5 Types Of Consumers Biology

Types Of Consumers In Ecosystem Examples of tertiary consumers are hawks, snakes, crocodiles and some big cats. tertiary consumers can be either omnivorous or carnivorous. they feed on primary and secondary consumers, and may also eat producers (plants). for a food chain to have a tertiary consumer, there must be a secondary consumer available for it to eat. Group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, and from prey, predators, scavengers, and decomposers. food web. noun. all related food chains in an ecosystem. also called a food cycle. herbivore. noun. organism that eats mainly plants and other producers. molecule.
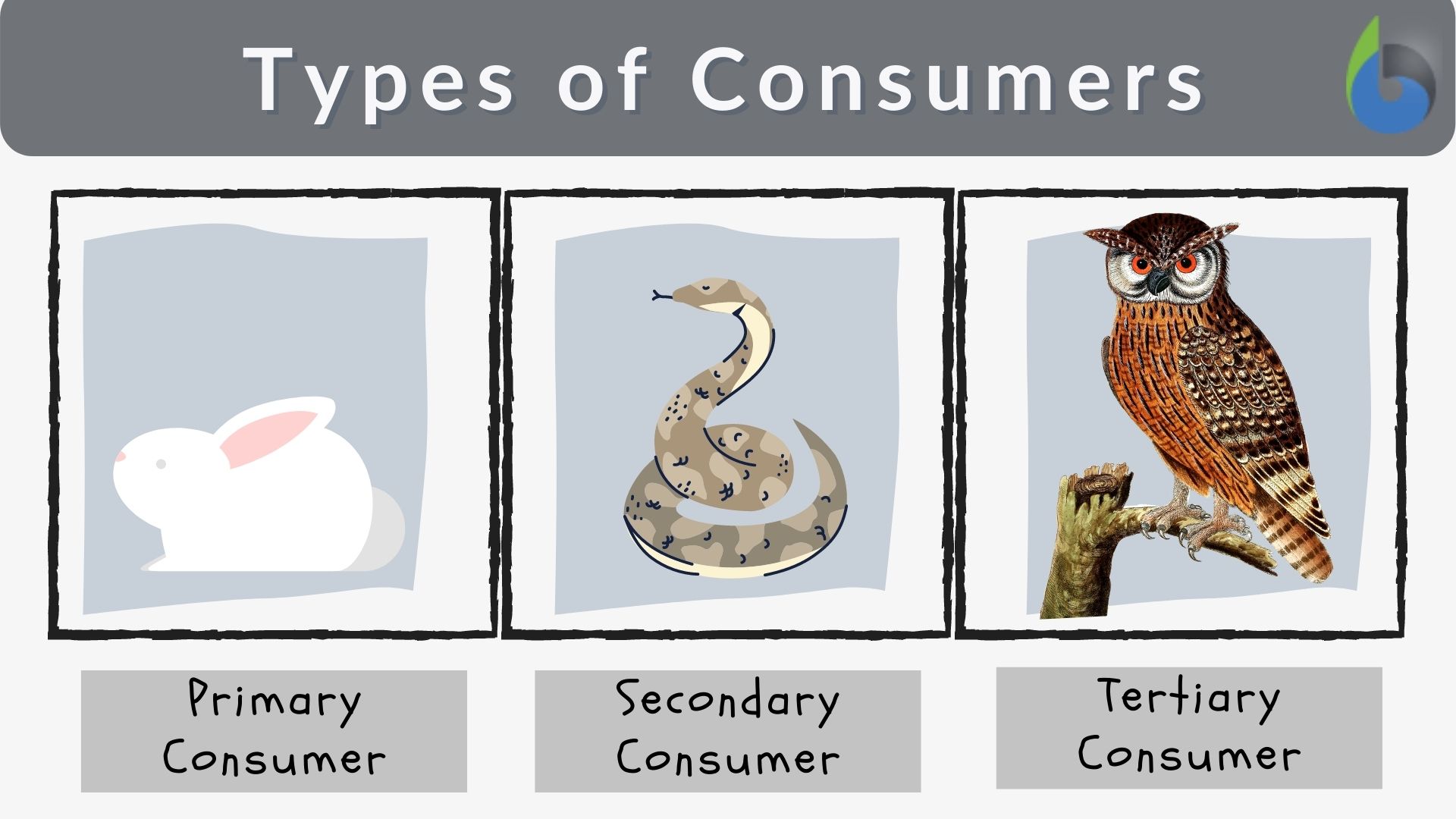
Biotic Factor Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary Types of consumer. 1. primary consumers. herbivores are the dominant consumers. their food source is the first trophic level in the food web, which consists of plants. plants are also considered autotrophs. autotrophs make their own energy from sunlight and basic nutrients through photosynthesis; the phrases producer and autotroph have the same. Learn the consumer definition in biology with examples. see the different classifications of consumers in an ecosystem. updated: 11 21 2023 there are four main types of consumers:. A consumer in a food chain is a living creature that eats organisms from a different population. a consumer is a heterotroph and a producer is an autotroph. like sea angels, they take in organic moles by consuming other organisms, so they are commonly called consumers. heterotrophs can be classified by what they usually eat as herbivores. Consumer hierarchy plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance and functionality of ecosystems. each level, from primary to quaternary consumers, contributes uniquely to energy flow and nutrient cycling. grasping this hierarchical structure allows for deeper insights into ecological relationships and the overall health of natural habitats.

What Kind Of Consumers Are Plants At Marian Corbett Blog A consumer in a food chain is a living creature that eats organisms from a different population. a consumer is a heterotroph and a producer is an autotroph. like sea angels, they take in organic moles by consuming other organisms, so they are commonly called consumers. heterotrophs can be classified by what they usually eat as herbivores. Consumer hierarchy plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance and functionality of ecosystems. each level, from primary to quaternary consumers, contributes uniquely to energy flow and nutrient cycling. grasping this hierarchical structure allows for deeper insights into ecological relationships and the overall health of natural habitats. Scavengers include vultures, raccoons, and blowflies. a tiny minority of plants—including venus flytraps and pitcher plants—are also carnivorous. these plants trap and digest insects. some fungi are carnivorous as well. carnivorous fungi capture and digest microscopic protozoan organisms such as amoebas. [figure 5]. Organisms that manufacture their own food are known as producers or autotrophs. energy from the sun or chemicals is one of the major ingredients of this food. with the help of water, producers convert this energy into sugar or food, which are usable forms of energy. producers are largely green plants, which use sunlight and water to generate.

Consumers In Ecosystem Definition Classifications Lesson Study Scavengers include vultures, raccoons, and blowflies. a tiny minority of plants—including venus flytraps and pitcher plants—are also carnivorous. these plants trap and digest insects. some fungi are carnivorous as well. carnivorous fungi capture and digest microscopic protozoan organisms such as amoebas. [figure 5]. Organisms that manufacture their own food are known as producers or autotrophs. energy from the sun or chemicals is one of the major ingredients of this food. with the help of water, producers convert this energy into sugar or food, which are usable forms of energy. producers are largely green plants, which use sunlight and water to generate.

Energy Flow Diagram Biology

Comments are closed.