Alcoholic Liver Disease Part 2 Morphology Clinical Features
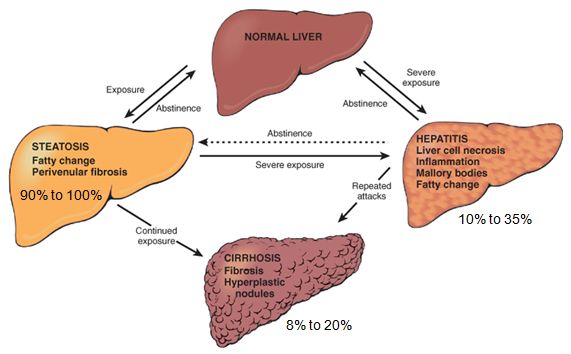
Alcoholic Liver Disease Morphology Clinical Features Complications Alcoholic hepatitis is an acute form of alcohol induced liver injury that occurs with the consumption of a large quantity of alcohol over a prolonged period. alcoholic hepatitis can range in severity from asymptomatic derangement of biochemistries to liver failure and death. cirrhosis involves replacement of the normal hepatic parenchyma with. Alcoholic cirrhosis is the stage described by progressive hepatic fibrosis and nodules. quantity and duration of the patient's alcohol intake are the highest risk factors for the development of liver disease. the beverage type plays a minimal role. women are more susceptible than men.

Alcoholic Liver Disease Part 2 Morphology Clinical Features During that year more than one million deaths worldwide were attributed to liver cirrhosis, and 47.9% of those were caused by chronic alcohol use. 1. as a pathologic entity, alcoholic liver disease (ald) can be defined as the manifold gross and microscopic manifestations of regular alcohol consumption on the liver. Alcohol is a hepatotoxin that is commonly consumed worldwide and is associated with a spectrum of liver injury including simple steatosis or fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis. alcoholic liver disease (ald) is a general term used to refer to this spectrum of alcohol related liver injuries [1, 2]. Diagnosis. alcoholic liver disease (j hepatol 2018;69:154): regular alcohol consumption of > 20 g day for females and > 30 g day for males. and clinical or biological abnormalities suggestive of liver injury. alcoholic hepatitis (hepatology 2020;71:306): recent onset (< 8 weeks) of jaundice. Ah is a clinical syndrome characterized by new onset jaundice and or ascites in the setting of ongoing alcohol abuse and underlying ald 14. patients typically present with rapidly progressive jaundice, which can be accompanied by fever, abdominal pain, anorexia, and weight loss.
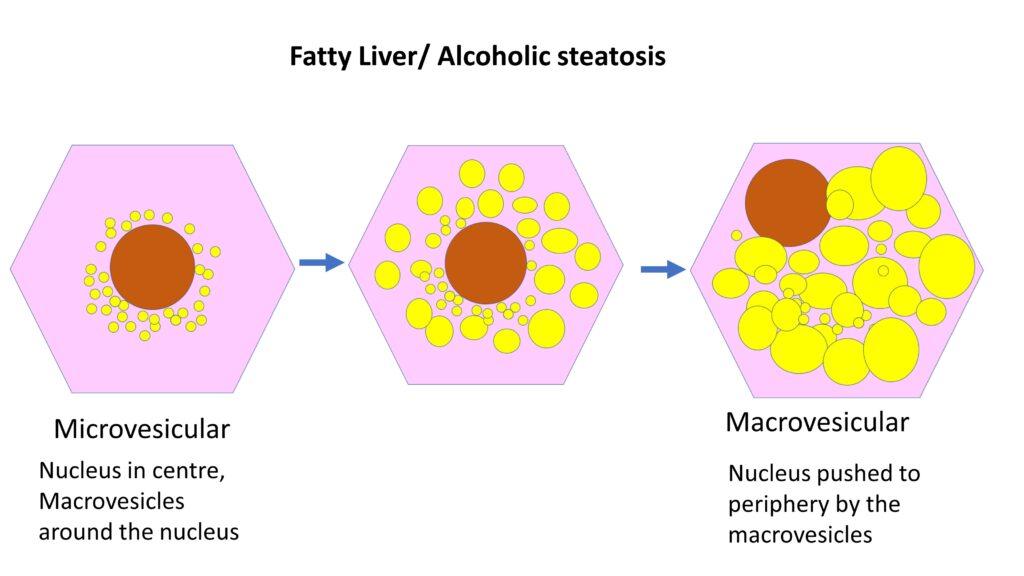
Morphology Of Alcoholic Liver Disease Medchrome Diagnosis. alcoholic liver disease (j hepatol 2018;69:154): regular alcohol consumption of > 20 g day for females and > 30 g day for males. and clinical or biological abnormalities suggestive of liver injury. alcoholic hepatitis (hepatology 2020;71:306): recent onset (< 8 weeks) of jaundice. Ah is a clinical syndrome characterized by new onset jaundice and or ascites in the setting of ongoing alcohol abuse and underlying ald 14. patients typically present with rapidly progressive jaundice, which can be accompanied by fever, abdominal pain, anorexia, and weight loss. The major pathologic manifestations of alcoholic liver injury have been well described, and include three major lesions: steatosis (fatty liver), steatohepatitis (formerly alcoholic hepatitis), and cirrhosis. recent attention to the problem of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) in individuals with obesity, diabetes, and other risk factors. Alcohol induced liver disease (ald) is the most common type of chronic liver disease in the world, accounting for more than 200 disease burdens and 3.2% of deaths worldwide 1, 2,3 . in the united.

Comments are closed.