An Example Of A Synoptic Scale Low Pressure System With Associated

An Example Of A Synoptic Scale Low Pressure System With Associated The synoptic scale refers to systems from 200 to 2000 km in size. examples of this scale are migratory pressure systems and fronts. in this unit, we examine these types of synoptic scale systems, beginning with the dynamics associated with them. 3–1. basic dynamics of the atmosphere. E. in meteorology, the synoptic scale (also called the large scale or cyclonic scale) is a horizontal length scale of the order of 1,000 km (620 mi) or more. [1] this corresponds to a horizontal scale typical of mid latitude depressions (e.g. extratropical cyclones). most high and low pressure areas seen on weather maps (such as surface.
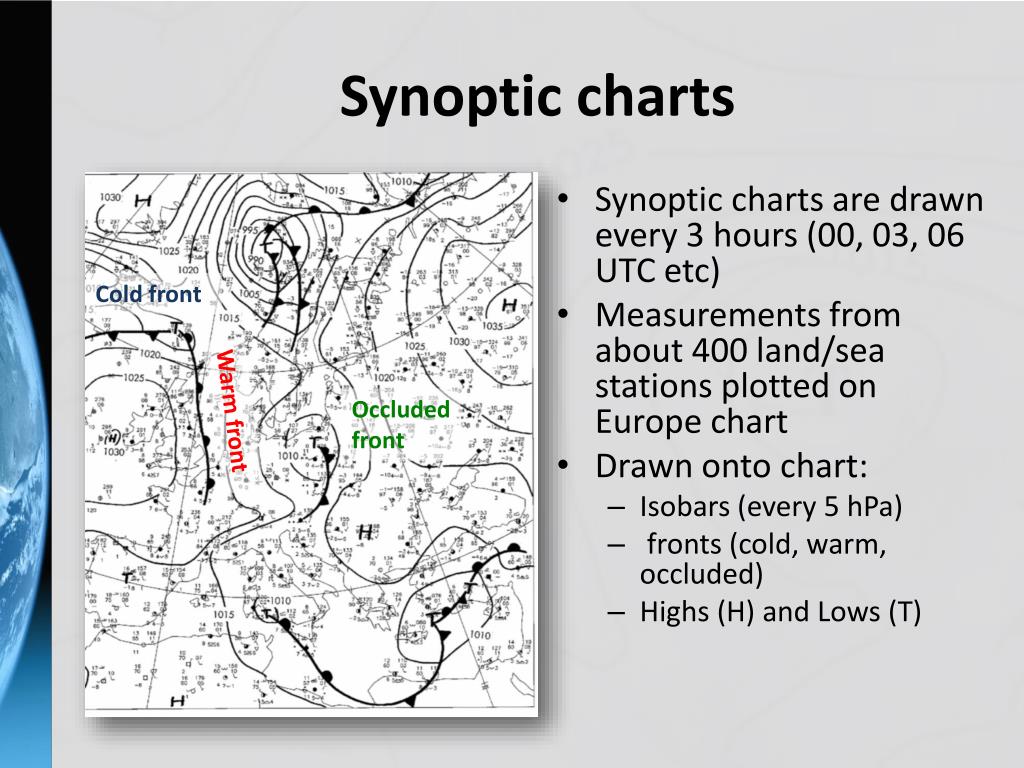
Synoptic Scale Pressure Charts Synoptic Charts Isobars Explainer Fronts The most common example of a synoptic structure is a low pressure system with cold and warm fronts (figure 2). synoptic weather systems can be thought of as the broad scale organizing mechanism. Weather phenomena that are small in size—too small to be shown on a weather map—are referred to as mesoscale. mesoscale events range from a few kilometers to several hundred kilometers in size. they last a day or less, and impact areas on a regional and local scale and include events such as: thunderstorms. tornadoes. Extratropical cyclones (synoptic scale low pressure systems) that occur within the mid latitude in both hemisphere and are associated with extreme precipitation, storm surges, extreme winds, sea level and wave build up. they usually form over ocean basin within the proximity of upper tropospheric jets streams, through conversion from tropical. When different parameters of the earth's atmosphere are viewed together at the synoptic scale, then large scale weather patterns emerge, such as extratropical cyclones and their associated fronts. the current surface synoptic weather map. it shows the positions of high and low pressure systems, surface weather plots, and locations of fronts.

Synoptic Chart Geography Extratropical cyclones (synoptic scale low pressure systems) that occur within the mid latitude in both hemisphere and are associated with extreme precipitation, storm surges, extreme winds, sea level and wave build up. they usually form over ocean basin within the proximity of upper tropospheric jets streams, through conversion from tropical. When different parameters of the earth's atmosphere are viewed together at the synoptic scale, then large scale weather patterns emerge, such as extratropical cyclones and their associated fronts. the current surface synoptic weather map. it shows the positions of high and low pressure systems, surface weather plots, and locations of fronts. High and low pressure systems seen on local weather forecasts, are synoptic in scale. pressure, much like convection, is an important meteorological principle that is at the root of large scale weather systems as diverse as hurricanes and bitter cold outbreaks. low pressure systems occur where the atmospheric pressure at the surface of earth. 3) synoptic scale: horizontal extension i.e. diameter of this scale systems is about 100 to 1000 kms and vertical extension is about 10 km. time scale is few days examples for this scale of systems are low pressure areas, high pressure areas, depressions, cyclonic storms, troughs and ridges etc. to study synoptic scale motions we should.

Conceptual Diagram Of Four Types Of Synoptic Scale Weather Systems That High and low pressure systems seen on local weather forecasts, are synoptic in scale. pressure, much like convection, is an important meteorological principle that is at the root of large scale weather systems as diverse as hurricanes and bitter cold outbreaks. low pressure systems occur where the atmospheric pressure at the surface of earth. 3) synoptic scale: horizontal extension i.e. diameter of this scale systems is about 100 to 1000 kms and vertical extension is about 10 km. time scale is few days examples for this scale of systems are low pressure areas, high pressure areas, depressions, cyclonic storms, troughs and ridges etc. to study synoptic scale motions we should.

Comments are closed.