Compilation Of Pharmaceutical Regulatory Authorities In Different

Compilation Of Pharmaceutical Regulatory Authorities In Different Pharmaceutical regulatory authorities explained. navigating the landscape of pharmaceutical regulatory authorities and compliance is crucial for ensuring that drug development and manufacturing processes meet stringent standards. this short guide aims to provide an in depth overview of this complex field, offering insights into the main. Regulatory authorities. modules 2–5 though are common to all regions and these comprise the main body of the ctd. module 2 contains the ctd overviews and sum maries. it starts with a general introduction to the drug, including its pharmacological class, mode of action, and proposed clinical use. module 2 then.
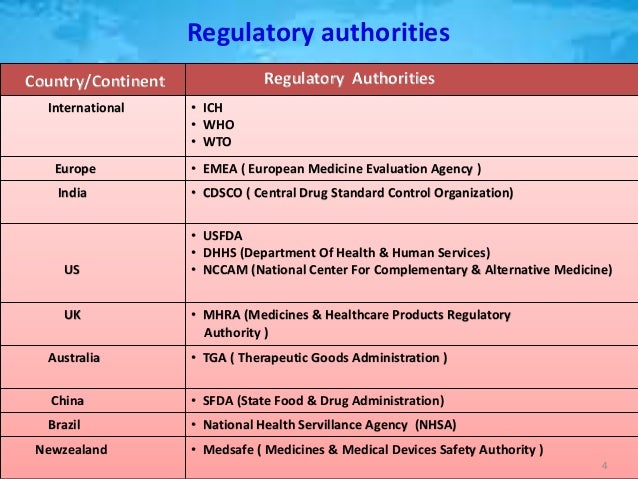
Regulatory Authorities Us Fda Who And Ich The role of drug regulatory authorities. drug regulatory authorities are responsible for overseeing the development, approval, and monitoring of pharmaceutical products. these authorities, including the fda and ema, ensure that all drug products meet the necessary safety and efficacy standards before they are approved for public use. they also. The ich was founded in april 1990 at a meeting of the european federation of pharmaceutical industries association (efpia) in brussels. ich is a unique undertaking that brings together the drug regulatory authorities and the pharmaceutical industry of europe, japan and the united states. The regulatory requirements for approval of generic medicines and the format of compiling drug dossiers vary among regulatory authorities. the variation is particularly wide between high income countries (hic) and lower and middle income countries (lmic) with different regulatory frameworks. International journal of pharmaceutical research and applications volume 7, issue 4 july aug 2022, pp: 808 818 ijprajournal issn: 2456 4494 doi: 10.35629 7781 0704808818 | impact factor value 7.429 | iso 9001: 2008 certified journal page 808 a review of the preparation of regulatory dossiers in ctd format and ectd submissions.

List Of Global Drug Regulatory Authorities Of Different Countries The regulatory requirements for approval of generic medicines and the format of compiling drug dossiers vary among regulatory authorities. the variation is particularly wide between high income countries (hic) and lower and middle income countries (lmic) with different regulatory frameworks. International journal of pharmaceutical research and applications volume 7, issue 4 july aug 2022, pp: 808 818 ijprajournal issn: 2456 4494 doi: 10.35629 7781 0704808818 | impact factor value 7.429 | iso 9001: 2008 certified journal page 808 a review of the preparation of regulatory dossiers in ctd format and ectd submissions. Abstract. a regulatory affair is a unique synergy of internal departments of an industry with the regulatory bodies, which starts with the conceptualization of the product to be developed by that industry, till the marketing of that product. it is a very important and salient feature of pharmaceutical product development. A national medicines policy is a first step in identifying and resolving problems within the pharmaceutical sector. medicine regulatory authorities (mras), whatever their official names, are a first step toward to ensuring a strong regulation of the market and the protection of public health; without a central authority monitoring, testing, and.

Illustrates The Regulatory Authorities Of Various Countries Download Abstract. a regulatory affair is a unique synergy of internal departments of an industry with the regulatory bodies, which starts with the conceptualization of the product to be developed by that industry, till the marketing of that product. it is a very important and salient feature of pharmaceutical product development. A national medicines policy is a first step in identifying and resolving problems within the pharmaceutical sector. medicine regulatory authorities (mras), whatever their official names, are a first step toward to ensuring a strong regulation of the market and the protection of public health; without a central authority monitoring, testing, and.

Comments are closed.