Anatomy Of Blood Vessels Veins

Anatomy Of Blood Vessels Cardiovascular Blood Vessels The function of blood vessels is to deliver blood to the organs and tissues in your body. the blood supplies them with the oxygen and nutrients they need to function. blood vessels also carry waste products and carbon dioxide away from your organs and tissues. each type of blood vessel serves a different function:. Veins are blood vessels located throughout your body that collect oxygen poor blood and return it to your heart. veins are part of your circulatory system. they work together with other blood vessels and your heart to keep your blood moving. veins hold most of the blood in your body. in fact, nearly 75% of your blood is in your veins.
14 4 Blood Vessels Human Biology The first blood vessels formed by vasculogenesis include the dorsal aorta and the cardinal veins. all other vasculature in the human body forms by angiogenesis. angiogenesis is the process in which new blood vessels derive from the endothelial layer of a pre existing vessel. Veins are a type of blood vessel that carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart from various parts of the body. explore how different veins look, work, and help support the cardiovascular system. the anatomy of the azygos vein. the anatomy of the retromandibular vein. the anatomy of the basilic vein. The walls of most blood vessels have three distinct layers: the tunica externa, the tunica media, and the tunica intima. these layers surround the lumen, the hollow interior through which blood flows. 2. oxygenated blood flows away from the heart through arteries. the left ventricle of the heart pumps oxygenated blood into the aorta. Figure 20.3 structure of blood vessels (a) arteries and (b) veins share the same general features, but the walls of arteries are much thicker because of the higher pressure of the blood that flows through them. (c) a micrograph shows the relative differences in thickness. lm × 160.
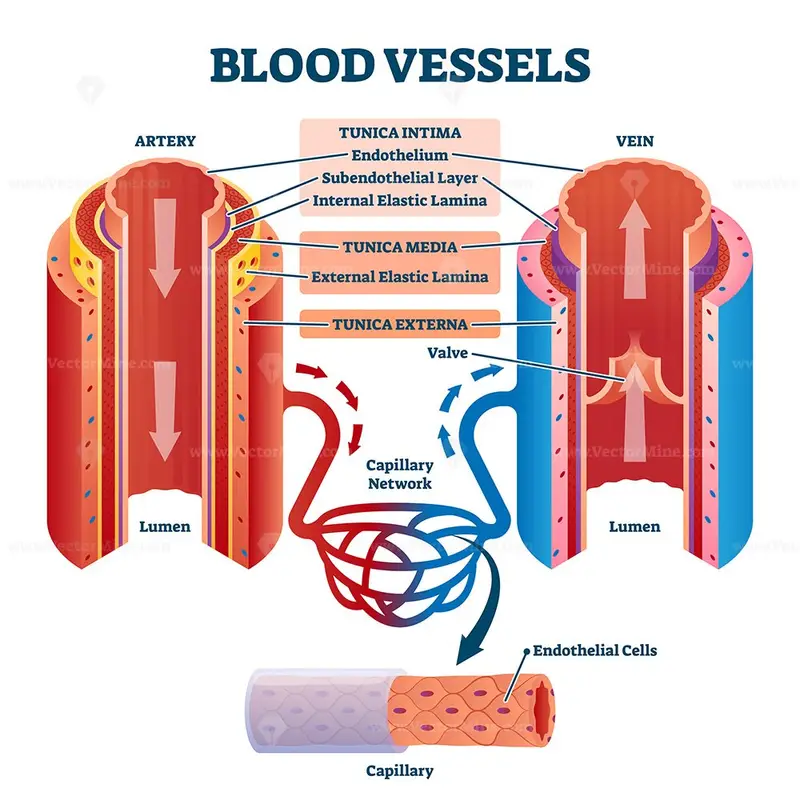
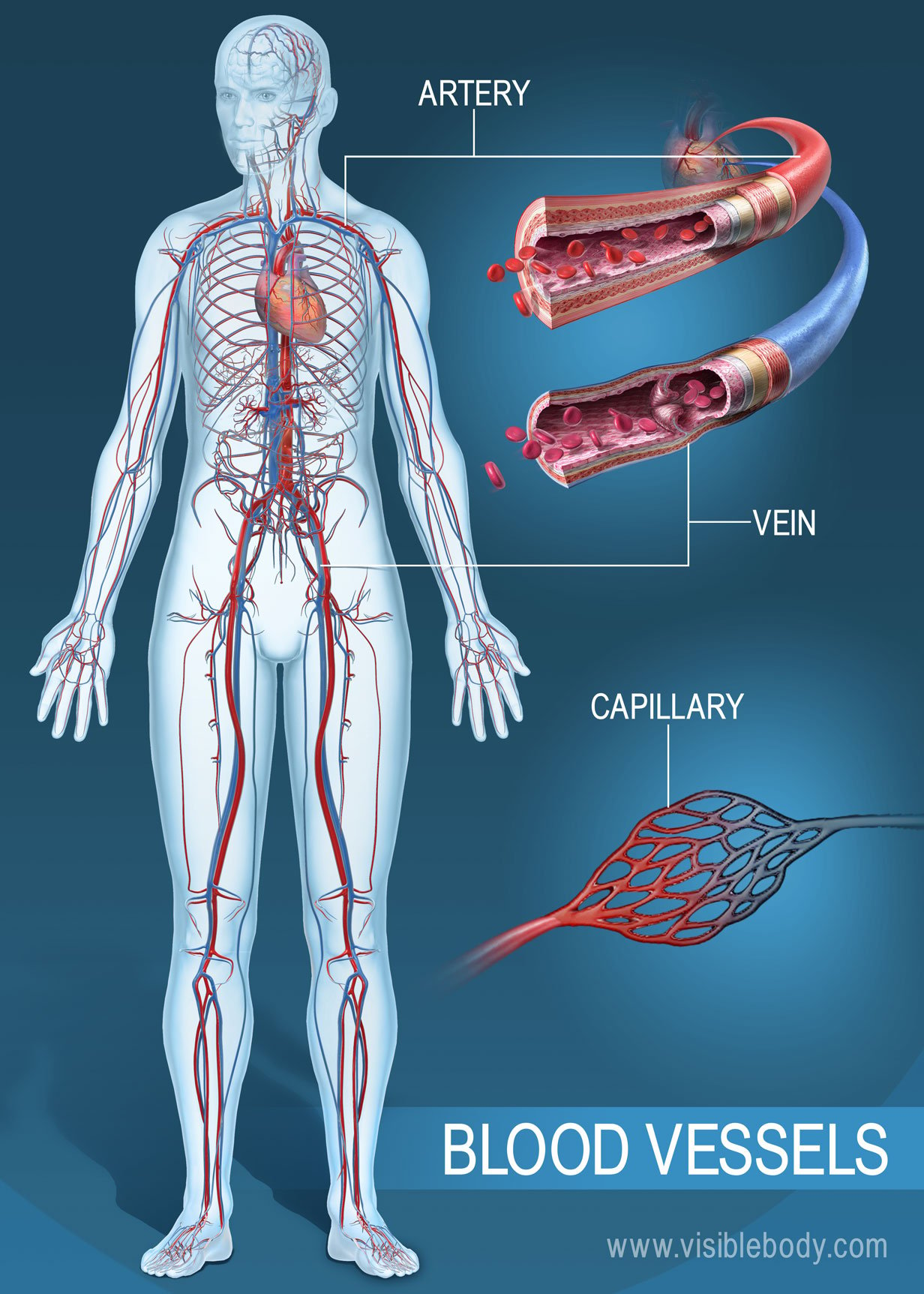
Blood Vessels With Artery And Vein Internal Structure Vector The walls of most blood vessels have three distinct layers: the tunica externa, the tunica media, and the tunica intima. these layers surround the lumen, the hollow interior through which blood flows. 2. oxygenated blood flows away from the heart through arteries. the left ventricle of the heart pumps oxygenated blood into the aorta. Figure 20.3 structure of blood vessels (a) arteries and (b) veins share the same general features, but the walls of arteries are much thicker because of the higher pressure of the blood that flows through them. (c) a micrograph shows the relative differences in thickness. lm × 160. Many conditions can affect your venous system. some of the most common ones include: deep vein thrombosis (dvt). a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in your leg. this clot can potentially. Blood vessel, a vessel in the human or animal body in which blood circulates. the vessels that carry blood away from the heart are called arteries. veins are vessels that return blood to the heart. learn more about the anatomy and types of blood vessels and the diseases that affect them.

