Consumer Food Chain

Food Chain Trophic Levels And Flow Of Energy In Ecosystem Online Learn about the different types of consumers in a food chain, such as herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and decomposers. find out how consumers are classified by their trophic levels and how they balance the ecosystem. Learn what a consumer is in an ecosystem and how it relates to producers and decomposers. find out the different types of consumers and their roles in food chains and food webs.
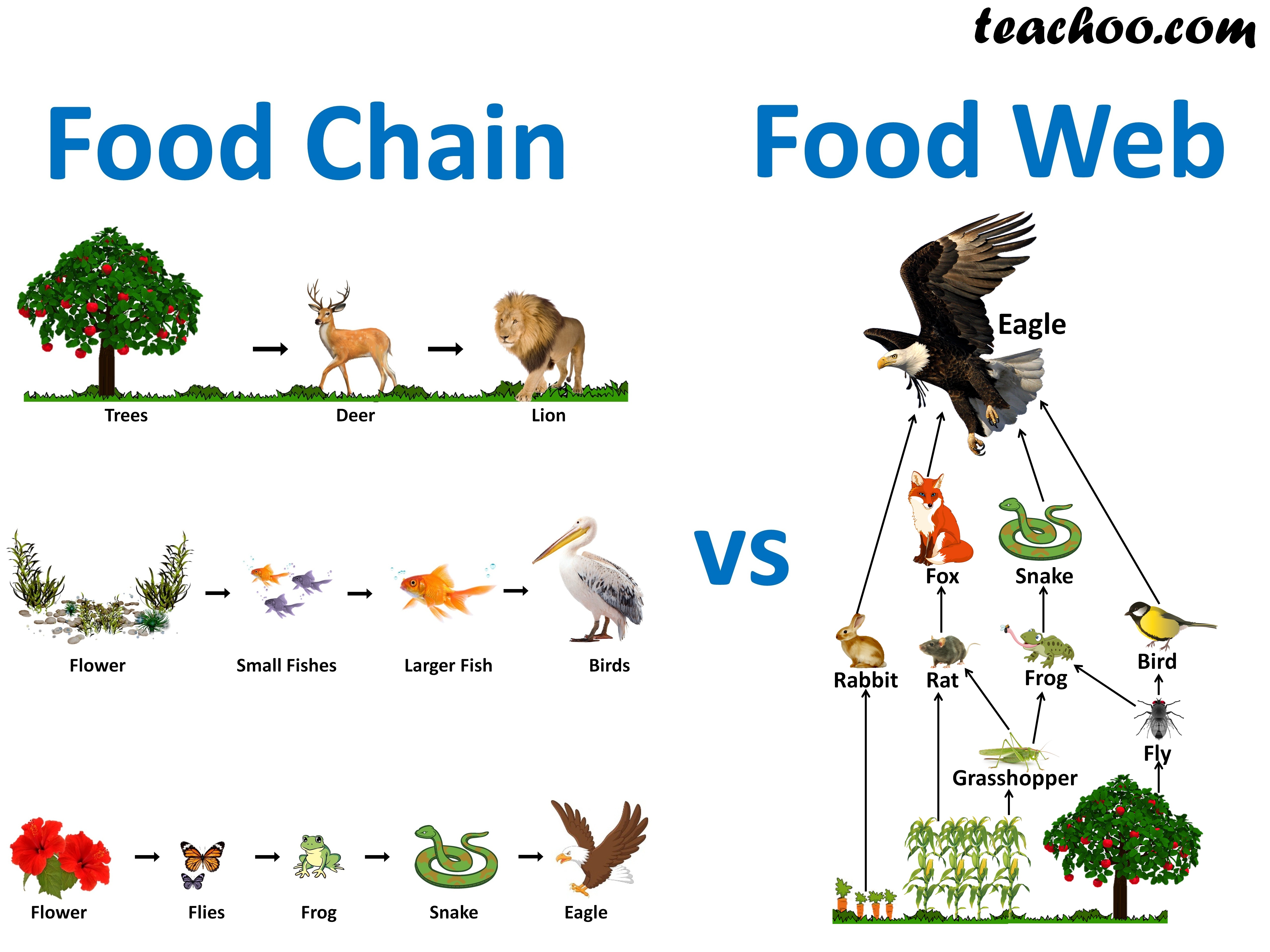
What Is The Difference Between Food Chain And Food Web Teachoo Organisms in the food chain are divided into trophic levels or feeding levels. the four essential parts are the sun, primary producers, consumers, and decomposers. every food chain originates with the sun providing light and energy for plants to grow and ends with the decomposition of the animals. Learn how organisms interact and transfer energy through trophic levels in food chains and food webs. explore the concepts of trophic level, trophic transfer efficiency, and biological magnification with examples and diagrams. Figure 46.1b. 1 46.1 b. 1: food chain: these are the trophic levels of a food chain in lake ontario. energy and nutrients flow from photosynthetic green algae at the bottom to the salmon at the top of the food chain. there are only four links in this chain because significant energy is lost between each successive trophic level. Higher level consumers feed on the next lower tropic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the apex consumers. in the lake ontario food chain shown in figure 1, the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the top of this food chain. one major factor that limits the length of food chains is energy.
