Chemical Nature Of Enzymes Worthington Biochemical
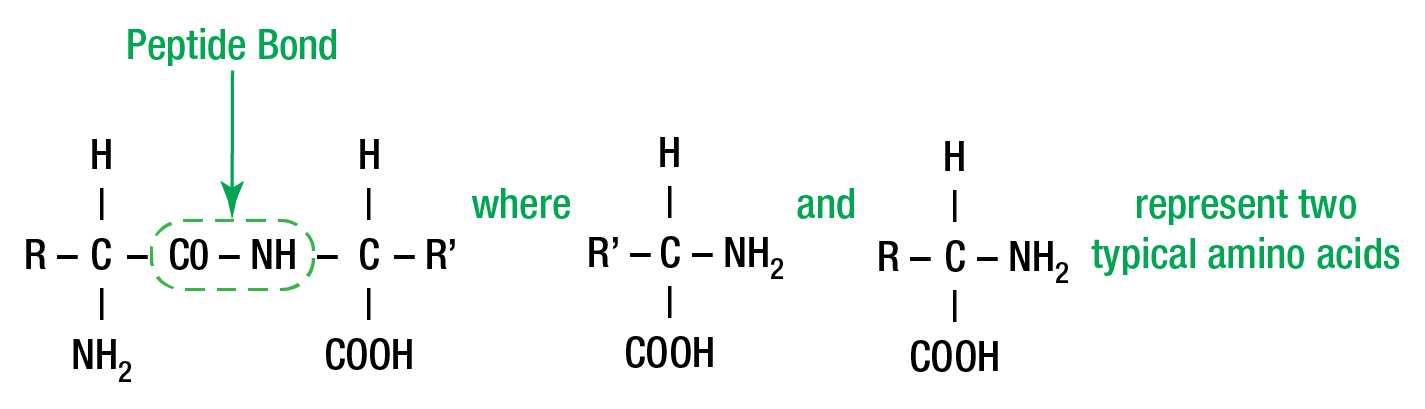
Chemical Nature Of Enzymes Worthington Biochemical Figure 1: typical protein structure – two amino acids joined by a peptide bond. enzymes can be denatured and precipitated with salts, solvents and other reagents. they have molecular weights ranging from 10,000 to 2,000,000. many enzymes require the presence of other compounds cofactors before their catalytic activity can be exerted. Charles c. worthington von worthington andrew worthington, ph.d. the use of enzymes in the diagnosis of disease is one of the important benefits derived from the intensive research in biochemistry since the 1940s. enzymes have provided the basis for the field of clinical chemistry. given the dramatic growth of life science research over recent.
Chemical Nature Of Enzymes Worthington Biochemical Introduction. the use of enzymes in the diagnosis of disease is one of the important benefits derived from the intensive research in biochemistry since the 1940s. enzymes have provided the basis for the field of clinical chemistry. given the dramatic growth of life science research over recent decades, interest in diagnostic enzymology has. The following has been excerpted from a very popular worthington publication which was originally published in 1972 as the manual of clinical enzyme measurements. while some of the presentation may seem somewhat dated, the basic concepts are still helpful for researchers who must use enzymes but who have little background in enzymology. The worthington enzyme manual contains technical information on enzymes including molecular weight, composition, activators, specificity, inhibitors, stability, assay method, optimum ph, ionic effects, temperature effects, extinction coefficient, and isoelectric point, as well as applications and extensive references. 1993 edition. Introduction to enzymes. the following has been excerpted from a very popular worthington publication which was originally published in 1972 as the manual of clinical enzyme measurements. while some of the presentation may seem somewhat dated, the basic concepts are still helpful for researchers who must use enzymes but who have little.
Biochemistry Topic 1 Chemical Nature Of Enzymes General The worthington enzyme manual contains technical information on enzymes including molecular weight, composition, activators, specificity, inhibitors, stability, assay method, optimum ph, ionic effects, temperature effects, extinction coefficient, and isoelectric point, as well as applications and extensive references. 1993 edition. Introduction to enzymes. the following has been excerpted from a very popular worthington publication which was originally published in 1972 as the manual of clinical enzyme measurements. while some of the presentation may seem somewhat dated, the basic concepts are still helpful for researchers who must use enzymes but who have little. Upon reaction catalysis, an enzyme turns back to its original form and becomes available to participate in the new biochemical reactions. in this post, we will discuss the reasons why enzymes are considered biocatalysts along with the enzyme’s general properties. you could also learn the physical and chemical nature of an enzyme in this context. Enzymes and life processes. the living cell is the site of tremendous biochemical activity called metabolism. this is the process of chemical and physical change which goes on continually in the living organism. build up of new tissue, replacement of old tissue, conversion of food to energy, disposal of waste materials, reproduction all the.

Chemical Nature Of Enzymes Introduction To Enzymes Upon reaction catalysis, an enzyme turns back to its original form and becomes available to participate in the new biochemical reactions. in this post, we will discuss the reasons why enzymes are considered biocatalysts along with the enzyme’s general properties. you could also learn the physical and chemical nature of an enzyme in this context. Enzymes and life processes. the living cell is the site of tremendous biochemical activity called metabolism. this is the process of chemical and physical change which goes on continually in the living organism. build up of new tissue, replacement of old tissue, conversion of food to energy, disposal of waste materials, reproduction all the.

Chemical Nature Of Enzymes Simple And Conjugate Class 11 Pw

Enzymes

Comments are closed.