Acls Tachycardia Algorithm Heart Start Cpr

Acls Tachycardia Algorithm Heart Start Cpr Figure 15. cardiac arrest in pregnancy in hospital acls algorithm. acls indicates advanced cardiovascular life support; bls, basic life support; cpr, cardiopulmonary resuscitation; et, endotracheal; iv, intravenous; and rosc, return of spontaneous circulation. American heart association subject: please contact the american heart association at [email protected] or 1 214 706 1886 to request a long description of this image. created date: 8 24 2020 8:53:54 am.
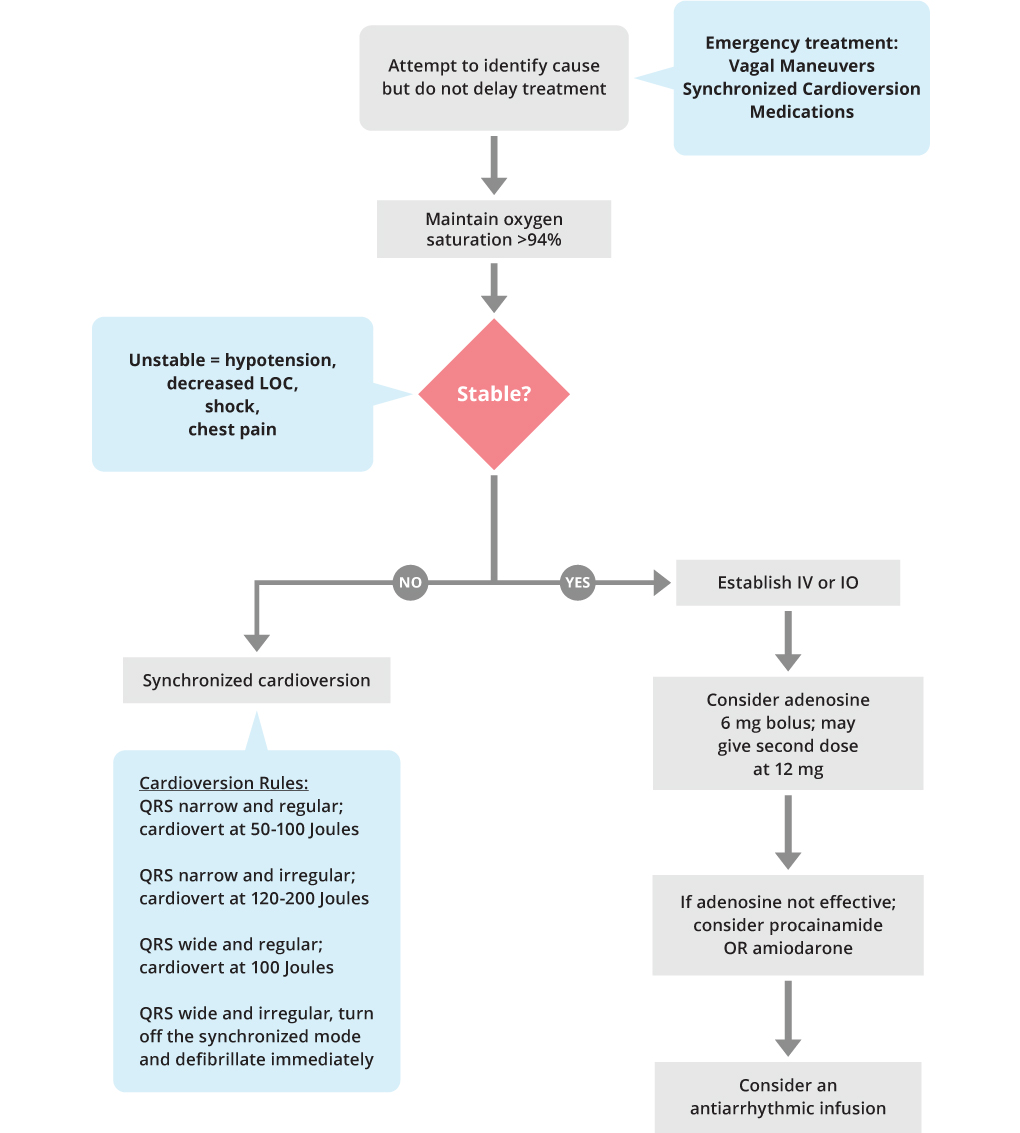
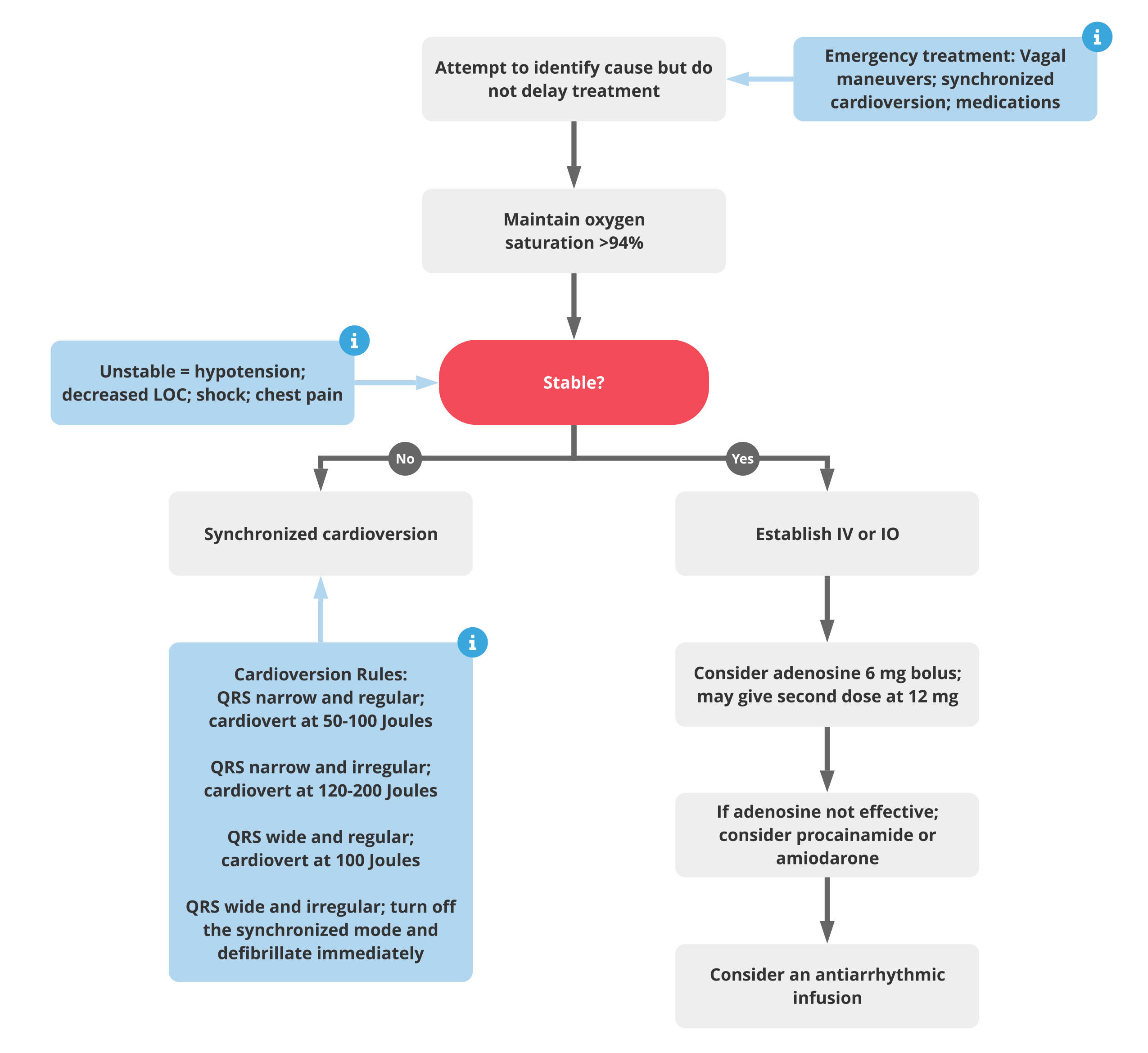
Acls Tachycardia Algorithm Acls Medical Training The acls tachycardia algorithm is a part of the advance cardiac life support (acls) algorithm used in emergency medicine to manage patients with fast heartbeat. a variety of factors, both physiological and pathological, can cause tachycardia. to name some conditions fever, shock, medication, stress, hypoxemia, etc., can cause a high heartbeat. The adult cardiac arrest algorithm guides emergency treatment for sudden cardiac arrest. it's part of the advanced cardiovascular life support (acls) guidelines. this algorithm stresses quality cpr, quick defibrillation, and advanced care. first, confirm cardiac arrest. then, start cpr and defibrillate if there's a shockable rhythm. Tachycardia procainamide iv dose: 20–50 mg min until arrhythmia suppressed, hypotension ensues, qrs duration increases > 50% or maximum dose 17 mg kg given. maintenance infusion: 1–4 mg min. avoid if prolonged qt or chf. tachycardia with a pulse algorithm wide qrs? >0.12 seconds second dose: 12 mg, if required. The american heart association is pleased to announce that the official 2020 american heart association guidelines for cpr & emergency cardiovascular care (2020 aha guidelines for cpr & ecc) will be published online in the aha’s flagship journal, circulation, on wednesday, october 21, 2020. learn more about the guidelines virtual experience.
