Brocas Aphasia And The Brain What We Know And What Were Still Learning

Broca S Aphasia And The Brain What We Know And What We Re Still .chapters0:00 introduction0:42 symptoms of broca's aphasia1:19 causes of broca's aphasia1:38 diagnosis of broca's aphasia2:01 treatment for broca's aphasia2. Symptoms of broca’s aphasia include: poor or absent grammar. difficulty forming complete sentences. omitting certain words, such as “the,” “an,” “and,” and “is” (a person with.
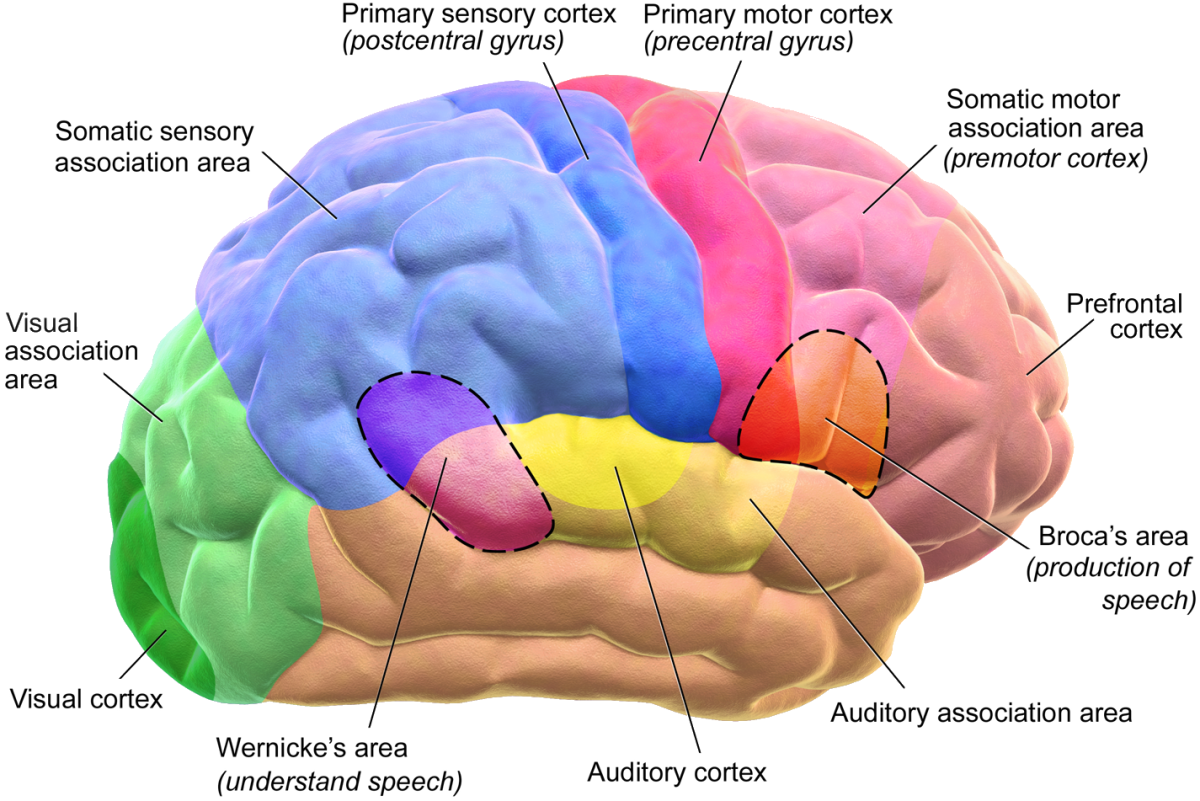
Brain Brocas Area Broca’s aphasia. the first language area within the left hemisphere to be discovered is called broca’s area, after paul broca. broca was a french neurologist who had a patient with severe language problems: although he could understand the speech of others with little difficulty, the only word he could produce was “tan.”. While evidence from patients with broca's aphasia as well as evidence from brain activations indicate that broca's area is important for processing syntactic information (caplan et al., 2000), other areas in the brain, such as wernicke's area, including portions of brodmann areas 22, 41, and 42 (just et al., 1996), or the anterior portion of. Aphasia is an impairment of language that affects a person’s ability to produce and comprehend speech as well as read or write. aphasia most commonly results from stroke, the leading cause of adult disability in the united states. a stroke can occur anywhere in the brain, and depending on wher e damage occurs, aphasia presents differently. Broca’s aphasia results from injury to speech and language brain areas such the left hemisphere inferior frontal gyrus, among others. such damage is often a result of stroke but may also occur due to brain trauma. like in other types of aphasia, intellectual and cognitive capabilities not related to speech and language may be fully preserved.

Broca S Aphasia Aphasia is an impairment of language that affects a person’s ability to produce and comprehend speech as well as read or write. aphasia most commonly results from stroke, the leading cause of adult disability in the united states. a stroke can occur anywhere in the brain, and depending on wher e damage occurs, aphasia presents differently. Broca’s aphasia results from injury to speech and language brain areas such the left hemisphere inferior frontal gyrus, among others. such damage is often a result of stroke but may also occur due to brain trauma. like in other types of aphasia, intellectual and cognitive capabilities not related to speech and language may be fully preserved. Broca (1824 1880) first described in 1861, after autopsying the brain of his famous patient “tan” (louis victor leborgne), the association between motor aphasia and a lesion in the middle part of the patient’s left frontal lobe, the cortical speech center, an area later named after him, as “broca’s area” [3, 4]. shortly after broca. Sfn: as broca and other physicians found more patients with these brain lesions, their speech deficits became known as broca’s aphasia, and the affected region of the brain, broca’s area. speech deficits usually appeared very suddenly as the result of stroke or other brain trauma, and individuals were left with a limited vocabulary often.

Brocas Aphasia Broca (1824 1880) first described in 1861, after autopsying the brain of his famous patient “tan” (louis victor leborgne), the association between motor aphasia and a lesion in the middle part of the patient’s left frontal lobe, the cortical speech center, an area later named after him, as “broca’s area” [3, 4]. shortly after broca. Sfn: as broca and other physicians found more patients with these brain lesions, their speech deficits became known as broca’s aphasia, and the affected region of the brain, broca’s area. speech deficits usually appeared very suddenly as the result of stroke or other brain trauma, and individuals were left with a limited vocabulary often.

Comments are closed.