Chronic Kidney Disease Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Pathology
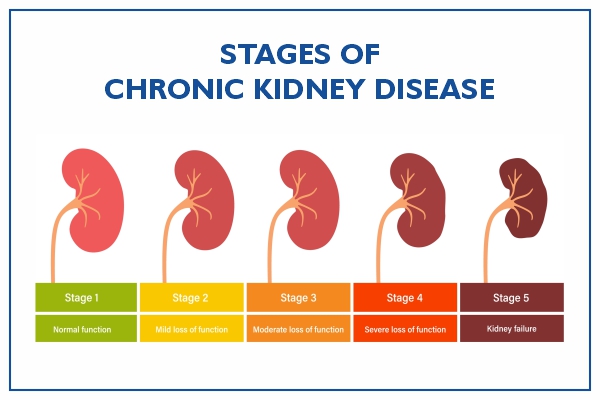
Chronic Kidney Disease Symptoms Stages Causes Risk 41 Off Generally, earlier stages are known as 1 to 3. and as kidney disease progresses, you may notice the following symptoms. nausea and vomiting, muscle cramps, loss of appetite, swelling via feet and ankles, dry, itchy skin, shortness of breath, trouble sleeping, urinating either too much or too little. Chronic kidney disease (ckd) is characterized by the presence of kidney damage or an estimated glomerular filtration rate (egfr) of less than 60 ml min 1.73 m², persisting for 3 months or more, irrespective of the cause.[1] ckd is a state of progressive loss of kidney function, ultimately resulting in the need for renal replacement therapy, such as dialysis or transplantation. kidney damage.

