Accounting Equation Accounting Corner
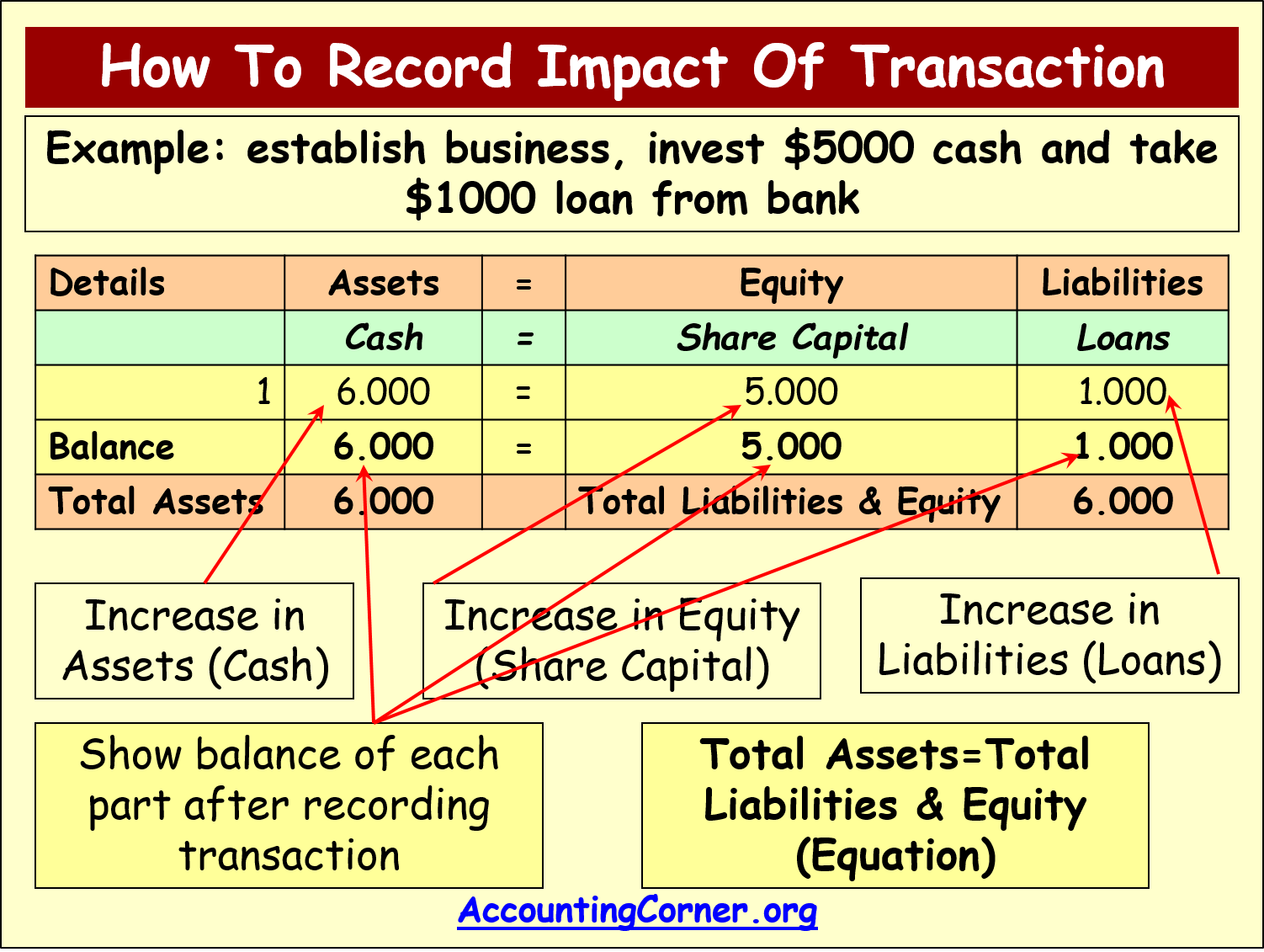
Accounting Equation Accounting Corner The accounting equation indicates different categories. therefore the assets, equity and liabilities, i.e. assets – cash, equity – share capital and liabilities – loans. these categories are impacted by the transaction analyzed. on the left side there is an increase in cash by $6,000. Balance sheet equation the balance sheet equation, also known as the accounting equation, is: assets=liabilities equityassets=liabilities equity definition assets: these are what a company owns or controls. they can be tangible, like machinery and real estate, or intangible, like patents and trademarks. liabilities: these are obligations that.
