At The Equilibrium Price Consumer Surplus Is Consumer S Equilibrium
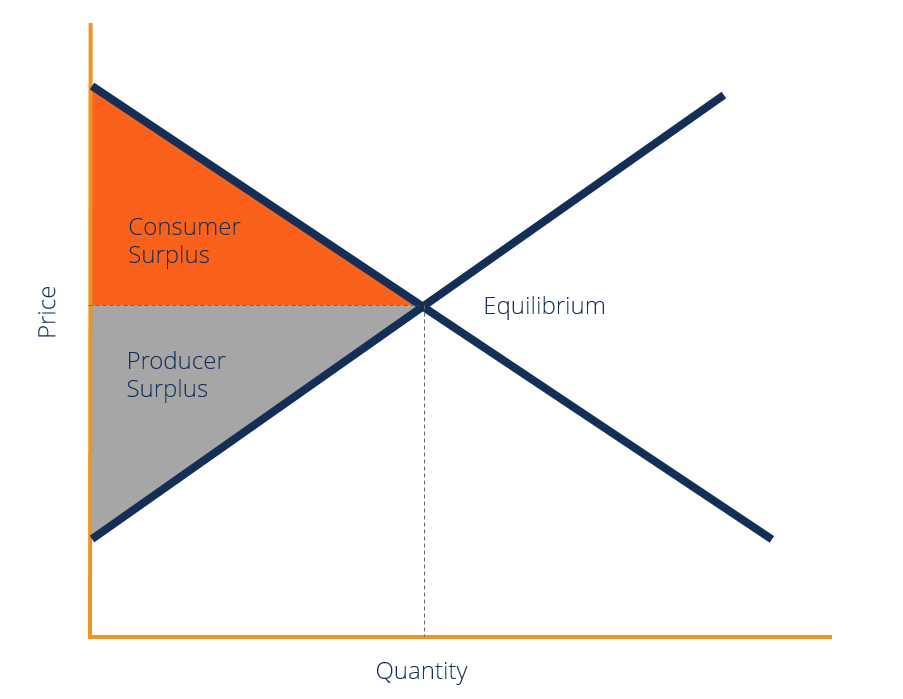
Refer To The Diagram Assuming Equilibrium Price P1 Consumer Surplus Is Consumer and producer surpluses are shown as the area where consumers would have been willing to pay a higher price for a good or the price where producers would have been willing to sell a good. in the sample market shown in the graph, equilibrium price is $10 and equilibrium quantity is 3 units. the consumer surplus area is highlighted above. Lesson 3: market equilibrium and changes in equilibrium. market equilibrium. market equilibrium. changes in market equilibrium. changes in equilibrium price and quantity when supply and demand change. changes in equilibrium price and quantity: the four step process. lesson summary: market equilibrium, disequilibrium, and changes in equilibrium.

At The Equilibrium Price Consumer Surplus Is Consumer S Equilibrium Consumer surplus will only increase as long as the benefit from the lower price exceeds the costs from the resulting shortage. consumer surplus always decreases when a binding price floor is instituted in a market above the equilibrium price. the total economic surplus equals the sum of the consumer and producer surpluses. From figure 1 the following formula can be derived for consumer and producer surplus: consumer surplus = (qe x (p2 – pe)) ÷ 2. producer surplus = (qe x (pe – p1)) ÷ 2. where: qe is the equilibrium price. pe is the equilibrium price. p2 is the y intercept of the demand curve. p1 is the y intercept of the supply curve. How far will the price fall? whenever there is a surplus, the price will drop until the surplus goes away. when the surplus is eliminated, the quantity supplied just equals the quantity demanded—that is, the amount that producers want to sell exactly equals the amount that consumers want to buy. we call this equilibrium, which means. Consumer surplus, also known as buyer’s surplus, is the economic measure of a customer’s excess benefit. it is calculated by analyzing the difference between the consumer’s willingness to pay for a product and the actual price they pay, also known as the equilibrium price. a surplus occurs when the consumer’s willingness to pay for a.

Equilibrium Price And Quantity Surplus How far will the price fall? whenever there is a surplus, the price will drop until the surplus goes away. when the surplus is eliminated, the quantity supplied just equals the quantity demanded—that is, the amount that producers want to sell exactly equals the amount that consumers want to buy. we call this equilibrium, which means. Consumer surplus, also known as buyer’s surplus, is the economic measure of a customer’s excess benefit. it is calculated by analyzing the difference between the consumer’s willingness to pay for a product and the actual price they pay, also known as the equilibrium price. a surplus occurs when the consumer’s willingness to pay for a. Therefore, if the price is above the equilibrium level, incentives built into the structure of demand and supply will create pressures for the price to fall toward the equilibrium. now suppose that the price is below its equilibrium level at $1.20 per gallon, as the dashed horizontal line at this price in figure 3.4 shows. at this lower price. The consumer surplus is the area between the equilibrium price (the level of price where the two curves cross each other) and the demand curve. now that you know what a consumer surplus is and how the consumer surplus graph looks like, let's find out how to calculate consumer surplus.

The Consumer S Equilibrium In Case Of Single And Two Commodities Therefore, if the price is above the equilibrium level, incentives built into the structure of demand and supply will create pressures for the price to fall toward the equilibrium. now suppose that the price is below its equilibrium level at $1.20 per gallon, as the dashed horizontal line at this price in figure 3.4 shows. at this lower price. The consumer surplus is the area between the equilibrium price (the level of price where the two curves cross each other) and the demand curve. now that you know what a consumer surplus is and how the consumer surplus graph looks like, let's find out how to calculate consumer surplus.
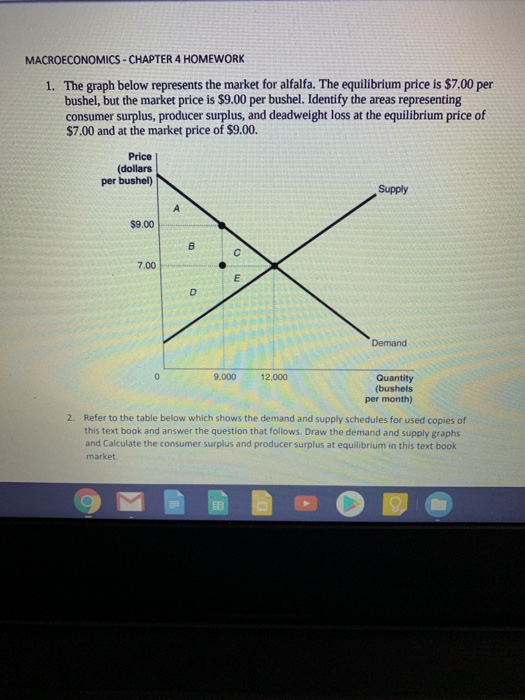
At The Equilibrium Price Consumer Surplus Is Consumer S Equilibrium

Comments are closed.