Cell Division Mitosis And Meiosis Owlcation
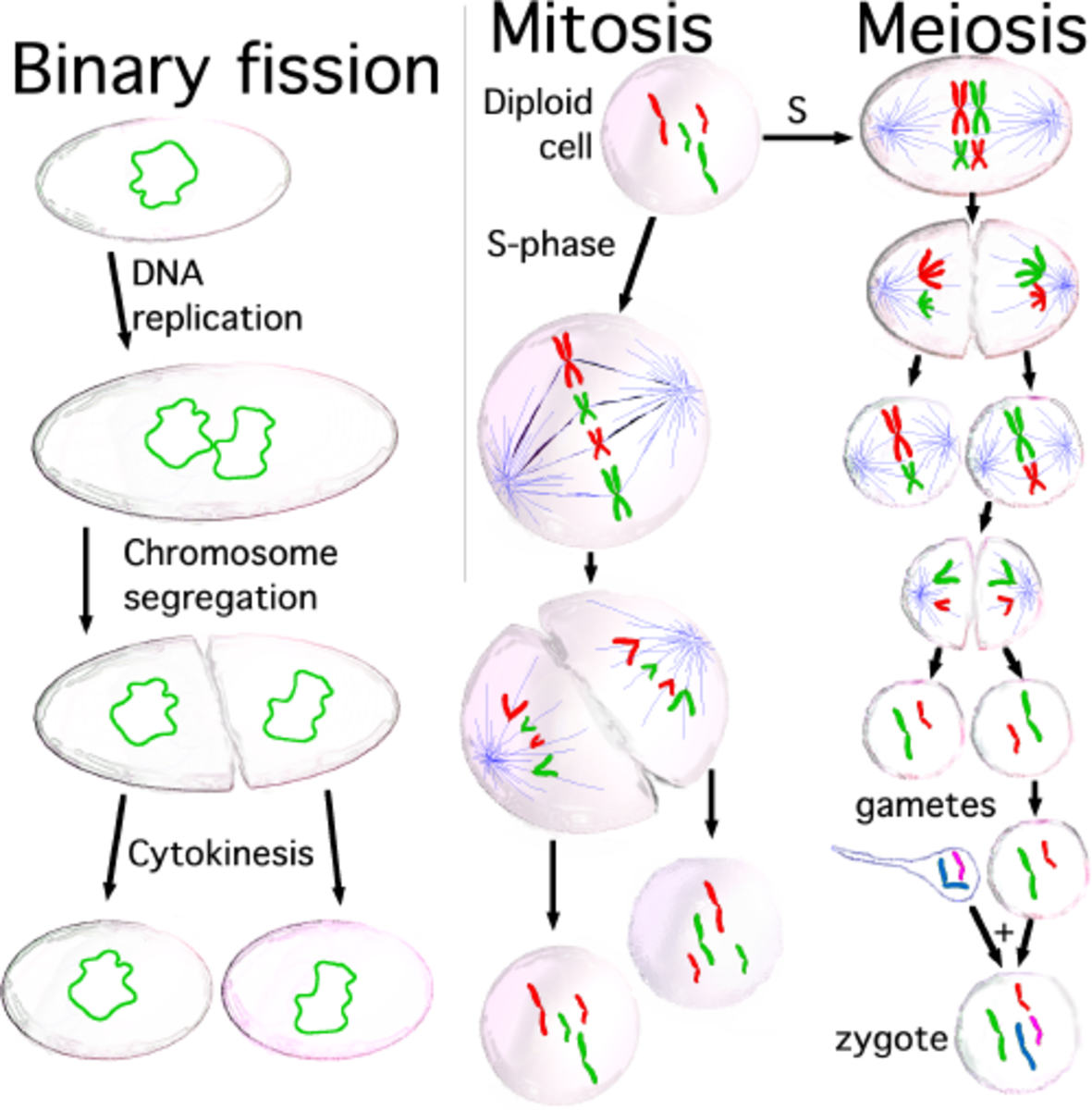
Cell Division Mitosis And Meiosis Owlcation Cell division is the process by which biological cells multiply. there are three major types of cell division: mitosis used by eukaryotic organisms to grow or reproduce asexually; meiosis used by eukaryotic organisms to create sex cells (gametes); binary fission used by prokaryotic organisms to reproduce. The cell cycle proper is split into: growth phase, where normal cellular processes take place and the cell grows to full size. interphase, where the dna is replicated. cytokinesis, where the cytoplasm divides. there is a very good reason why mitosis occupies such a small proportion of the cell cycle.
