Adiabatic Cooling Of Rising Air Diagram
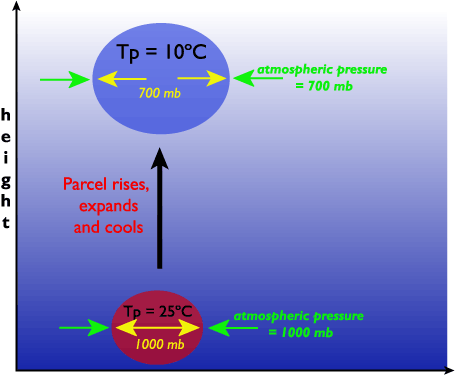
Rising Air Parcels Adiabatic Cooling In meteorology, the adiabatic process primarily describes the action of heating or cooling a body of air without any energy exchanged with the surrounding atmosphere. the temperature changes occur as a result of an air pocket's compression or expansion due to pressure changes in the surrounding air. think of the internal combustion engine (ice. Definition. adiabatic cooling refers to the process where the temperature of an air parcel decreases as it expands without exchanging heat with its surroundings. this phenomenon is critical in understanding how air rises in the atmosphere, cools, and leads to cloud formation, playing a significant role in moisture processes and cloud dynamics.
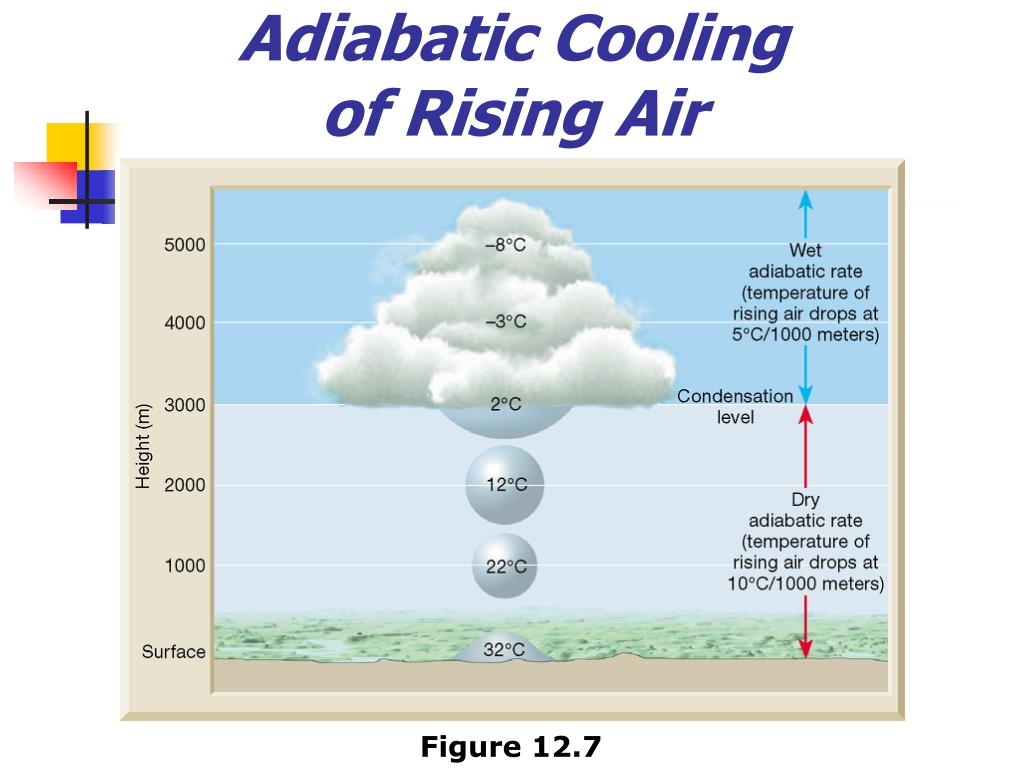
Ppt Chapter 12 Clouds And Precipitation Powerpoint Presentation Free As the parcel rises, it will adiabatically expand and cool (recall our discussion in chapter 5 about rising parcels of air) adiabatic a process where the parcel temperature changes due to an expansion or compression, no heat is added or taken away from the parcel. the parcel expands since the lower pressure outside allows the air molecules to. A thermodynamic diagram showing the stability of the atmosphere based on the dry (Γ d = 9.8 k km 1) and moist (Γ m = 4.5 k km 1) adiabatic lapse rates (created by britt seifert). the atmosphere is said to be absolutely stable if the environmental lapse rate is less than the moist adiabatic lapse rate. The warmth from the forest fire heats the air, causing instability near the surface. warm, less dense air (and smoke) bubbles upward, expanding and cooling as it rises. eventually the rising air cools to its dew point, condensation begins, and a cumulus cloud forms. 2. destabilize the atmosphere by mixing. The adiabatic lapse rate is the lapse rate of a dry parcel of air rising adiabatically through the atmosphere. more accurately we should call this the dry adiabatic lapse rate to distinguish it from a process in which condensation or evaporation of water droplets is occurring (the moist or saturated adiabatic lapse rate).
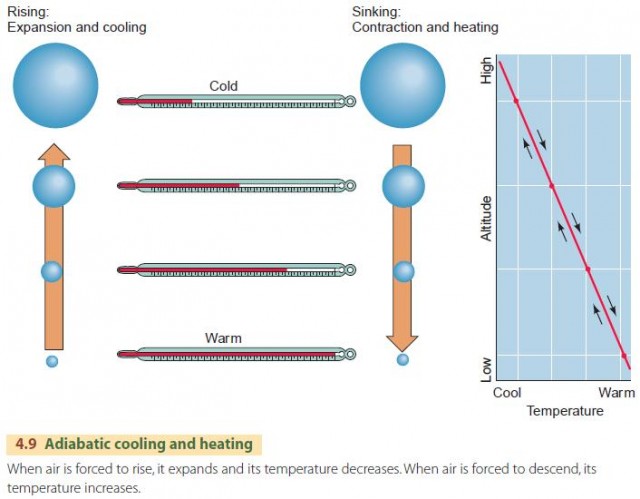
The Adiabatic Process The warmth from the forest fire heats the air, causing instability near the surface. warm, less dense air (and smoke) bubbles upward, expanding and cooling as it rises. eventually the rising air cools to its dew point, condensation begins, and a cumulus cloud forms. 2. destabilize the atmosphere by mixing. The adiabatic lapse rate is the lapse rate of a dry parcel of air rising adiabatically through the atmosphere. more accurately we should call this the dry adiabatic lapse rate to distinguish it from a process in which condensation or evaporation of water droplets is occurring (the moist or saturated adiabatic lapse rate). Other. category. v. t. e. an adiabatic process (adiabatic from ancient greek ἀδιάβατος (adiábatos) 'impassable') is a type of thermodynamic process that occurs without transferring heat or mass between the thermodynamic system and its environment. unlike an isothermal process, an adiabatic process transfers energy to the surroundings. As air pressure decreases with altitude, the air parcel expands. expansion causes air to cool. when the air cools to its so called dew point, the water vapor in the air condenses and becomes visible as a cloud. if there's enough moisture and the adiabatic cooling is strong enough, it rains or snows.

