Alcoholic Liver Disease Morphology Clinical Features Complications
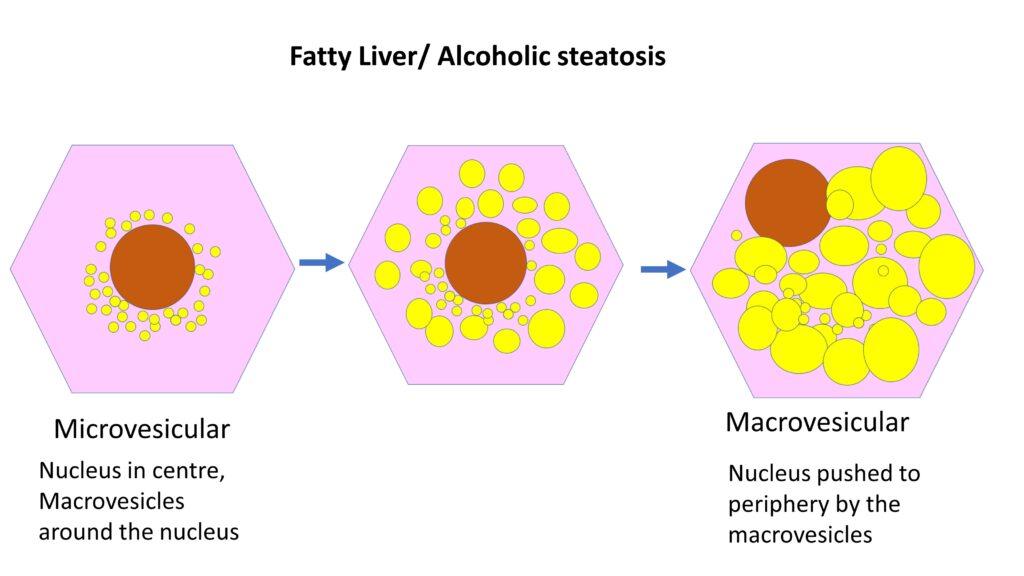
Alcoholic Liver Disease Morphology Clinical Features Complications Alcoholic cirrhosis is the stage described by progressive hepatic fibrosis and nodules. quantity and duration of the patient's alcohol intake are the highest risk factors for the development of liver disease. the beverage type plays a minimal role. women are more susceptible than men. Alcoholic hepatitis is an acute form of alcohol induced liver injury that occurs with the consumption of a large quantity of alcohol over a prolonged period. alcoholic hepatitis can range in severity from asymptomatic derangement of biochemistries to liver failure and death. cirrhosis involves replacement of the normal hepatic parenchyma with.

Alcoholic Liver Disease Part 2 Morphology Clinical Features The spectrum of alcohol associated liver disease (ald) encompasses a diverse range of clinical entities, from asymptomatic isolated steatosis to decompensated cirrhosis, and in some cases, acute or chronic liver failure. consequently, it is important for healthcare practitioners to maintain awareness and systematically screen for ald. Ald is one of the main causes of chronic liver disease worldwide and is the leading cause of liver related mortality in the united states (3). globally, there are 3 million deaths annually attributed to harmful alcohol use, accounting for 5.3% of all deaths and 13.5% of deaths in people aged 20–39 years (4). Alcohol related liver disease (ald) is a major healthcare economic burden and one of the leading causes of liver transplantation. new epidemiological studies that detail the course of the disease are needed since, despite its high prevalence, it is still a stigmatised condition with underlying pathology. alcoholic hepatitis, as the highest. Ah is a clinical syndrome characterized by new onset jaundice and or ascites in the setting of ongoing alcohol abuse and underlying ald 14. patients typically present with rapidly progressive jaundice, which can be accompanied by fever, abdominal pain, anorexia, and weight loss.
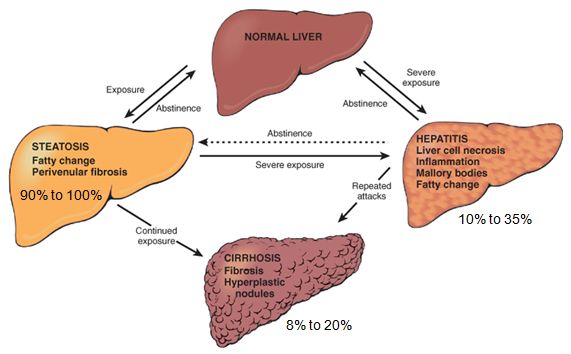
Morphology Of Alcoholic Liver Disease Medchrome Alcohol related liver disease (ald) is a major healthcare economic burden and one of the leading causes of liver transplantation. new epidemiological studies that detail the course of the disease are needed since, despite its high prevalence, it is still a stigmatised condition with underlying pathology. alcoholic hepatitis, as the highest. Ah is a clinical syndrome characterized by new onset jaundice and or ascites in the setting of ongoing alcohol abuse and underlying ald 14. patients typically present with rapidly progressive jaundice, which can be accompanied by fever, abdominal pain, anorexia, and weight loss. Excessive alcohol consumption is a global healthcare problem with enormous social, economic, and clinical consequences, accounting for 3.3 million deaths in 2012 (world health organization 2014). excessive drinking over decades damages nearly every organ in the body. however, the liver sustains the earliest and the greatest degree of tissue. Of ald requires documentation of chronic heavy alcohol use and exclusion of other causes of liver disease. prolonged abstinence is the most effective strategy to prevent disease progression. ah presents with rapid onset or worsening of jaundice, and in severe cases may transition to acute on chronic liver failure when the risk for mortality, depending on the number of extra hepatic organ.

Alcoholic Liver Disease Morphology Clinical Features Complications Excessive alcohol consumption is a global healthcare problem with enormous social, economic, and clinical consequences, accounting for 3.3 million deaths in 2012 (world health organization 2014). excessive drinking over decades damages nearly every organ in the body. however, the liver sustains the earliest and the greatest degree of tissue. Of ald requires documentation of chronic heavy alcohol use and exclusion of other causes of liver disease. prolonged abstinence is the most effective strategy to prevent disease progression. ah presents with rapid onset or worsening of jaundice, and in severe cases may transition to acute on chronic liver failure when the risk for mortality, depending on the number of extra hepatic organ.

Alcoholic Liver Disease Liz Paton Medical Art

Comments are closed.