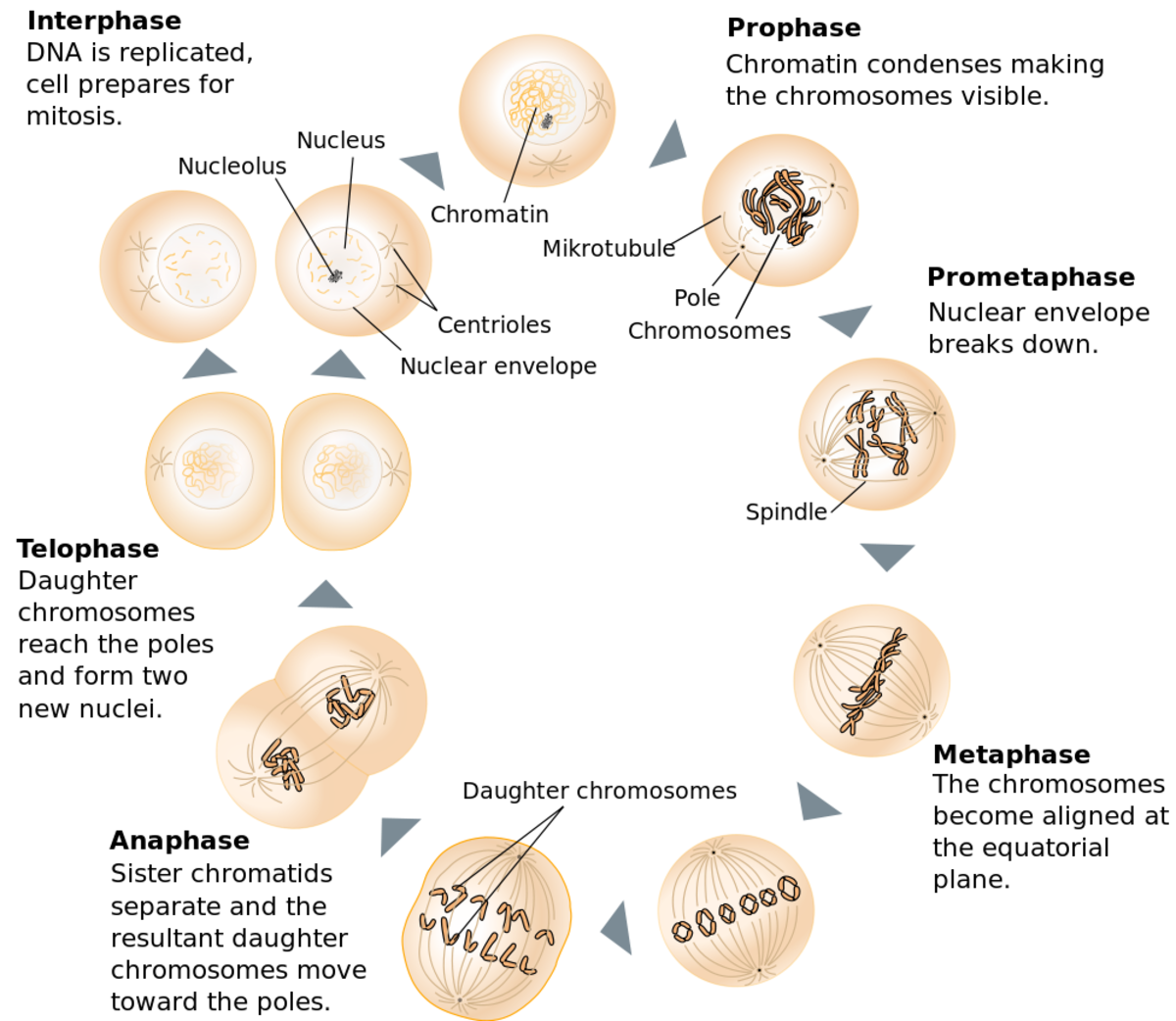
Cell Division Mitosis And Meiosis Owlcation It is the phase of a cell when it is not undergoing mitosis, and it is the longest phase of the cell cycle. during interphase, cells make copies of their dna and grow. from interphase, the cell enters prophase. after a mother cell is divided, the two daughter cells enter interphase until mitosis occurs again. Mitosis. mitosis produces two daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other, and to the parental cell. a diploid cell starts with 2n chromosomes and 2x dna content. after dna replication, the cells is still genetically diploid (2n chromosome number), but has 4x dna content because each chromosome has replicated its dna. Mitosis and meiosis are both types of cell division. mitosis is the process by which most cells in the body divide, involves a single round of cell division, and produces two identical, diploid daughter cells. meiosis is the process by which gametes are produced. meiosis involves two rounds of cell division and produces four non identical. Meiosis: two rounds of cell division. outcome. while mitosis yields two daughter cells that are genetically identical (2n) to the parent cell, meiosis produces four haploid (n) cells that are genetically different from the parent cell. mitosis: two identical daughter cells. meiosis: four non identical daughter cells with half the chromosome number.
