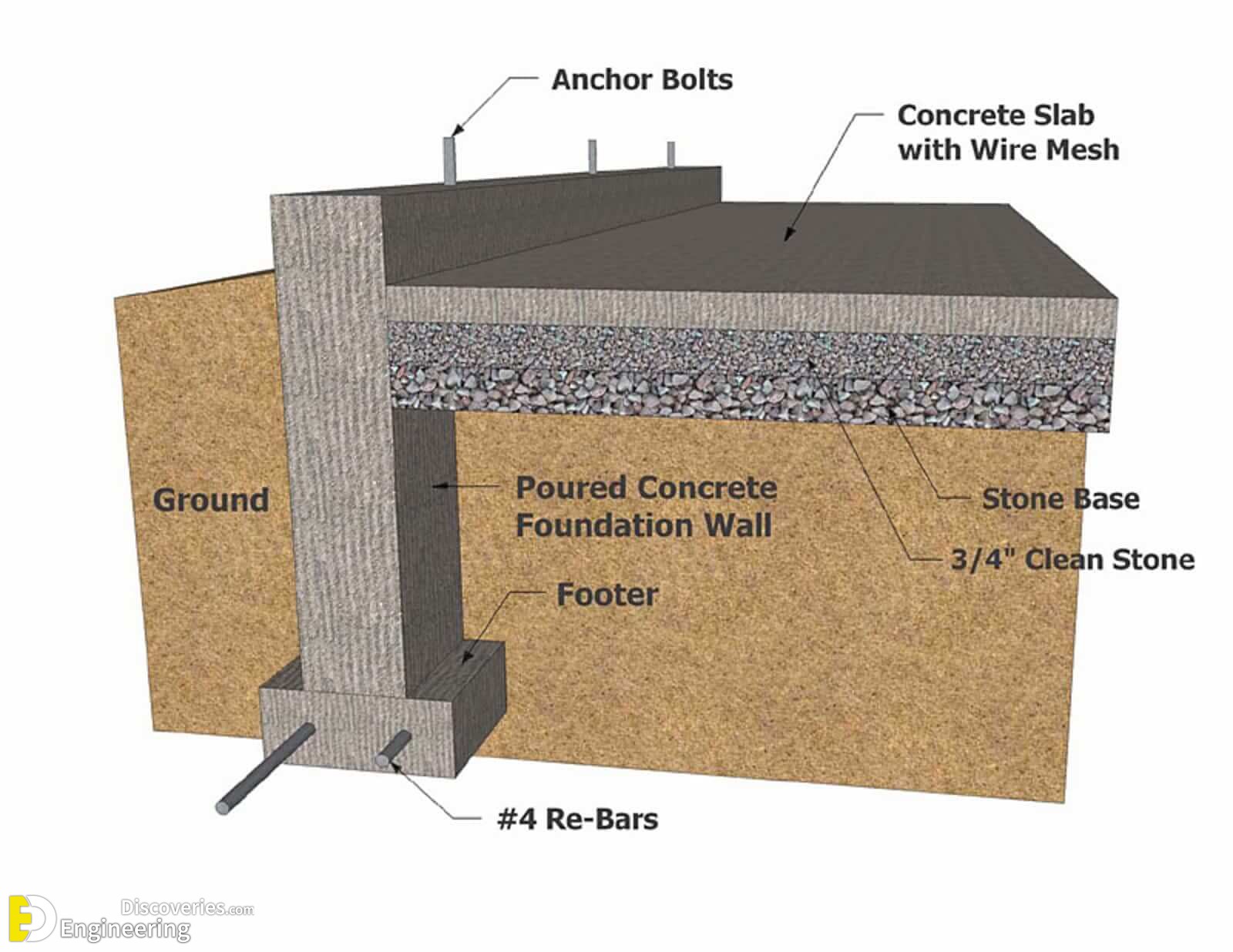
3 Types Of Concrete Foundations Engineering Discoveries For the sake of keeping this article organized, we’ll discuss the three types of foundations you’re most likely to encounter in this market, starting with the least expensive, concrete slab foundation. 1. concrete slab foundation. a concrete slab is one of the most common types of house foundations, requiring the least amount of lot prep to. Strip foundations. strip foundations are the cheapest and most common. in the method, each strip foundation supports a load bearing wall (or row of columns). trenches for the strips are dug out by digger to match the plan of the building’s load bearing walls, then a relatively shallow slab of concrete is poured into the bottom of each trench.

Comments are closed.