Lec 8 6 Adiabatic Cooling Youtube Other. category. v. t. e. an adiabatic process (adiabatic from ancient greek ἀδιάβατος (adiábatos) 'impassable') is a type of thermodynamic process that occurs without transferring heat or mass between the thermodynamic system and its environment. unlike an isothermal process, an adiabatic process transfers energy to the surroundings. As air pressure decreases with altitude, the air parcel expands. expansion causes air to cool. when the air cools to its so called dew point, the water vapor in the air condenses and becomes visible as a cloud. if there's enough moisture and the adiabatic cooling is strong enough, it rains or snows.
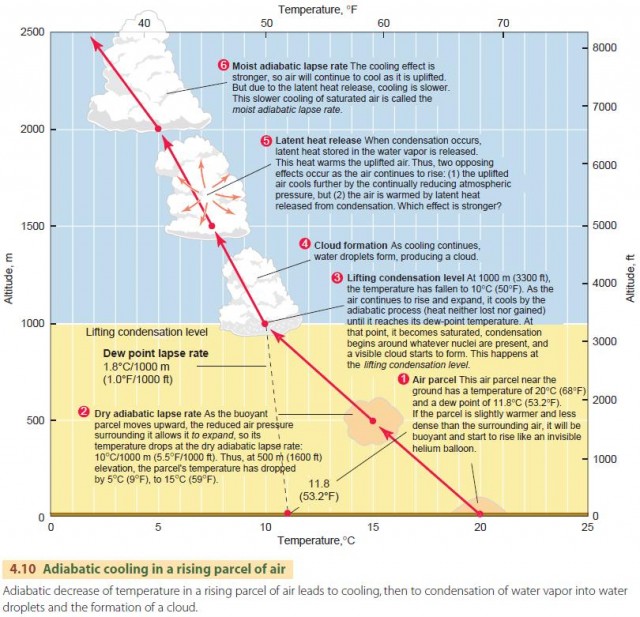
The Adiabatic Process

Adiabatic Cooling Blower Settings And Why You Care Hvac School

Comments are closed.