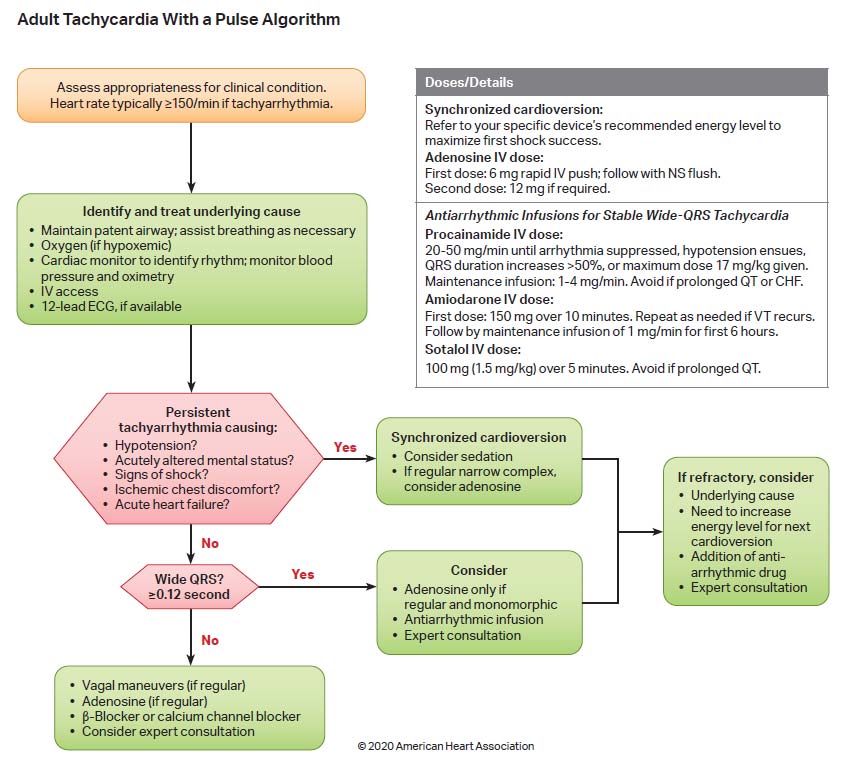
Algorithms American Heart Association Cpr First Aid Tachycardia procainamide iv dose: 20–50 mg min until arrhythmia suppressed, hypotension ensues, qrs duration increases > 50% or maximum dose 17 mg kg given. maintenance infusion: 1–4 mg min. avoid if prolonged qt or chf. tachycardia with a pulse algorithm wide qrs? >0.12 seconds second dose: 12 mg, if required. The american heart association is pleased to announce that the official 2020 american heart association guidelines for cpr & emergency cardiovascular care (2020 aha guidelines for cpr & ecc) will be published online in the aha’s flagship journal, circulation, on wednesday, october 21, 2020. learn more about the guidelines virtual experience. Merchant et al executive summary: 2020 aha guidelines for cpr and ecc rapid recognition, prompt provision of cpr, and defibril lation of ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia. since 2010, the aha has directed efforts at minimizing the time to provision of chest compres sions by focusing the universal sequence of responses. Consider sedation prior to cardioversion but do not delay treatment. if the rhythm is regular with narrow complexes, consider adenosine 6 mg iv rapid push. if the patient is stable, measure the qrs. if qrs is wider than 0.12 seconds, establish iv access and obtain a 12 lead ecg. consider adenosine only if the rhythm is regular and monomorphic.
Svt Acls Training Advanced Cardiac Life Support Merchant et al executive summary: 2020 aha guidelines for cpr and ecc rapid recognition, prompt provision of cpr, and defibril lation of ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia. since 2010, the aha has directed efforts at minimizing the time to provision of chest compres sions by focusing the universal sequence of responses. Consider sedation prior to cardioversion but do not delay treatment. if the rhythm is regular with narrow complexes, consider adenosine 6 mg iv rapid push. if the patient is stable, measure the qrs. if qrs is wider than 0.12 seconds, establish iv access and obtain a 12 lead ecg. consider adenosine only if the rhythm is regular and monomorphic.

Comments are closed.