Chronic Kidney Disease Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment This is a chemical imbalance (acid base) in your blood caused by a decrease in kidney function. high blood pressure. heart disease and blood vessel disease, including increased risk of stroke and heart attack. nerve damage. high potassium (hyperkalemia), which affects your heart’s ability to function correctly. Next, your doctor performs a physical exam, checking for signs of problems with your heart or blood vessels, and conducts a neurological exam. for kidney disease diagnosis, you might also need certain tests and procedures to determine how severe your kidney disease is (stage). tests might include: blood tests. 1.1 classification of ckd. chronic kidney disease (ckd) is far more prevalent worldwide than was previously assumed. it affects 10 15% of the adult population in the western countries, many of whom require costly treatments or renal replacement therapy. according to the third national health and nutrition examination survey and the national. Kdigo 2017 clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of chronic kidney disease–mineral and bone disorder (ckd mbd) kidney int suppl 7(1):1 59, 2017. 4. determining drug dosing in adults with chronic kidney disease. 5. munar my, singh hd: drug dosing adjustments in patients with chronic kidney disease.
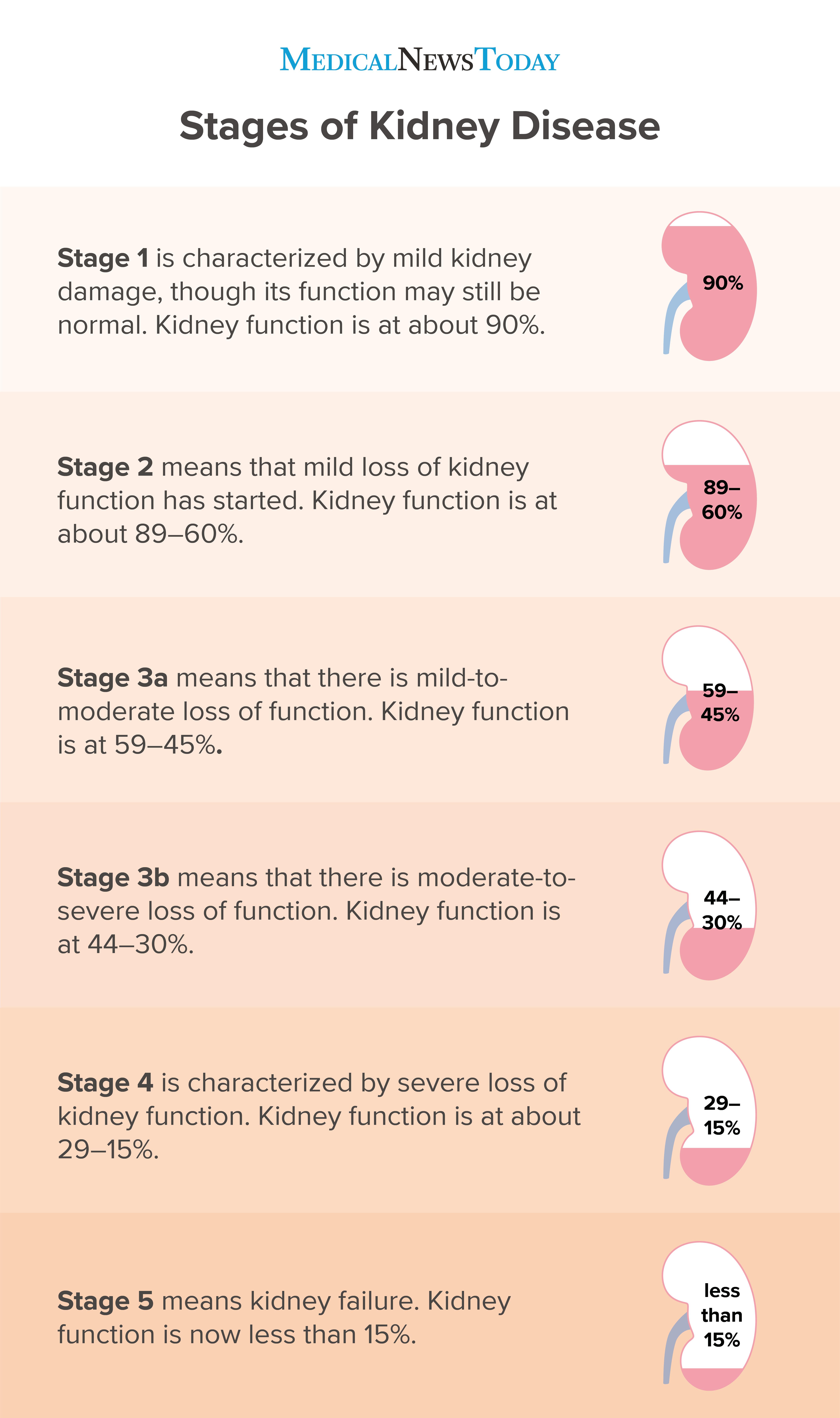
Stages Of Chronic Kidney Disease Chart 1.1 classification of ckd. chronic kidney disease (ckd) is far more prevalent worldwide than was previously assumed. it affects 10 15% of the adult population in the western countries, many of whom require costly treatments or renal replacement therapy. according to the third national health and nutrition examination survey and the national. Kdigo 2017 clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of chronic kidney disease–mineral and bone disorder (ckd mbd) kidney int suppl 7(1):1 59, 2017. 4. determining drug dosing in adults with chronic kidney disease. 5. munar my, singh hd: drug dosing adjustments in patients with chronic kidney disease. Chronic kidney disease (ckd) is a common condition that is often unrecognized until the most advanced stages. diagnosis is determined only by laboratory studies: proteinuria or hematuria, and or a reduction in the glomerular filtration rate, for more than 3 months' duration. the most common causes are diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Importancechronic kidney disease (ckd) is the 16th leading cause of years of life lost worldwide. appropriate screening, diagnosis, and management by primary care clinicians are necessary to prevent adverse ckd associated outcomes, including cardiovascular disease, end stage kidney disease, and death. observationsdefined as a persistent.

Chronic Kidney Disease Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Chronic kidney disease (ckd) is a common condition that is often unrecognized until the most advanced stages. diagnosis is determined only by laboratory studies: proteinuria or hematuria, and or a reduction in the glomerular filtration rate, for more than 3 months' duration. the most common causes are diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Importancechronic kidney disease (ckd) is the 16th leading cause of years of life lost worldwide. appropriate screening, diagnosis, and management by primary care clinicians are necessary to prevent adverse ckd associated outcomes, including cardiovascular disease, end stage kidney disease, and death. observationsdefined as a persistent.
Chronic Kidney Disease Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment

Comments are closed.