Pin Di Nursing Many conditions can affect your venous system. some of the most common ones include: deep vein thrombosis (dvt). a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in your leg. this clot can potentially. Blood vessel, a vessel in the human or animal body in which blood circulates. the vessels that carry blood away from the heart are called arteries. veins are vessels that return blood to the heart. learn more about the anatomy and types of blood vessels and the diseases that affect them.
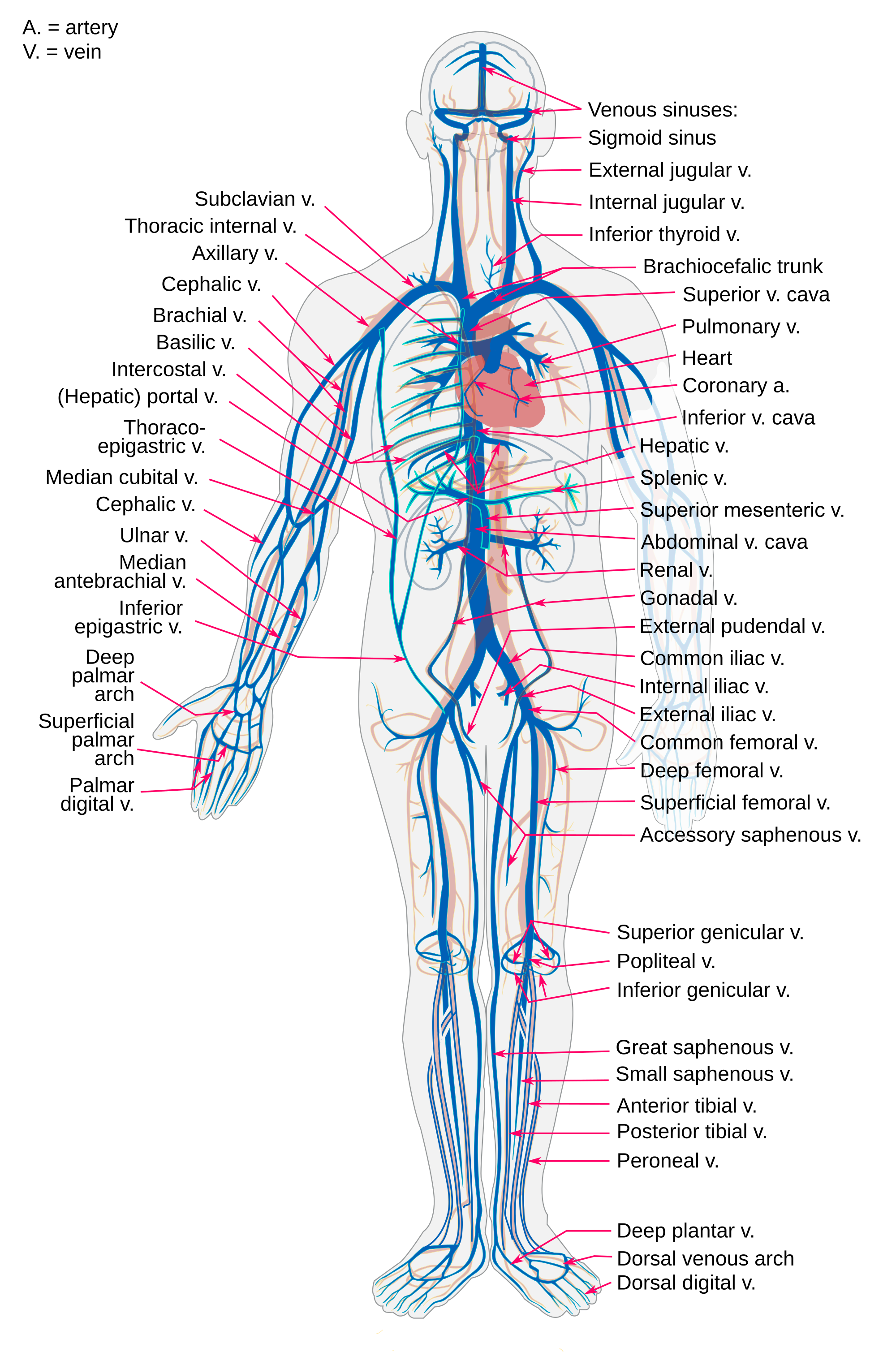
Major Blood Vessel Chart Major Arteries Veins And Nerves Of The Body

Interesting Facts About Blood Vessels Arteries Veins And Capillaries

Comments are closed.