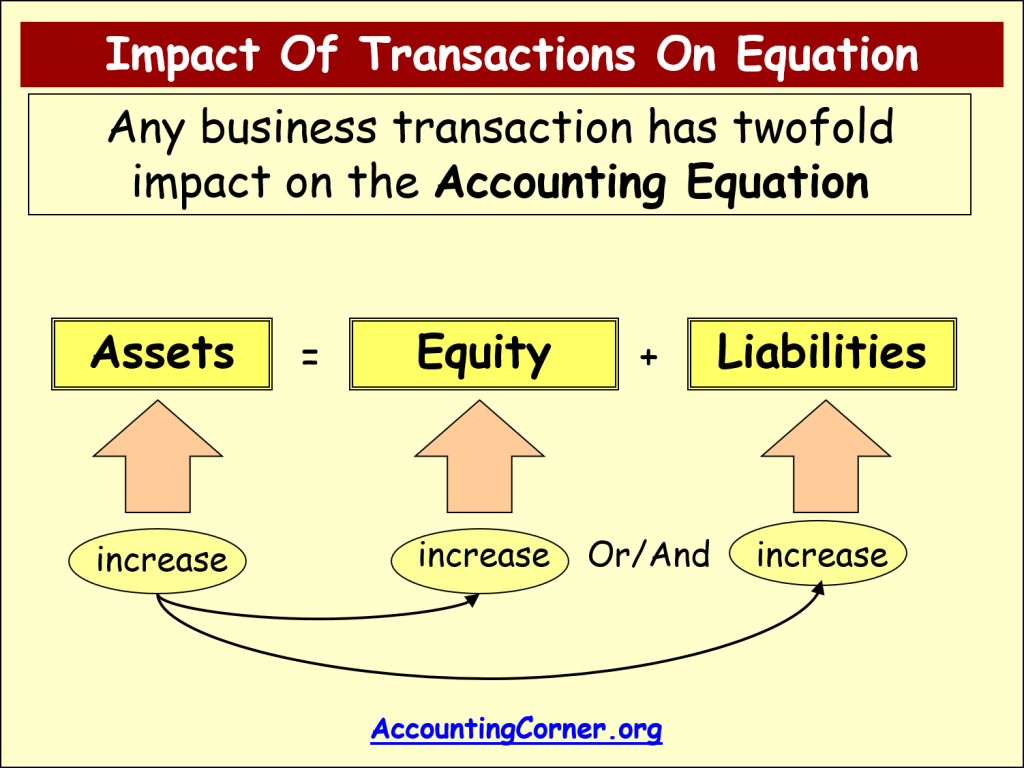
Accounting Equation Accounting Corner The accounting equation. the foundation of the balance sheet is the accounting equation: assets=liabilities equity. this equation ensures that the resources of a company (assets) are balanced by the claims against those resources (liabilities and equity). it reflects how a business is financed, either through external debts or internal investments. Like the accounting equation, it shows that a company’s total amount of assets equals the total amount of liabilities plus owner’s (or stockholders’) equity. the income statement is the financial statement that reports a company’s revenues and expenses and the resulting net income. The accounting equation is a basic principle of accounting and a fundamental element of the balance sheet. the equation is as follows: assets = liabilities shareholder’s equity. this equation sets the foundation of double entry accounting, also known as double entry bookkeeping, and highlights the structure of the balance sheet. The three elements of the accounting equation are assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity. the formula is straightforward: a company’s total assets are equal to its liabilities plus its.

