Consumer Surplus And Producer Surplus Formula
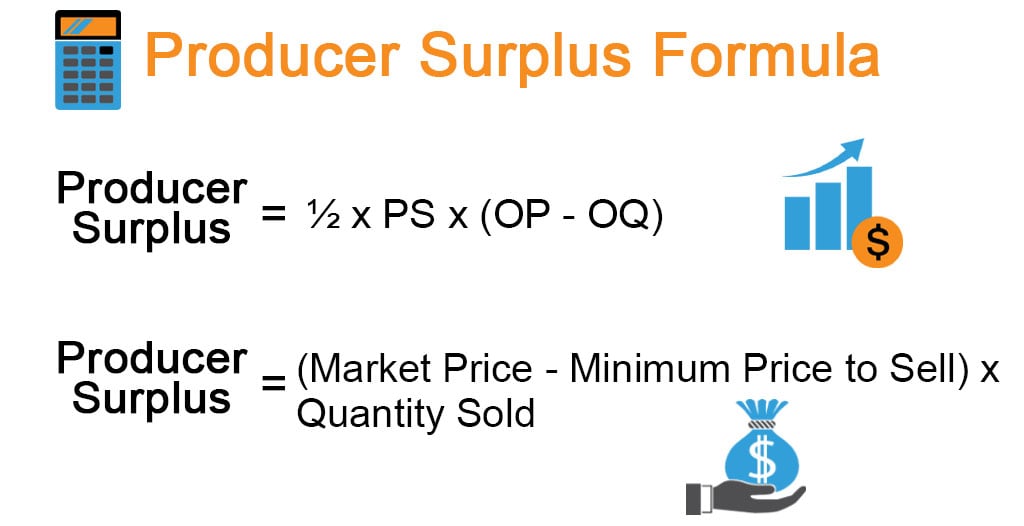
Producer Surplus Formula Calculator Examples With Excel Template In the previous example, the total consumer surplus was $3, and the total producer surplus $4, respectively. the total surplus, therefore, will be $7 ($3 $4). below is the formula: total surplus = consumer surplus producer surplus. in the above example, the total surplus does not depict the equilibrium. there is a deadweight to shed off. The formula for producer surplus is: total revenue marginal cost = producer surplus. the size of the producer surplus and its triangular depiction on the graph increases as the market price for.
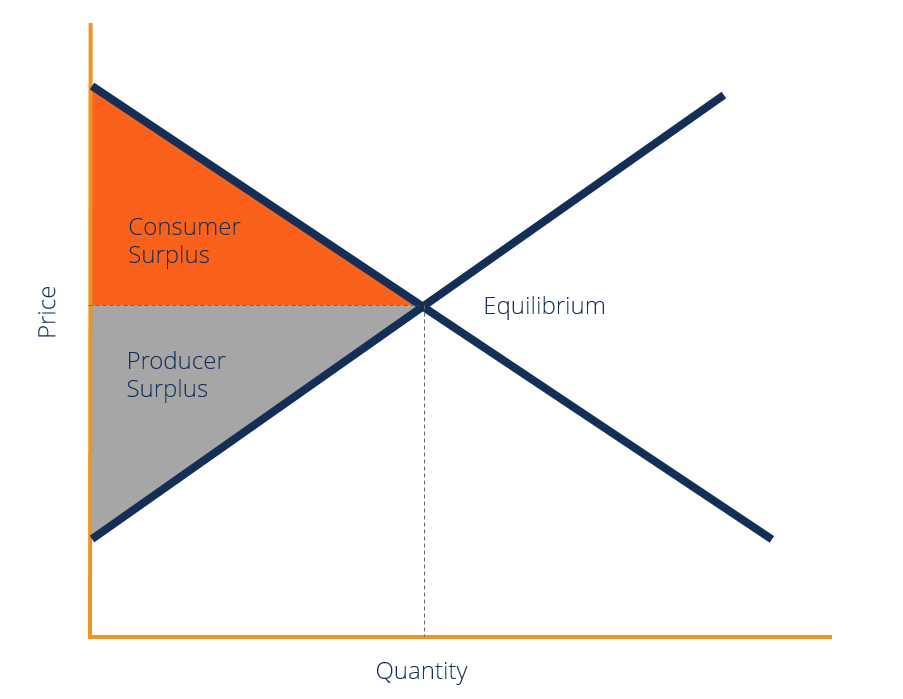
Consumer Surplus Formula Guide Examples How To Calculate Course: ap®︎ college microeconomics > unit 2. lesson 6: market equilibrium and consumer and producer surplus. market equilibrium. market equilibrium. demand curve as marginal benefit curve. consumer surplus introduction. total consumer surplus as area. producer surplus. equilibrium, allocative efficiency and total surplus. Learn about producer surplus and how it is calculated in this khan academy video. Consumer surplus is the benefit or good feeling of getting a good deal. for example, let’s say that you bought an airline ticket for a flight to disney world during school vacation week for $100. From figure 1 the following formula can be derived for consumer and producer surplus: consumer surplus = (qe x (p2 – pe)) ÷ 2. producer surplus = (qe x (pe – p1)) ÷ 2. where: qe is the equilibrium price. pe is the equilibrium price. p2 is the y intercept of the demand curve. p1 is the y intercept of the supply curve.