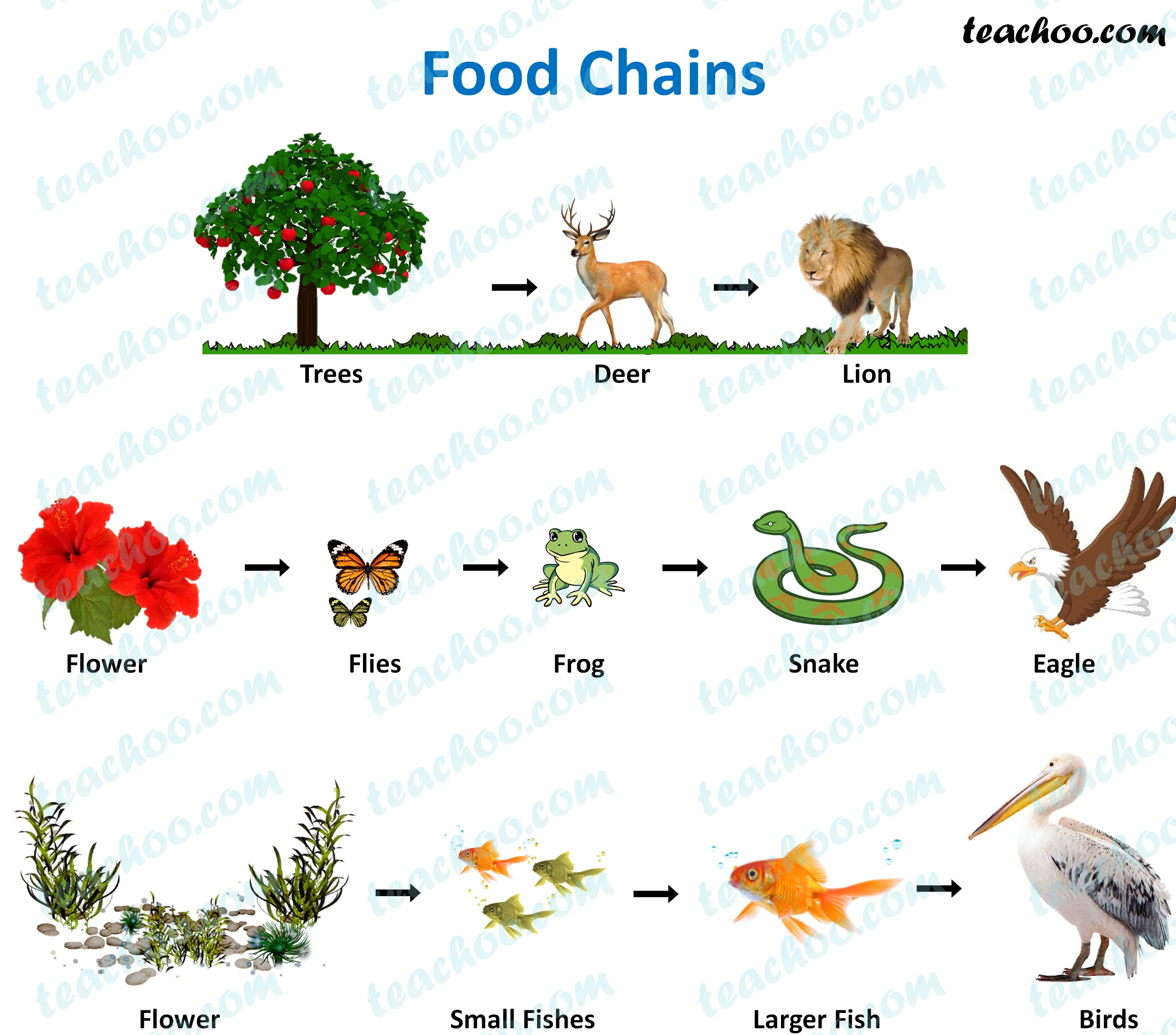
Food Chain And Food Web Meaning Diagrams Examples Teachoo Figure 46.1b. 1 46.1 b. 1: food chain: these are the trophic levels of a food chain in lake ontario. energy and nutrients flow from photosynthetic green algae at the bottom to the salmon at the top of the food chain. there are only four links in this chain because significant energy is lost between each successive trophic level. Higher level consumers feed on the next lower tropic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the apex consumers. in the lake ontario food chain shown in figure 1, the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the top of this food chain. one major factor that limits the length of food chains is energy. A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and. The cow and human are consumers. a food chain is a list of organisms in a. habitat. that shows their feeding relationship, i.e what eats what. the organisms are joined by arrows which show the.
