Alcoholic Liver Disease Spectrum Morphology And Pathophysiology

The Spectrum Of Alcoholic Liver Disease Adapted From Reference 78 Alcoholic cirrhosis is the stage described by progressive hepatic fibrosis and nodules. quantity and duration of the patient's alcohol intake are the highest risk factors for the development of liver disease. the beverage type plays a minimal role. women are more susceptible than men. The spectrum of alcohol associated liver disease (ald) encompasses a diverse range of clinical entities, from asymptomatic isolated steatosis to decompensated cirrhosis, and in some cases, acute or chronic liver failure. consequently, it is important for healthcare practitioners to maintain awareness and systematically screen for ald.
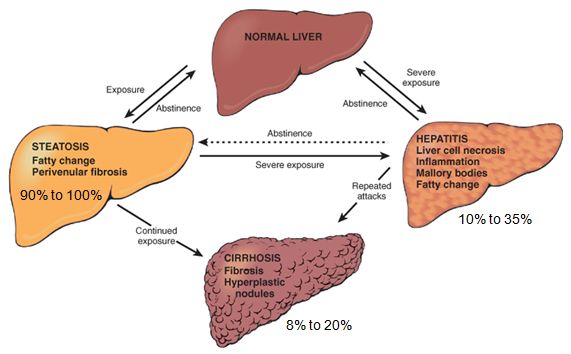
Morphology Of Alcoholic Liver Disease Medchrome Alcoholic liver disease spans a clinical and histological spectrum, from fatty liver to alcoholic hepatitis to alcoholic cirrhosis. fatty liver develops in most people who abuse alcohol for a period of days. however, this condition is generally asymptomatic and entirely reversible with abstinence. although the majority of people who abuse. 3. disease spectrum and pathogenesis. ald comprises different stages of liver disease as a result of susceptibility factors and duration of alcohol abuse. these stages include steatosis, alcoholic steatohepatitis (ash), progressive fibrosis, cirrhosis, decompensated cirrhosis and superimposed hepatocellular carcinoma (hcc) (figure 1). Alcoholic liver disease (ald) includes a broad spectrum of disorders, such as simple steatosis, cirrhosis, acute alcoholic hepatitis (ah) with or without cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (hcc) as a complication of cirrhosis. ald can also be superimposed on other common liver diseases, including nonalcoholic liver disease (nafld) and. Alcoholic liver disease (ald) is a major cause of chronic liver disease worldwide and can lead to fibrosis and cirrhosis. the latest surveillance report published by the national institute on alcohol abuse and alcoholism showed that liver cirrhosis was the 12th leading cause of death in the united states, with a total of 29,925 deaths in 2007.

The Spectrum Of Alcoholic Liver Disease Adapted From Reference 78 Alcoholic liver disease (ald) includes a broad spectrum of disorders, such as simple steatosis, cirrhosis, acute alcoholic hepatitis (ah) with or without cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (hcc) as a complication of cirrhosis. ald can also be superimposed on other common liver diseases, including nonalcoholic liver disease (nafld) and. Alcoholic liver disease (ald) is a major cause of chronic liver disease worldwide and can lead to fibrosis and cirrhosis. the latest surveillance report published by the national institute on alcohol abuse and alcoholism showed that liver cirrhosis was the 12th leading cause of death in the united states, with a total of 29,925 deaths in 2007. Excessive alcohol consumption is a global healthcare problem with enormous social, economic, and clinical consequences, accounting for 3.3 million deaths in 2012 (world health organization 2014). excessive drinking over decades damages nearly every organ in the body. however, the liver sustains the earliest and the greatest degree of tissue. The spectrum of alcoholic liver disease encompasses simple steatosis, steatohepatitis, progressive fibrosis, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma j. h. morphology of alcoholic liver disease.

Alcoholic Liver Disease Spectrum Morphology And Pathophysiology Excessive alcohol consumption is a global healthcare problem with enormous social, economic, and clinical consequences, accounting for 3.3 million deaths in 2012 (world health organization 2014). excessive drinking over decades damages nearly every organ in the body. however, the liver sustains the earliest and the greatest degree of tissue. The spectrum of alcoholic liver disease encompasses simple steatosis, steatohepatitis, progressive fibrosis, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma j. h. morphology of alcoholic liver disease.

Natural History Spectrum And Pathophysiology Of Alcoholic Liver Disease

Comments are closed.