Accounting Equation Accounting Corner The accounting equation is a basic principle of accounting and a fundamental element of the balance sheet. the equation is as follows: assets = liabilities shareholder’s equity. this equation sets the foundation of double entry accounting, also known as double entry bookkeeping, and highlights the structure of the balance sheet. The three elements of the accounting equation are assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity. the formula is straightforward: a company’s total assets are equal to its liabilities plus its. In fact, the entire double entry accounting concept is based on the basic accounting equation. this simple equation illustrates two facts about a company: what it owns and what it owes. the accounting equation equates a company’s assets to its liabilities and equity. this shows all company assets are acquired by either debt or equity financing. The accounting equation is the fundamental principle of accounting. it represents the relationship between a company's assets, liabilities, and equity. the accounting equation is the cornerstone of double entry accounting, ensuring that every financial transaction affects at least two accounts and maintaining the equation's balance.
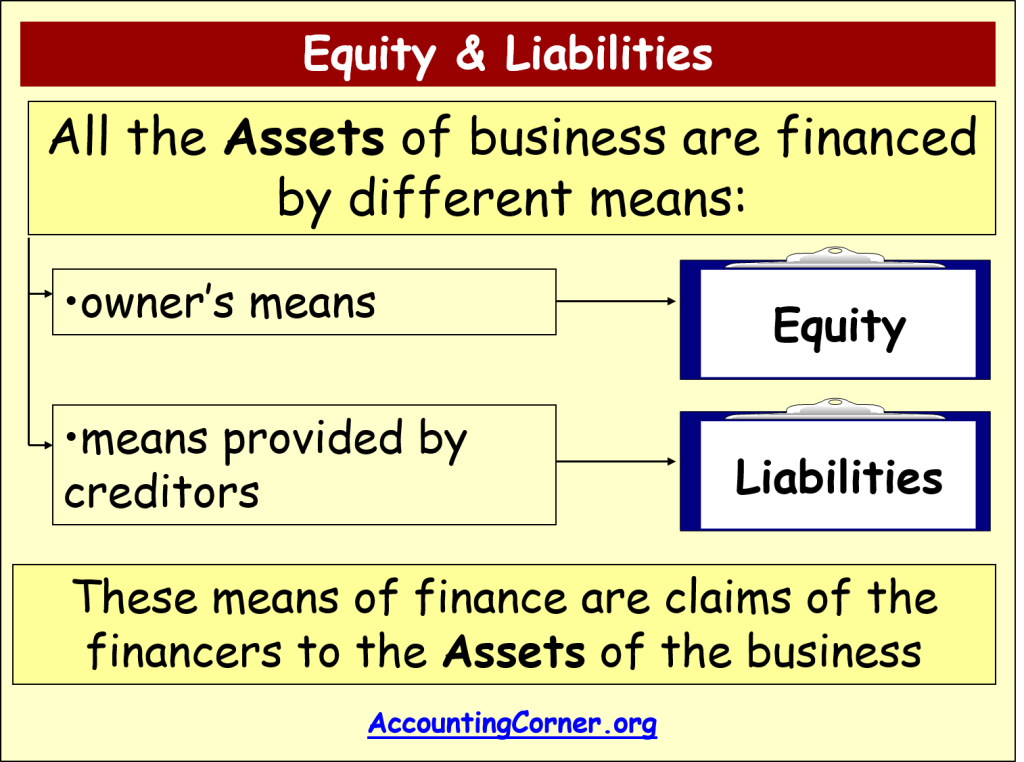
Accounting Equation Accounting Corner In fact, the entire double entry accounting concept is based on the basic accounting equation. this simple equation illustrates two facts about a company: what it owns and what it owes. the accounting equation equates a company’s assets to its liabilities and equity. this shows all company assets are acquired by either debt or equity financing. The accounting equation is the fundamental principle of accounting. it represents the relationship between a company's assets, liabilities, and equity. the accounting equation is the cornerstone of double entry accounting, ensuring that every financial transaction affects at least two accounts and maintaining the equation's balance.

Comments are closed.