Class V Amalgam Restoration Condensation And Carving
Class V Tooth Preparation For Amalgam Restorations Third part of the procedure, amalgam condensation and carving. orig. air date: mar 8 74this is part of the open.michigan collection at: open.umich.edu. A class ii restoration has at least two surfaces open and therefore lacks the box like shape for proper condensation. a matrix band is a thin strip of material that is placed around the tooth to establish the missing sides of the box and allows adequate condensation of amalgam (see fig. 26.1a ).

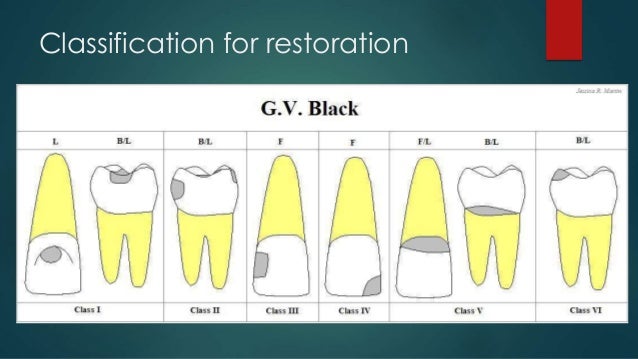
Class V Buccal Amalgam Restorations Consisting Of 25 50 75 And 100 5 restorative technique for class i (simple and compound), ii, and v preparations 5 application of the matrix and wedge for class ii and v restorations 5 trituration and condensation 5 pre carve burnishing procedure 5 carving of occlusal and smooth surfaces 5 post carve burnishing procedure 5 occlusal adjustment or a new restoration. 11.3.3 restoration of class v preparations (site 3) the amalgam restorations on class v preparations are indicated on areas where esthetics is not a concern, the access and the visibility are limited, and the moisture control is difficult . the cavosurface angles of the gingival wall in class v preparation are many times located inside the. Condensation and carving instruments to develop proper tooth anatomy. you can smooth the surface of a restoration by wiping over the amalgam with a cotton ball or cotton roll saturated with water (assuming the amalgam is partially set). p.s.: newly placed amalgam restorations may fracture at the marginal ridge because of the following reasons:. Place and cure resin based composite at the line angle to form a temporary wall to support the class v amalgam restoration during its condensation. etch and bond if needed. condense the class v amalgam restoration and then quickly finish it . remove the resin based composite using a sharp scaler, a no. 15 scalpel blade or a handpiece.

Amalgam Condensation And Carving Technique Tutorial In Office To Condensation and carving instruments to develop proper tooth anatomy. you can smooth the surface of a restoration by wiping over the amalgam with a cotton ball or cotton roll saturated with water (assuming the amalgam is partially set). p.s.: newly placed amalgam restorations may fracture at the marginal ridge because of the following reasons:. Place and cure resin based composite at the line angle to form a temporary wall to support the class v amalgam restoration during its condensation. etch and bond if needed. condense the class v amalgam restoration and then quickly finish it . remove the resin based composite using a sharp scaler, a no. 15 scalpel blade or a handpiece. 1.to commence the process ofcondensation, insert small increments of amalgam inthe retentive portion of the cavity preparation andcondense italong the mesial and distal walls with a small amalgam condenser. 2. build upthe rest ofthe central portion to sufficient bulk to allow for carving. For class v •indications are same as for class iii, and also for •restoration on partial denture abutment teeth, because amalgam is more resistant to wear as clasps move over the restoration. •when the carious lesion extends gingivally enough that a soft tissue flap must be reflected for adequate access and visibility.

Composite Class V Restorations Lesion Specific Approaches 1.to commence the process ofcondensation, insert small increments of amalgam inthe retentive portion of the cavity preparation andcondense italong the mesial and distal walls with a small amalgam condenser. 2. build upthe rest ofthe central portion to sufficient bulk to allow for carving. For class v •indications are same as for class iii, and also for •restoration on partial denture abutment teeth, because amalgam is more resistant to wear as clasps move over the restoration. •when the carious lesion extends gingivally enough that a soft tissue flap must be reflected for adequate access and visibility.

Comments are closed.