A Market With 40000 Consumers And 20000 Firms Solve For Equilibrium

A Market With 40000 Consumers And 20000 Firms Solve For Equilibrium There are 40,000 consumers, each with utility given by u = xy. consumer's income = $500 and price of good y = $1.there are 20,000 firms, each with a product. Course: ap®︎ college macroeconomics > unit 1. lesson 6: market equilibrium, disequilibrium, and changes in equilibrium. market equilibrium. changes in market equilibrium. changes in equilibrium price and quantity when supply and demand change. lesson summary: market equilibrium, disequilibrium, and changes in equilibrium.
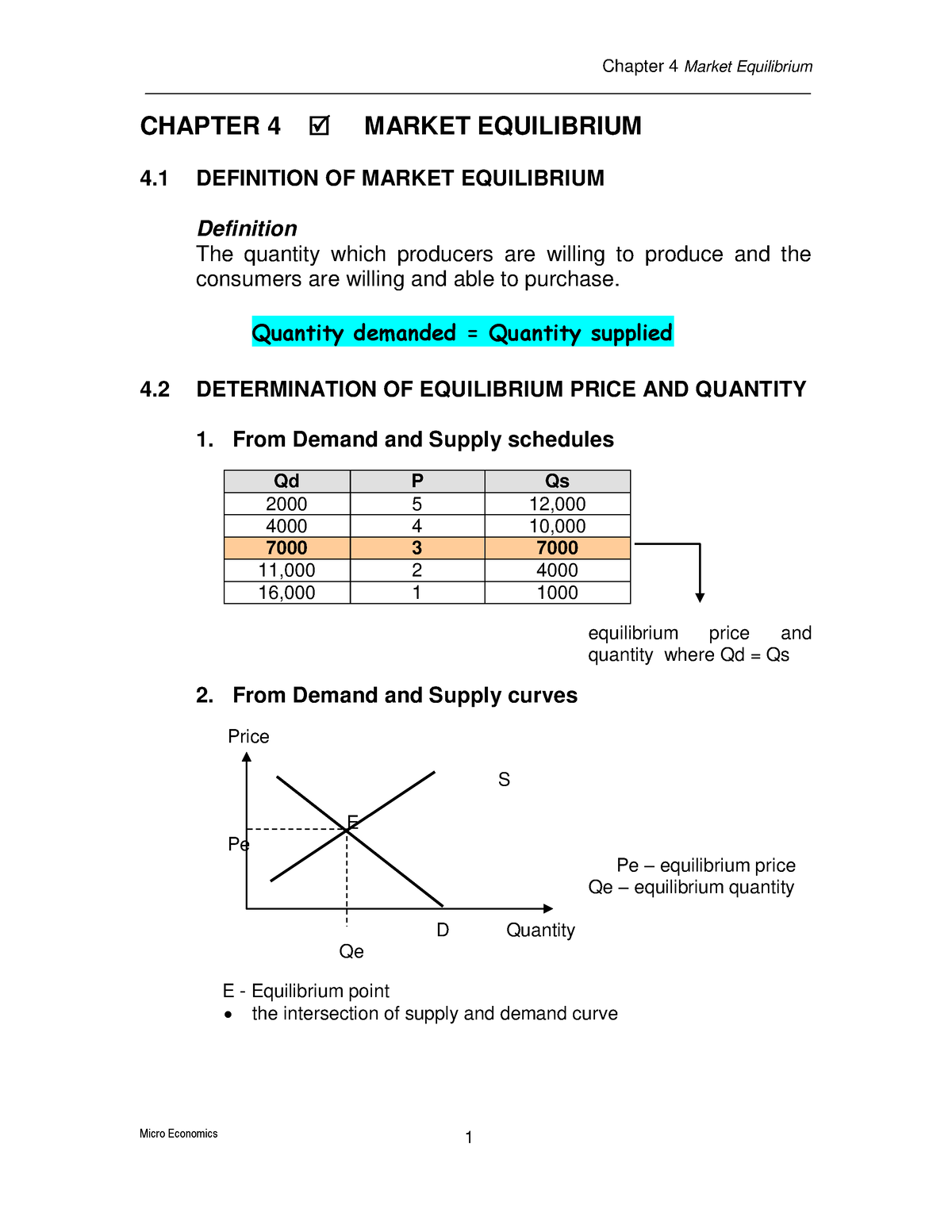
Chapter 4 Market Equilibrium Studocu Once the supply and demand curves are substituted into the equilibrium condition, it's relatively straightforward to solve for p. this p is referred to as the market price p*, since it is the price where quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded. to find the market quantity q*, simply plug the equilibrium price back into either the supply. Figure 3.4 demand and supply for gasoline the demand curve (d) and the supply curve (s) intersect at the equilibrium point e, with a price of $1.40 and a quantity of 600. the equilibrium price is the only price where quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied. at a price above equilibrium like $1.80, quantity supplied exceeds the quantity. The question is: suppose that our market consists of three consumers (say consumer 1, 2, and 3) with the individual demand curves q1 = 5 – p, q2 = 10 – 2p, and q3 = 7 .5p respectively. suppose that there are 4 identical firms with the marginal cost curves mc(q) = 1 .25q. The equations will be in terms of price (p) 3) solve for p, this is going to be your equilibrium price for the problem. 4) plug your equilibrium price into either your demand or supply function (or both but most times it will be easier to plug into supply) and solve for q, which will give you equilibrium quantity.

Solved Problem 1 Market Equilibrium And Efficiency Suppose Chegg The question is: suppose that our market consists of three consumers (say consumer 1, 2, and 3) with the individual demand curves q1 = 5 – p, q2 = 10 – 2p, and q3 = 7 .5p respectively. suppose that there are 4 identical firms with the marginal cost curves mc(q) = 1 .25q. The equations will be in terms of price (p) 3) solve for p, this is going to be your equilibrium price for the problem. 4) plug your equilibrium price into either your demand or supply function (or both but most times it will be easier to plug into supply) and solve for q, which will give you equilibrium quantity. Plug your numbers into the supply and demand equations: qs = x yp. qd = x yp. use qd = qs to find the equilibrium price. plug the price, or p, into either the supply equation or the demand equation to solve for equilibrium quantity. 1. plug your numbers into the supply function. download article. In the diagram below, the equilibrium price is p1. the equilibrium quantity is q1. if price is below the equilibrium. in the above diagram, price (p2) is below the equilibrium. at this price, demand would be greater than the supply. therefore there is a shortage of (q2 – q1) if there is a shortage, firms will put up prices and supply more.

Comments are closed.