Coastal And Open Ocean Biomes Ask A Biologist
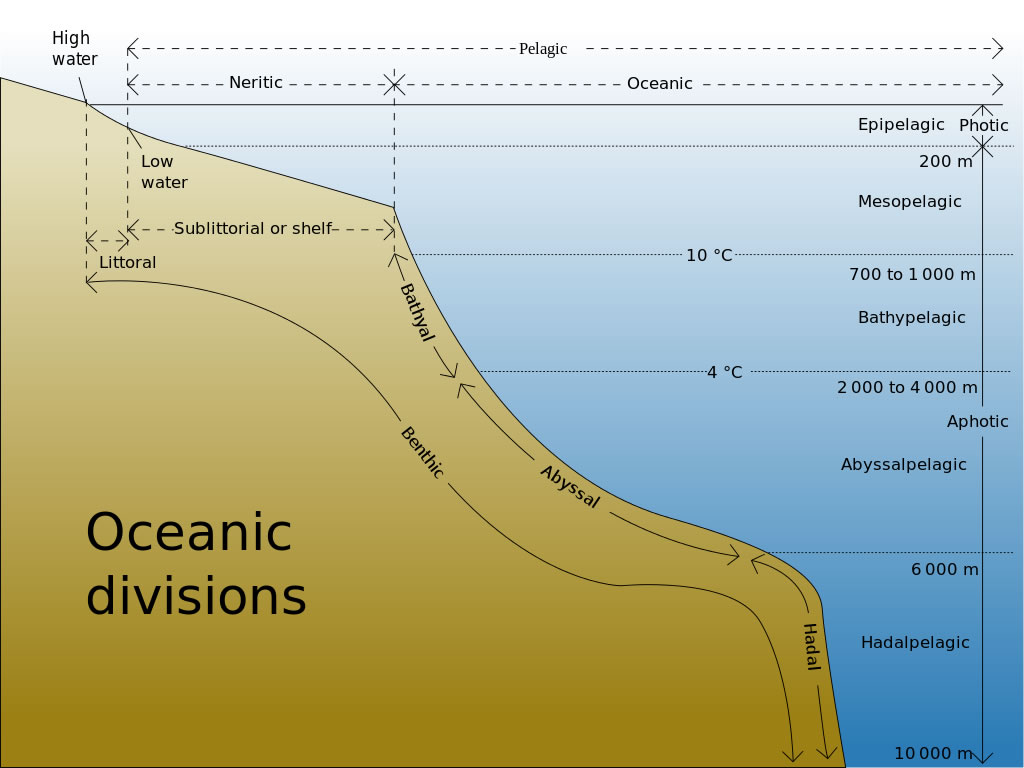
Coastal And Open Ocean Biomes Ask A Biologist The open ocean stretches from the edges of the coast between the continents for hundreds of miles. this biome also dives beneath the ocean surface to the very bottom of the deepest ocean trench. as the largest biome, the open ocean covers over 45% of earth’s surface. but compared to the coast, the open ocean is sparsely populated, almost like. The region of the ocean that you can see from shore is the coastal, or nearshore, marine biome. it stretches from the high water line on shore out to the continental shelf, where earth’s crust suddenly drops off into the depths of the ocean. the continental shelf is just that – a shelf – that raises the creatures living on it up into.

Coastal And Open Ocean Biomes Asu Ask A Biologist The coastal biome has two fairly well defined borders: the high water line near on the shore, and the steep edge of the underwater continental shelf far offshore. coasts are found on the continental shelves. click for more detail. the border on shore is the intertidal zone, or the area that is sometimes exposed to the air during low tide. This biome also dives beneath the ocean surface to the very bottom of the deepest ocean trench. as the largest biome, the open ocean covers over 45% of earth’s surface. but compared to the coast, the open ocean is sparsely populated, almost like an ocean desert. the ocean is a large place and can be divided up in many ways. click for more detail. The open ocean biome is the largest biome on earth. it covers nearly half of the earth's surface. the part of the open ocean that is not close to the ocean floor is called the pelagic zone. you are floating, face up, in the middle of a big swimming pool. with your eyes closed and your ears under the water, you don't see or hear much. But the biggest difference between symbiosis in the shallow coastal biome and the deep ocean is that the producers don’t use sunlight to make food. instead, the crabs, mussels, and worms near these vents and seeps eat special bacteria or hold it in their skin. the diversity of animals at deep sea hydrothermal vents is breathtaking.
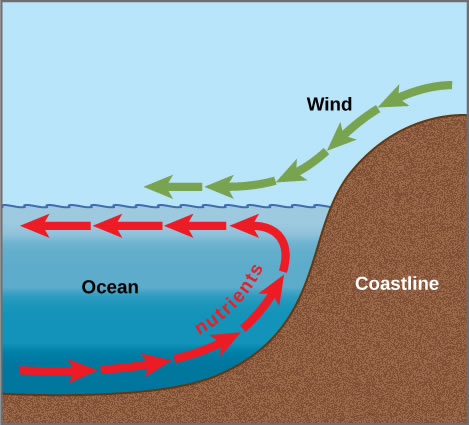
Coastal And Open Ocean Biomes Ask A Biologist The open ocean biome is the largest biome on earth. it covers nearly half of the earth's surface. the part of the open ocean that is not close to the ocean floor is called the pelagic zone. you are floating, face up, in the middle of a big swimming pool. with your eyes closed and your ears under the water, you don't see or hear much. But the biggest difference between symbiosis in the shallow coastal biome and the deep ocean is that the producers don’t use sunlight to make food. instead, the crabs, mussels, and worms near these vents and seeps eat special bacteria or hold it in their skin. the diversity of animals at deep sea hydrothermal vents is breathtaking. Because this biome is found at the edges of the land, the coastal biome exists on every continent and in every climate. this combination of sunlight, water, and various climates results in a wide range of habitats along the coast. some of these environments are coral reefs, kelp forests, river estuaries, sea grass meadows, and salt marshes. For the largest biome of the world, the climate ranges between 40 degrees fahrenheit and over 100 degrees fahrenheit. climate is a significant factor that affects ocean biome. hurricanes and typhoons impact species like the polar bear, fish, plankton, walrus, penguin, and seabird. some species have adapted to the style of seasonal disasters.

Comments are closed.