Chemical Equilibrium The Haber Process Youtube

Chemical Equilibrium The Haber Process Youtube 👀 watch the entire chemical equilibrium series on clickview free: clickv.ie w rcaw#chemical #haberprocess #equilibrium #chemistry #clickviewhow is c. This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the haber process. it includes a discussion of le chatelier's principle of chemical equilib.

Haber Process And Le Chatelier S Principle Of Chemical Equilibrium Organized by textbook: learncheme describes how to use an interactive simulation that calculates chemical equilibrium for the gas phase reaction. The haber process combines nitrogen from the air with hydrogen derived mainly from natural gas (methane) into ammonia. the reaction is reversible and the production of ammonia is exothermic. a flow scheme for the haber process looks like this: some notes on the conditions. the catalyst. The haber process is used in the manufacturing of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen, and then goes on to explain the reasons for the conditions used in the process. the process combines nitrogen from the air with hydrogen derived mainly from natural gas (methane) into ammonia. the reaction is reversible and the production of ammonia is exothermic. The equilibrium properties of the haber process. as we just covered, the haber process is exothermic and increases spontaneity at lower temperatures. with this information, chemists can increase the yield of the reaction by lowering temperatures. the explanation for this phenomenon involves the principles of chemical equilibrium.

Chemical Equilibrium In The Haber Process Interactive Simulation The haber process is used in the manufacturing of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen, and then goes on to explain the reasons for the conditions used in the process. the process combines nitrogen from the air with hydrogen derived mainly from natural gas (methane) into ammonia. the reaction is reversible and the production of ammonia is exothermic. The equilibrium properties of the haber process. as we just covered, the haber process is exothermic and increases spontaneity at lower temperatures. with this information, chemists can increase the yield of the reaction by lowering temperatures. the explanation for this phenomenon involves the principles of chemical equilibrium. It’s called the haber process, which turns the nitrogen in the air into ammonia, easily converted in soil to the nitrate plants need to survive. though it has increased food supply worldwide, the haber process has also taken an unforeseen toll on the environment. daniel d. dulek delves into the chemistry and consequences. the chemical. Ammonia is used as a chemical feedstock to synthesize a wide range of commercially useful compounds, including fertilizers, plastics, dyes, and explosives. most industrial production of ammonia uses the haber bosch process based on the following equilibrium reaction: n 2(g) 3h 2 (g) ⇌ 2n h 3 (g) Δh = −92.2kj n 2 (g) 3 h 2 (g) ⇌ 2 n h 3.

The Haber Process Equilibrium Youtube It’s called the haber process, which turns the nitrogen in the air into ammonia, easily converted in soil to the nitrate plants need to survive. though it has increased food supply worldwide, the haber process has also taken an unforeseen toll on the environment. daniel d. dulek delves into the chemistry and consequences. the chemical. Ammonia is used as a chemical feedstock to synthesize a wide range of commercially useful compounds, including fertilizers, plastics, dyes, and explosives. most industrial production of ammonia uses the haber bosch process based on the following equilibrium reaction: n 2(g) 3h 2 (g) ⇌ 2n h 3 (g) Δh = −92.2kj n 2 (g) 3 h 2 (g) ⇌ 2 n h 3.
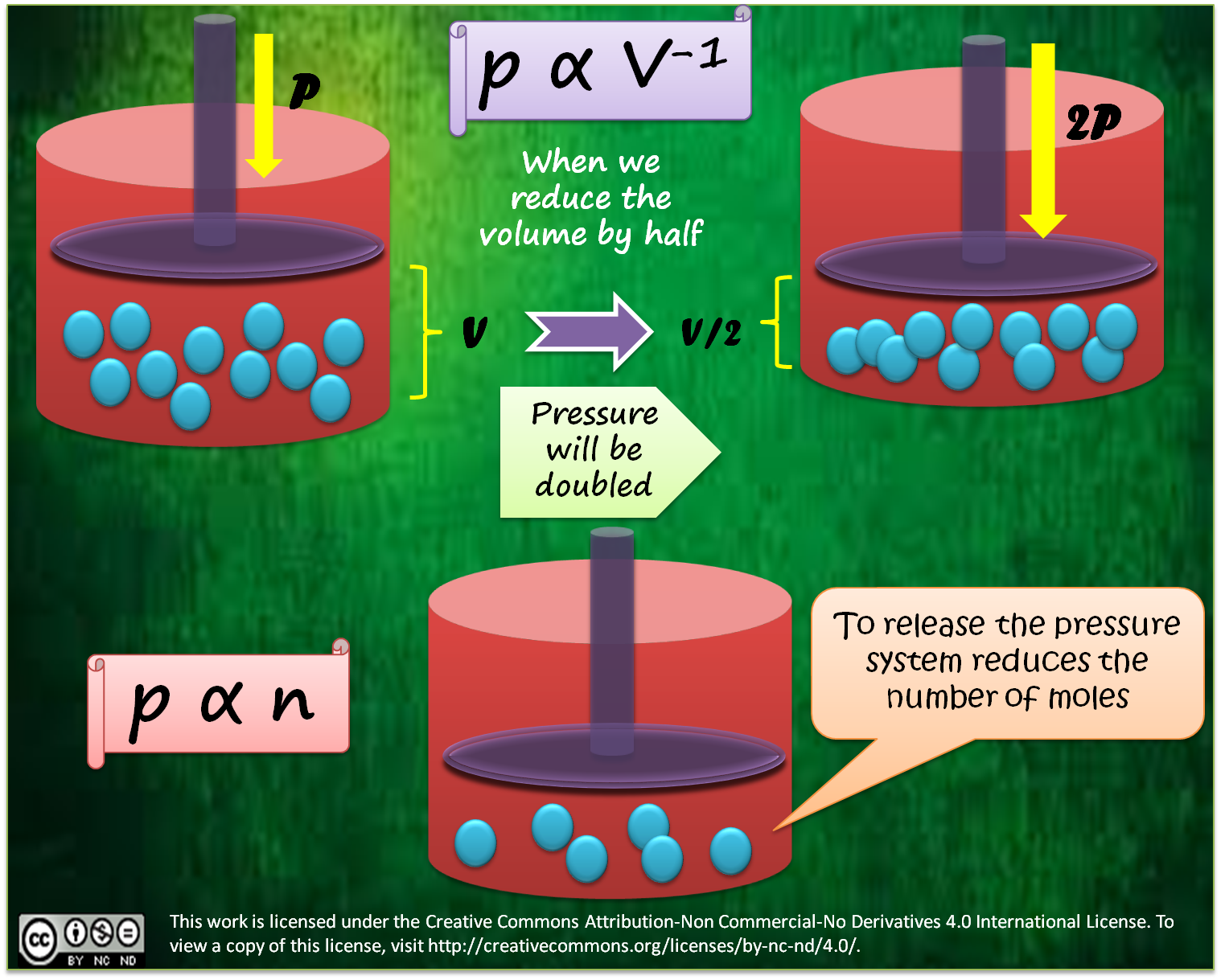
Applications Of Chemical Equilibrium The Haber Process

How The Haber Process Works Le Chatelier S Principle Youtube

Comments are closed.