Consumer Animals

Consumer Animals Learn what a consumer is in biology, and how consumers are categorized into four groups based on their food source. find out the difference between producers, decomposers, and trophic levels in food chains and food webs. Learn about the different types of consumers in a food chain, such as herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and decomposers. find out how consumers are classified by their trophic levels and how they balance the ecosystem.
Animals That Can Eat Both Producers And Or Other Consumers At Heidi Primary consumers are herbivores that eat only plants or algae. learn about 12 examples of primary consumers from different ecosystems, such as butterflies, grasshoppers, deer, zebras, and aphids. Primary consumers are animals that eat only vegetation, also known as herbivores. learn about 12 examples of primary consumers, such as rabbits, caribou, horses, zebras, cows, goats, and more. Some secondary consumers eat both plants and animals. they are called omnivores , from the latin words that mean “eats everything.” a raccoon is an example of an omnivore; it eats plant matter such as berries and acorns, but it also catches crayfish, frogs, fish, and other small animals. Learn what a secondary consumer is, how it differs from a primary consumer, and what types of secondary consumers exist in different habitats. find out how secondary consumers fit into the food chain and why they are important for the ecosystem.
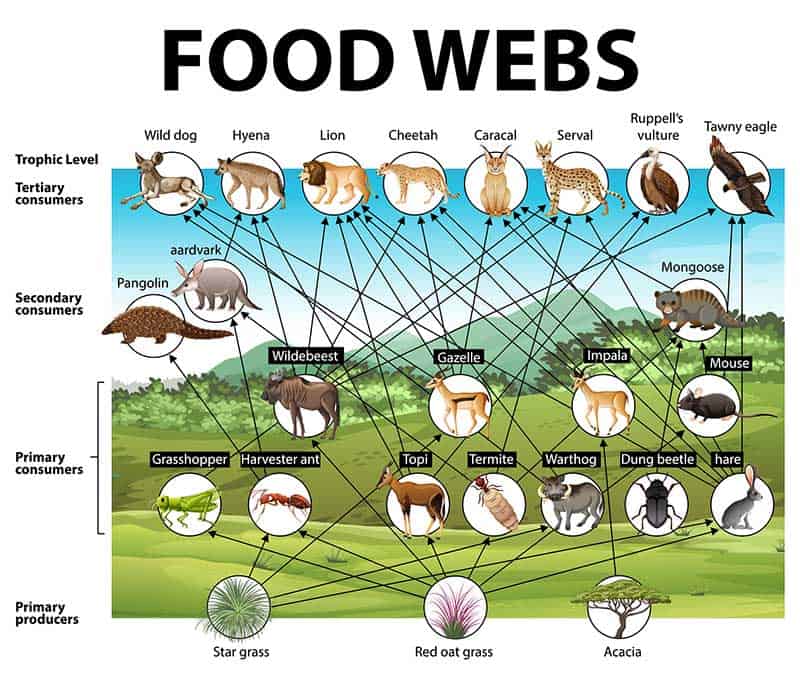
Consumer Animals List Some secondary consumers eat both plants and animals. they are called omnivores , from the latin words that mean “eats everything.” a raccoon is an example of an omnivore; it eats plant matter such as berries and acorns, but it also catches crayfish, frogs, fish, and other small animals. Learn what a secondary consumer is, how it differs from a primary consumer, and what types of secondary consumers exist in different habitats. find out how secondary consumers fit into the food chain and why they are important for the ecosystem. A primary consumer is an organism that feeds on primary producers, such as plants or algae. learn about the different types of primary consumers, their feeding strategies, adaptations and examples, such as ruminants, zooplankton and herbivorous birds. A consumer is a living thing that eats other plants and animals. the arrows in a food chain show the way in which energy is moving. a predator is an animal that eats other animals.

Consumer Animals A primary consumer is an organism that feeds on primary producers, such as plants or algae. learn about the different types of primary consumers, their feeding strategies, adaptations and examples, such as ruminants, zooplankton and herbivorous birds. A consumer is a living thing that eats other plants and animals. the arrows in a food chain show the way in which energy is moving. a predator is an animal that eats other animals.

Consumer Animals List

Comments are closed.