Ccd Vs Cmos Sensors

Ccd Vs Cmos Sensors Youtube In other words, we are talking about ccd and cmos sensor tech in stills cameras for the sake of brevity. an expanded conversation that goes into the tech across multiple disciplines would be the. Ccd sensors create high quality images with low noise (grain). they are more sensitive to light. however, ccd sensors consume around 100 times more power than equivalent cmos sensors. cmos images tend to have more noise and need more light to create images at the proper exposure. however, cmos sensors are much more power efficient, leading to.
Image Sensors World Ccd Vs Cmos Infographic Plus, the lower resolution makes the images softer, less sterile and more film like. but when using ccd and cmos sensors, the main difference is the nostalgia and the experience of using outdated, less perfect technology. many ccd photographers don’t care about the sensor itself. The decades old competition between imaging sensor tech: charge coupled device (ccd) and complementary metal oxide semiconductor (cmos) sensors, often referred to as “ccd vs cmos,” has been a significant topic of discussion. this guide serves to compare the two technologies' history, strengths, and current and future applications. Now let us look at why going for a cmos sensor would be ideal. lower power consumption: cmos sensors consume relatively lower power (up to 100 times less) than an equivalent ccd sensor. higher speed and frame rate: cmos sensors have relatively higher frame rates than ccd sensors due to the fast reading of the pixels. If you’re comparing ccd vs. cmos sensor components, the active material is a good place to start when selecting candidate sensors. si: this is the most common material used in imaging sensors. its indirect bandgap of 1.1 ev (~1100 nm absorption edge) makes it best suited for visible and nir wavelengths. ingaas: this iii v material provides ir.

Image Sensors Explained How Ccd And Cmos Sensors Works Ccd Vs Cmos Now let us look at why going for a cmos sensor would be ideal. lower power consumption: cmos sensors consume relatively lower power (up to 100 times less) than an equivalent ccd sensor. higher speed and frame rate: cmos sensors have relatively higher frame rates than ccd sensors due to the fast reading of the pixels. If you’re comparing ccd vs. cmos sensor components, the active material is a good place to start when selecting candidate sensors. si: this is the most common material used in imaging sensors. its indirect bandgap of 1.1 ev (~1100 nm absorption edge) makes it best suited for visible and nir wavelengths. ingaas: this iii v material provides ir. Both ccd (charge coupled device) and cmos (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) sensors convert light (photons) into electrical signals (electrons). the main difference between the two sensor types lies in their technical structure. in the ccd sensor, the charge is shifted per pixel. with the cmos sensor, on the other hand, each pixel is. In general, monochrome ccd sensors are considered more light sensitive than color sensors, including both osc ccd and cmos sensors. this heightened sensitivity is attributed to the fact that monochrome ccd pixels capture the entire spectrum of light without the hindrance of color filters, allowing each pixel to receive 100% of the incident light.
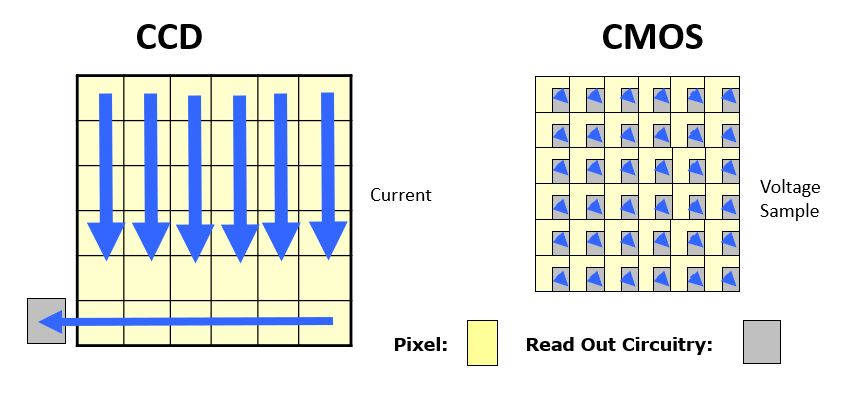
What Are The Benefits Of Cmos Based Machine Vision Cameras Vs Ccd Both ccd (charge coupled device) and cmos (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) sensors convert light (photons) into electrical signals (electrons). the main difference between the two sensor types lies in their technical structure. in the ccd sensor, the charge is shifted per pixel. with the cmos sensor, on the other hand, each pixel is. In general, monochrome ccd sensors are considered more light sensitive than color sensors, including both osc ccd and cmos sensors. this heightened sensitivity is attributed to the fact that monochrome ccd pixels capture the entire spectrum of light without the hindrance of color filters, allowing each pixel to receive 100% of the incident light.

Comments are closed.