Anatomical Difference Between Kids And Adults Drawing Reference

Human Anatomy Fundamentals Advanced Body Proportions The most noticeable difference with adult faces at this point is the size of the eyes, which are still large. the bone structure is in place but still softened by a full face. as the nose take its adult shape, it looks longer. in males, the neck is thicker, the adam’s apple appears. in females, the neck remains slender, with no adam’s apple. Human anatomy fundamentals: balance and movement. in our last session we learned the basic, generic proportions and joint alignments of the human figure, and if you've been practicing you should be ready for some diversity. the most obvious differentiation may be between men and women, but an illustrator must also be familiar with the ways the.
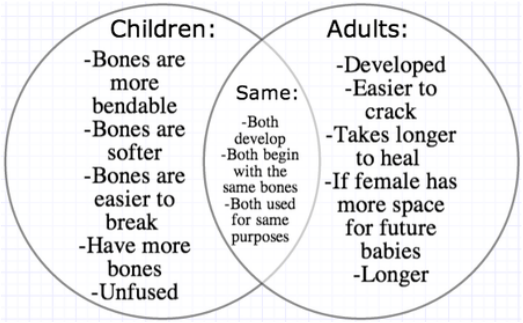
Diagram World Of The Human Skeleton This is one of the key proportions to remember when drawing children. a child’s body averages around 4 6 heads high, depending on their age. though the head is also built using a circle and shield, the shield is much shorter. younger children, both male and female, have shorter faces. Figure 1: anatomical differences between adult and child bone. the epiphysis is completely or mostly cartilaginous in infants. initially it consists of articular cartilage and growth cartilage until these become differentiated by the development of a secondary ossification centre (figure 2). figure 2: the proximal femoral epiphyseal secondary. Vascular access in young children and infants can be difficult. there is increased workload for the cardiovascular system due to a higher metabolic rate. chq nss 51033 anatomical and physiological differences in children. developed by the state wide emergency care of children working group, january 2024. 1 4. Fractures in children’s bones. the bone structure of a child and an adult are different as well. the differences are significant for accurate evaluation and treatment of fractures. a child’s bones heal quicker than an adult’s bone. adult’s bones are thicker, stronger, and more active dense fibrous membrane (periosteum) covers the.

Differences And Similarities In Bone Structure Between Children And Vascular access in young children and infants can be difficult. there is increased workload for the cardiovascular system due to a higher metabolic rate. chq nss 51033 anatomical and physiological differences in children. developed by the state wide emergency care of children working group, january 2024. 1 4. Fractures in children’s bones. the bone structure of a child and an adult are different as well. the differences are significant for accurate evaluation and treatment of fractures. a child’s bones heal quicker than an adult’s bone. adult’s bones are thicker, stronger, and more active dense fibrous membrane (periosteum) covers the. In this review, anatomical differences between child and adult were mentioned. these differences are especially apparent in infancy and preschool term. when the child reaches the school age term, the differences begin to decrease gradually. when the child reaches the age of 18, the child has the same characteristics as the adult. 1st division is where the middle of the eye is gonna be placed. the end of the nose is gonna be below the 2nd division. and try to draw a nice long nose bridge. 3rd division line is where the middle of the lips rests. since i’m drawing a female, the jaw is gonna be rounder but still angular.

Adult Vs Children Bones Our Skeletal System In this review, anatomical differences between child and adult were mentioned. these differences are especially apparent in infancy and preschool term. when the child reaches the school age term, the differences begin to decrease gradually. when the child reaches the age of 18, the child has the same characteristics as the adult. 1st division is where the middle of the eye is gonna be placed. the end of the nose is gonna be below the 2nd division. and try to draw a nice long nose bridge. 3rd division line is where the middle of the lips rests. since i’m drawing a female, the jaw is gonna be rounder but still angular.

