At The Equilibrium Price Consumer Surplus Is

Equilibrium Price And Quantity Surplus Course: ap®︎ college microeconomics > unit 2. lesson 6: market equilibrium and consumer and producer surplus. market equilibrium. market equilibrium. demand curve as marginal benefit curve. consumer surplus introduction. total consumer surplus as area. producer surplus. equilibrium, allocative efficiency and total surplus. Consumer surplus always increases as the price of a good falls and decreases as the price of a good rises. for example, suppose consumers are willing to pay $50 for the first unit of product a and.

Chapter 3 Supply And Demand Consumer and producer surpluses are shown as the area where consumers would have been willing to pay a higher price for a good or the price where producers would have been willing to sell a good. in the sample market shown in the graph, equilibrium price is $10 and equilibrium quantity is 3 units. the consumer surplus area is highlighted above. Consumer surplus always decreases when a binding price floor is instituted in a market above the equilibrium price. the total economic surplus equals the sum of the consumer and producer surpluses. price helps define consumer surplus, but overall surplus is maximized when the price is pareto optimal, or at equilibrium. The area above the supply level and below the equilibrium price is called product surplus (ps), and the area below the demand level and above the equilibrium price is the consumer surplus (cs). while taking into consideration the demand and supply curves, the formula for consumer surplus is cs = ½ (base) (height). in our example, cs = ½ (40. The consumer surplus is the area between the equilibrium price (the level of price where the two curves cross each other) and the demand curve. now that you know what a consumer surplus is and how the consumer surplus graph looks like, let's find out how to calculate consumer surplus.
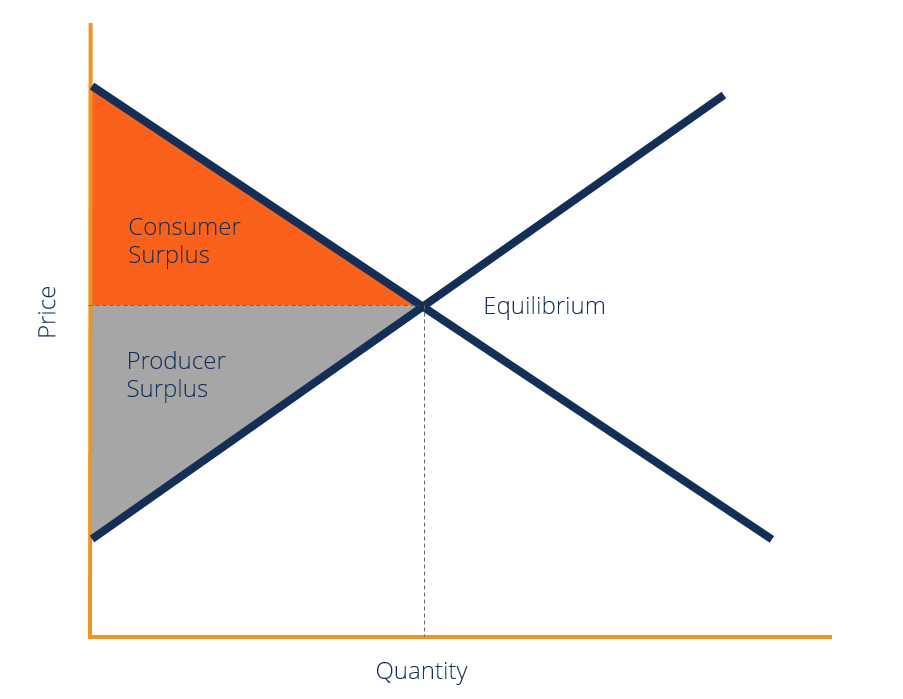
Consumer Surplus Formula Guide Examples How To Calculate The area above the supply level and below the equilibrium price is called product surplus (ps), and the area below the demand level and above the equilibrium price is the consumer surplus (cs). while taking into consideration the demand and supply curves, the formula for consumer surplus is cs = ½ (base) (height). in our example, cs = ½ (40. The consumer surplus is the area between the equilibrium price (the level of price where the two curves cross each other) and the demand curve. now that you know what a consumer surplus is and how the consumer surplus graph looks like, let's find out how to calculate consumer surplus. Extended consumer surplus formula. where: qd = quantity demanded at equilibrium, where demand and supply are equal. Δp = pmax – pd. pmax = price the buyer is willing to pay. pd = price at equilibrium, where demand and supply are equal. Consumer surplus is a measure of the economic benefit consumers receive from the purchase of a good or service. the size of the consumer surplus depends on the slope of the demand curve and the difference between the market price and the maximum price consumers are willing to pay. an increase in the market price of a good or service will.
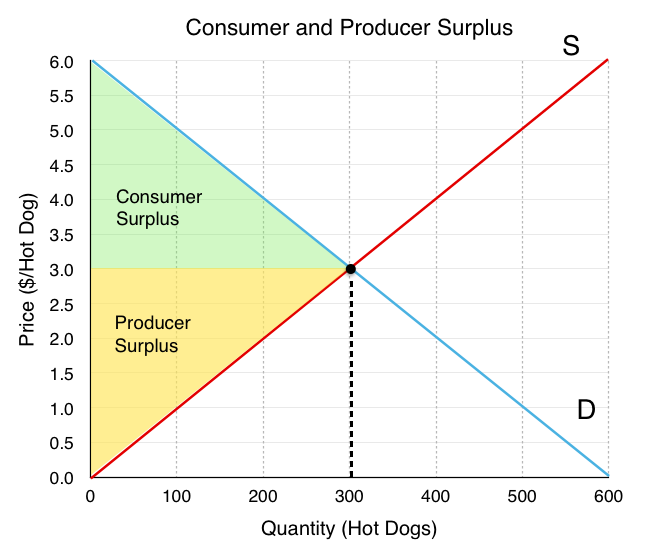
At The Equilibrium Price Producer Surplus Is What Is Consumer Surplus Extended consumer surplus formula. where: qd = quantity demanded at equilibrium, where demand and supply are equal. Δp = pmax – pd. pmax = price the buyer is willing to pay. pd = price at equilibrium, where demand and supply are equal. Consumer surplus is a measure of the economic benefit consumers receive from the purchase of a good or service. the size of the consumer surplus depends on the slope of the demand curve and the difference between the market price and the maximum price consumers are willing to pay. an increase in the market price of a good or service will.

Comments are closed.