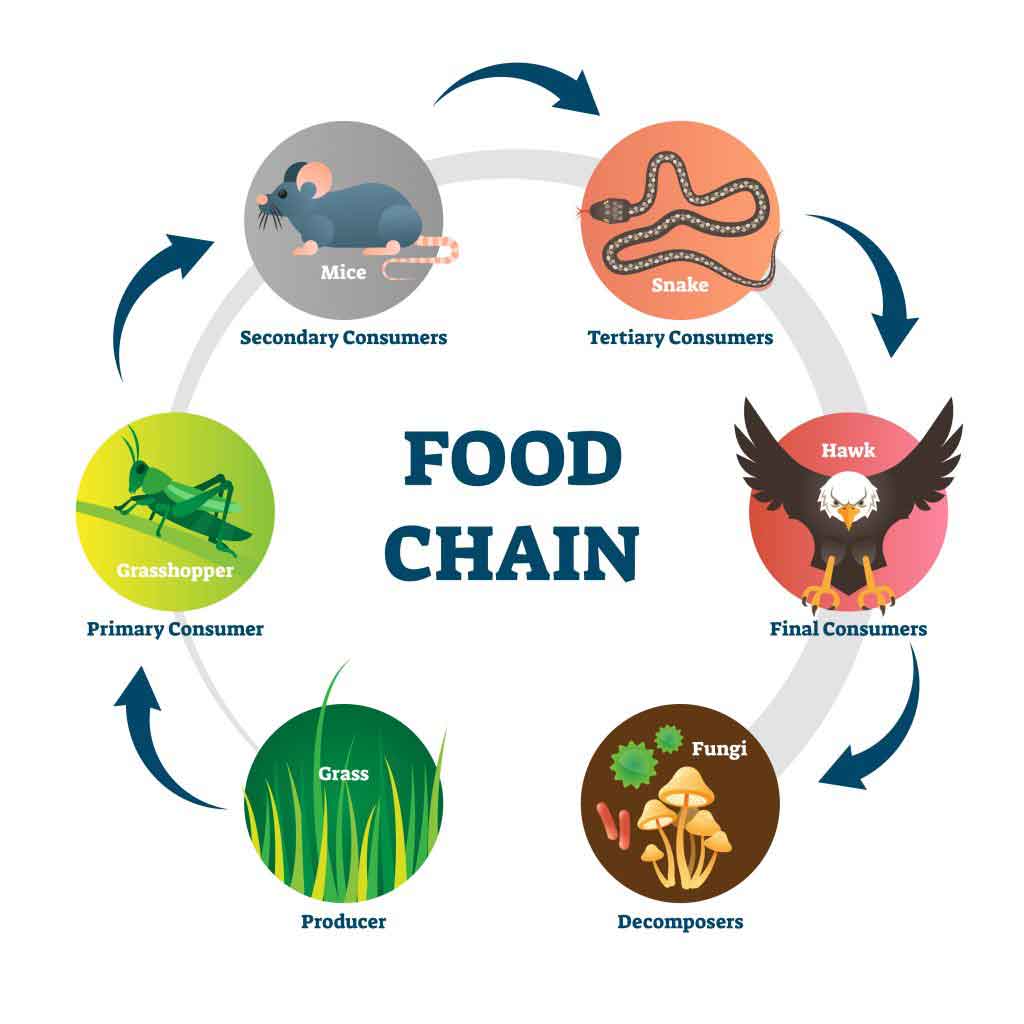
Explain The Difference Between Food Chain And Food Web Bitwise Academy A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and. The cow and human are consumers. a food chain is a list of organisms in a. habitat. that shows their feeding relationship, i.e what eats what. the organisms are joined by arrows which show the.