Anatomical And Physiological Differences Between Children And Adults
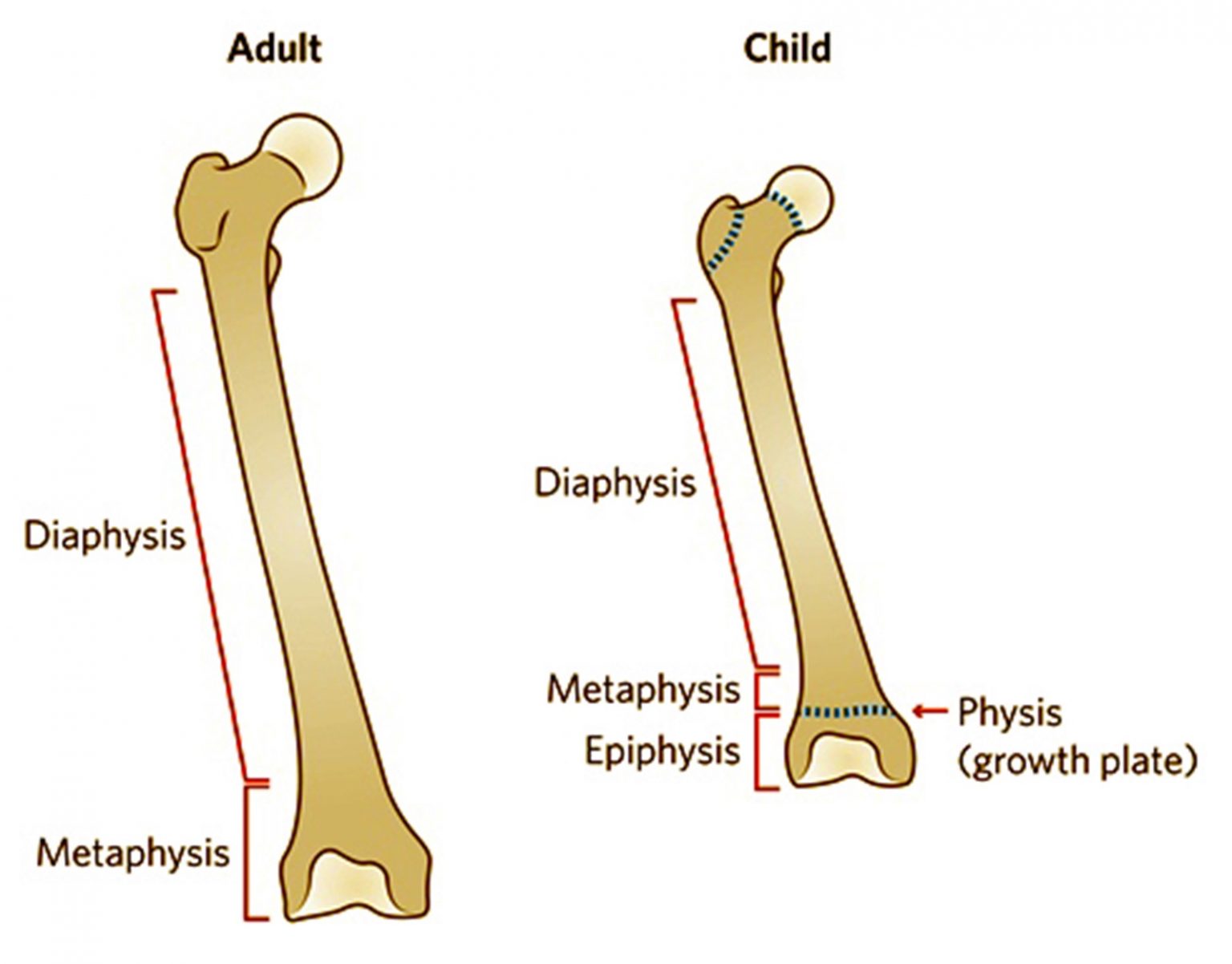
How Are Children S Bones Different From Adult S Bones Young Bones Clinic

Comments are closed.