5 Years Energy Consumption Over Routes During Peak Hours Peak 1

5 Years Energy Consumption Over Routes During Peak Hours Peak 1 Download scientific diagram | 5 years energy consumption over routes during peak hours (peak 1, peak 2, and peak 3). from publication: a novel simulated annealing based electric bus system design. The impact of solar on peak demand. peak demand typically occurs during the heat of the day in summer, which are the exact same times when solar panels produce the most electricity. as a result, solar can help offset your pull from the grid during those peak hours, lowering the overall need for power and reducing your individual peak demand.
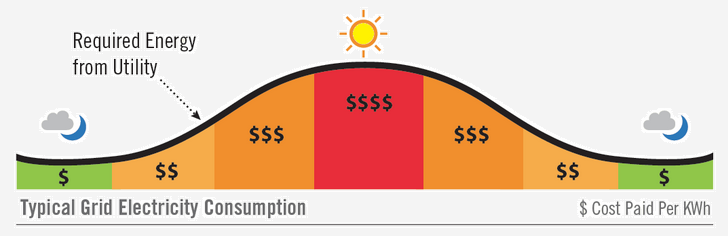
Missed Opportunity Time Of Use Rates For Large Energy Consumers These are typically the hours when a large number of people and businesses are actively using electrical appliances, devices, and machinery, resulting in a significant strain on the electrical grid. off peak hours, on the other hand, denote times of lower electricity demand when consumption is reduced, usually during less busy or nighttime periods. Shift chores to off peak hours (or delay them for longer if possible) wash clothes in cold water and hang them to dry; if needed, give them a one minute spin in the dryer (after peak) to soften and reduce wrinkles. take a shower rather than a bath to save 45 to 50 gallons of water; challenge yourself to keep it under five minutes [1]. Peak hours vary depending on the time of year and region of the country. as a general rule, think of peak hours as the time during which most people are getting home from work for the day. Capacity produced continuously over a period of one year. 1 amw = 1 mw x 8760 hours year = 8760 mwh • load factor. the ratio of average energy savings to peak energy savings. this is also known as “peak coincidence factor” (nyserda 2008). more generally, load factor is the average demand divided by any number of peak demands, such as load.

Comparison Of Energy Consumption Per Packet During Peak And Non Peak Peak hours vary depending on the time of year and region of the country. as a general rule, think of peak hours as the time during which most people are getting home from work for the day. Capacity produced continuously over a period of one year. 1 amw = 1 mw x 8760 hours year = 8760 mwh • load factor. the ratio of average energy savings to peak energy savings. this is also known as “peak coincidence factor” (nyserda 2008). more generally, load factor is the average demand divided by any number of peak demands, such as load. In texas, for example, peak hours often occur from early afternoon until the evening (approximately 1 pm to 5 pm), depending on the time of year and specific location. off peak hours are when the demand for electricity drops, and thus, the cost is lower. this usually includes nighttime and early morning hours. Generally, school and working hours typically range between 8 am and 5 pm, meaning the electricity demand is low during these times. remember that these off peak hours are only relevant for weekdays because energy usage will differ on weekends. here are the standard off peak electricity hours for various time zones. peak hours electricity vs.
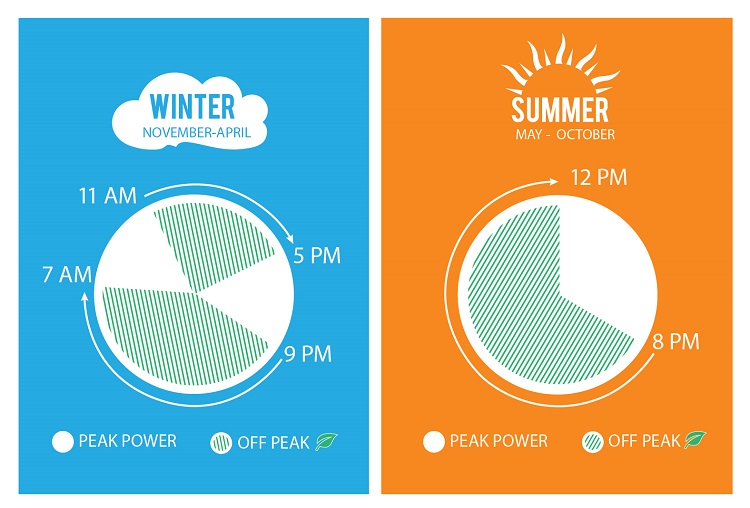
Understanding Peak Power Eweb In texas, for example, peak hours often occur from early afternoon until the evening (approximately 1 pm to 5 pm), depending on the time of year and specific location. off peak hours are when the demand for electricity drops, and thus, the cost is lower. this usually includes nighttime and early morning hours. Generally, school and working hours typically range between 8 am and 5 pm, meaning the electricity demand is low during these times. remember that these off peak hours are only relevant for weekdays because energy usage will differ on weekends. here are the standard off peak electricity hours for various time zones. peak hours electricity vs.

Comments are closed.