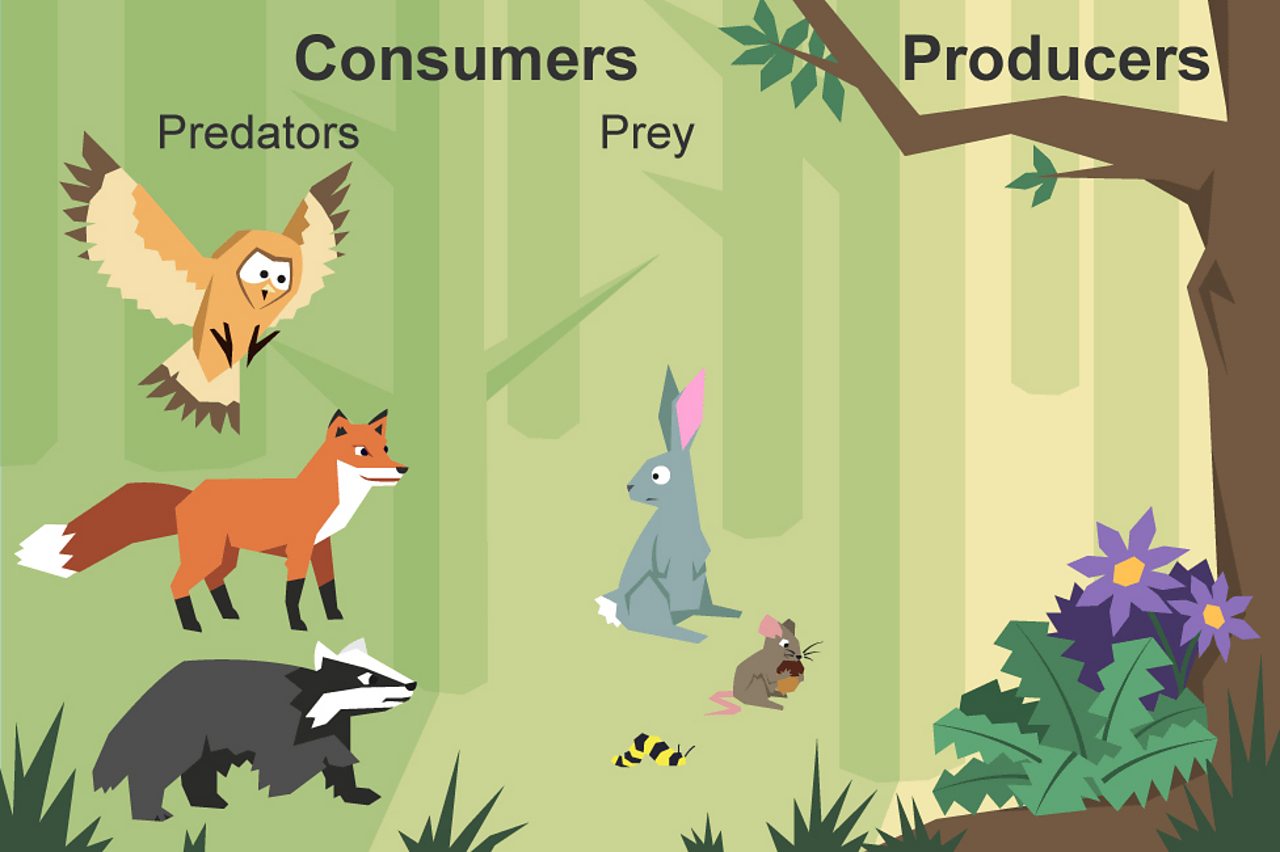
What Is A Food Chain Bbc Bitesize

Comments are closed.