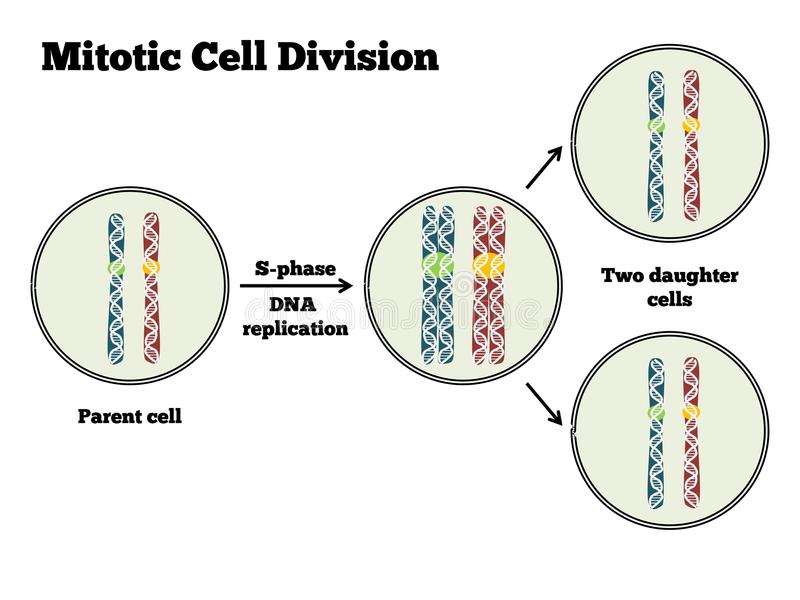
Cell Division Mitosis And Meiosis Owlcation Mitosis and meiosis are both types of cell division. mitosis is the process by which most cells in the body divide, involves a single round of cell division, and produces two identical, diploid daughter cells. meiosis is the process by which gametes are produced. meiosis involves two rounds of cell division and produces four non identical. Meiosis: two rounds of cell division. outcome. while mitosis yields two daughter cells that are genetically identical (2n) to the parent cell, meiosis produces four haploid (n) cells that are genetically different from the parent cell. mitosis: two identical daughter cells. meiosis: four non identical daughter cells with half the chromosome number. Mitosis occurs in somatic cells; this means that it takes place in all types of cells that are not involved in the production of gametes.prior to each mitotic division, a copy of every chromosome. Meiosis is a specialized cell division that only occurs in germ cells that divide to produce sperm or eggs. it produces cells that have only one copy of each type of chromosome (are haploid) both mitosis and meiosis result in eukaryotic cell division. the primary difference between these divisions is the differing goals of each process.

Cell Division Mitosis And Meiosis Owlcation Education Mitosis occurs in somatic cells; this means that it takes place in all types of cells that are not involved in the production of gametes.prior to each mitotic division, a copy of every chromosome. Meiosis is a specialized cell division that only occurs in germ cells that divide to produce sperm or eggs. it produces cells that have only one copy of each type of chromosome (are haploid) both mitosis and meiosis result in eukaryotic cell division. the primary difference between these divisions is the differing goals of each process.

Comments are closed.