Cavity Design Amalgam V S Composite Restorations

Cavity Design Amalgam V S Composite Restorations Youtube In this video, we talk about cavity design and preparation that is used for amalgam and composite restoration and at the same time comparing the difference o. Amalgam is a restorative material that has been widely used to treat dental caries for more than 150 years. but because dental amalgam is partly composed of mercury (hg), its use has fuelled concern for decades about risks to human health. composite resin is the most common alternative to dental amalgam; although data indicate that rates of restoration failure and secondary caries — as well.

Cavity Design For Composite Restoration Youtube Amalgam requires specific cavity design to allow for an appropriate restoration. there must be a minimum 2mm depth. there must be some form of retention, primarily an undercut cavity. unsupported enamel should be removed, whilst maintaining a 90° cavosurface angle. the cavity still must be caries free, with margins in cleansable areas. 9.9 for the composite group and 9.0 for the amalgam one. this could be in favor of using the amalgam restoration. approaches in patients with impaired kidneys, however, at. a 7 year follow up. Among the alternatives to the use of amalgam as a restorative material for dental caries, composite resin is the most common, having been in use for more than 50 years (although experience with newer iterations of composite resin would be shorter). 21 throughout that time, composite resin materials have undergone considerable development and. As amalgam is partly composed of mercury, a known toxic substance, there are concerns about the safety of this filling material for human health, and for the environmental impact of mercury released from amalgam waste generated by dental offices. resin based composite is the most common alternative dental filling material to amalgam. however, concerns have also been raised about the potential.

Unveiling The Distinctions Amalgam Fillings Vs Composite Fillings Among the alternatives to the use of amalgam as a restorative material for dental caries, composite resin is the most common, having been in use for more than 50 years (although experience with newer iterations of composite resin would be shorter). 21 throughout that time, composite resin materials have undergone considerable development and. As amalgam is partly composed of mercury, a known toxic substance, there are concerns about the safety of this filling material for human health, and for the environmental impact of mercury released from amalgam waste generated by dental offices. resin based composite is the most common alternative dental filling material to amalgam. however, concerns have also been raised about the potential. In mandibular molar. a, design for an amalgam restora tion. b, design for a composite restoration. fig. 2. proximal view of class ii preparation for restora tion with composite. facial, lingual, and gingival reten tive grooves are placed in proximal box form. amalgam reduces the need for thick insulating bases, t~ 11. Abstract. an increase in concern regarding the safety and inferior aesthetics of amalgam restorations in dentistry has resulted in a transition from amalgam to other alternative dental materials such as composite resins. this article would critically analyze both the materials and the need for this changeover by means of scientific literature.
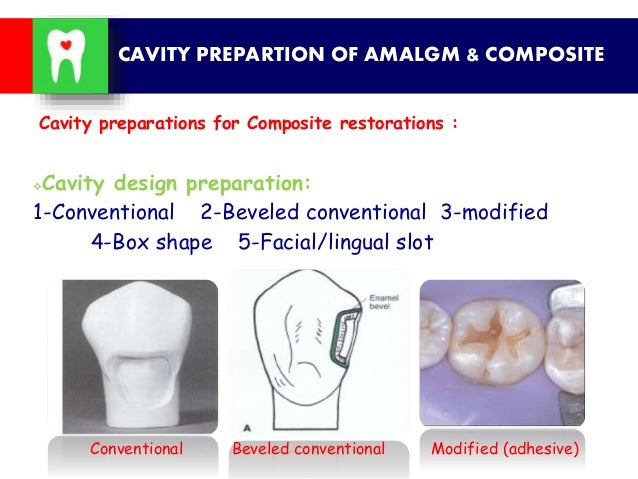
Amalgam Composite In mandibular molar. a, design for an amalgam restora tion. b, design for a composite restoration. fig. 2. proximal view of class ii preparation for restora tion with composite. facial, lingual, and gingival reten tive grooves are placed in proximal box form. amalgam reduces the need for thick insulating bases, t~ 11. Abstract. an increase in concern regarding the safety and inferior aesthetics of amalgam restorations in dentistry has resulted in a transition from amalgam to other alternative dental materials such as composite resins. this article would critically analyze both the materials and the need for this changeover by means of scientific literature.

Cavity Design For Amalgam Restoration Pptx

Amalgam Restoration вљєпёџ Class I Amalgam Cavity Preparation Restoration

Comments are closed.