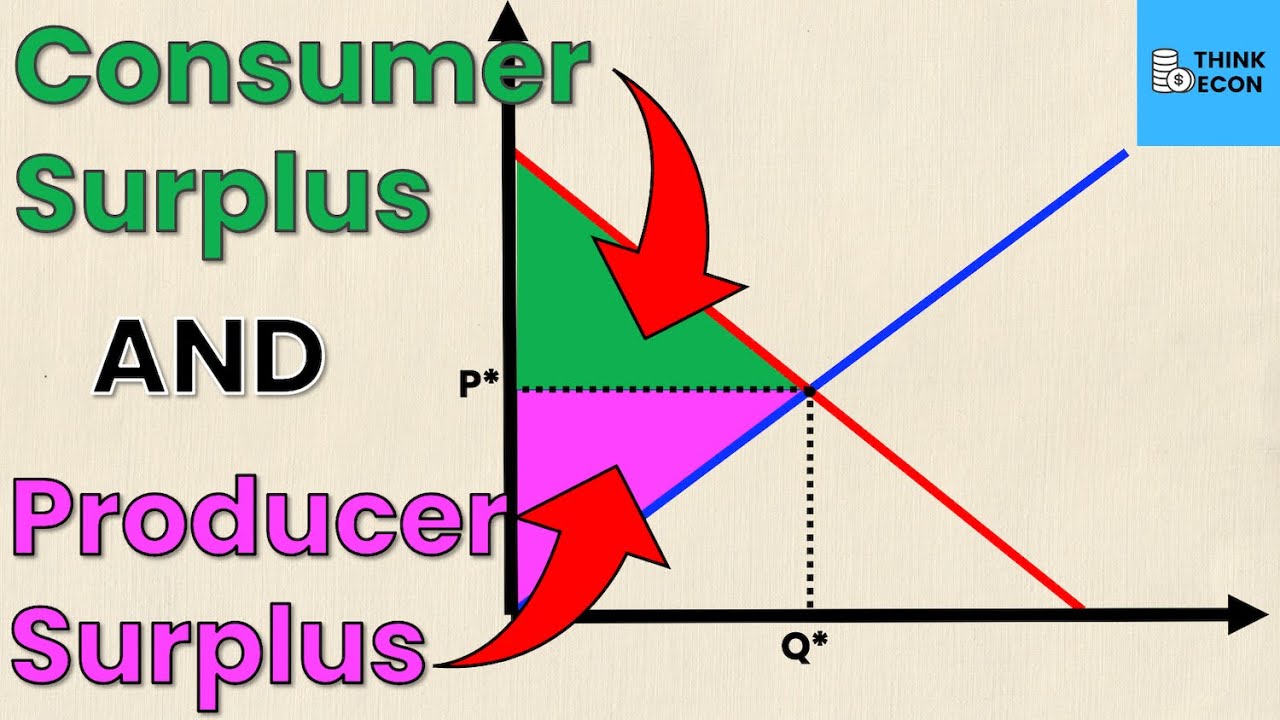
How To Calculate Producer Surplus And Consumer Surplus From Supply And Consumer surplus is the benefit or good feeling of getting a good deal. for example, let’s say that you bought an airline ticket for a flight to disney world during school vacation week for $100. From figure 1 the following formula can be derived for consumer and producer surplus: consumer surplus = (qe x (p2 – pe)) ÷ 2. producer surplus = (qe x (pe – p1)) ÷ 2. where: qe is the equilibrium price. pe is the equilibrium price. p2 is the y intercept of the demand curve. p1 is the y intercept of the supply curve. The amount that a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s actual cost is called producer surplus. in figure 1, producer surplus is the area labeled g—that is, the area between the market price and the segment of the supply curve below the equilibrium. to summarize, producers created and sold 28 tablets to consumers. The amount that a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s actual cost is called producer surplus. in figure 1, producer surplus is the area labeled g—that is, the area between the market price and the segment of the supply curve below the equilibrium. to summarize, producers created and sold 28 tablets to consumers.
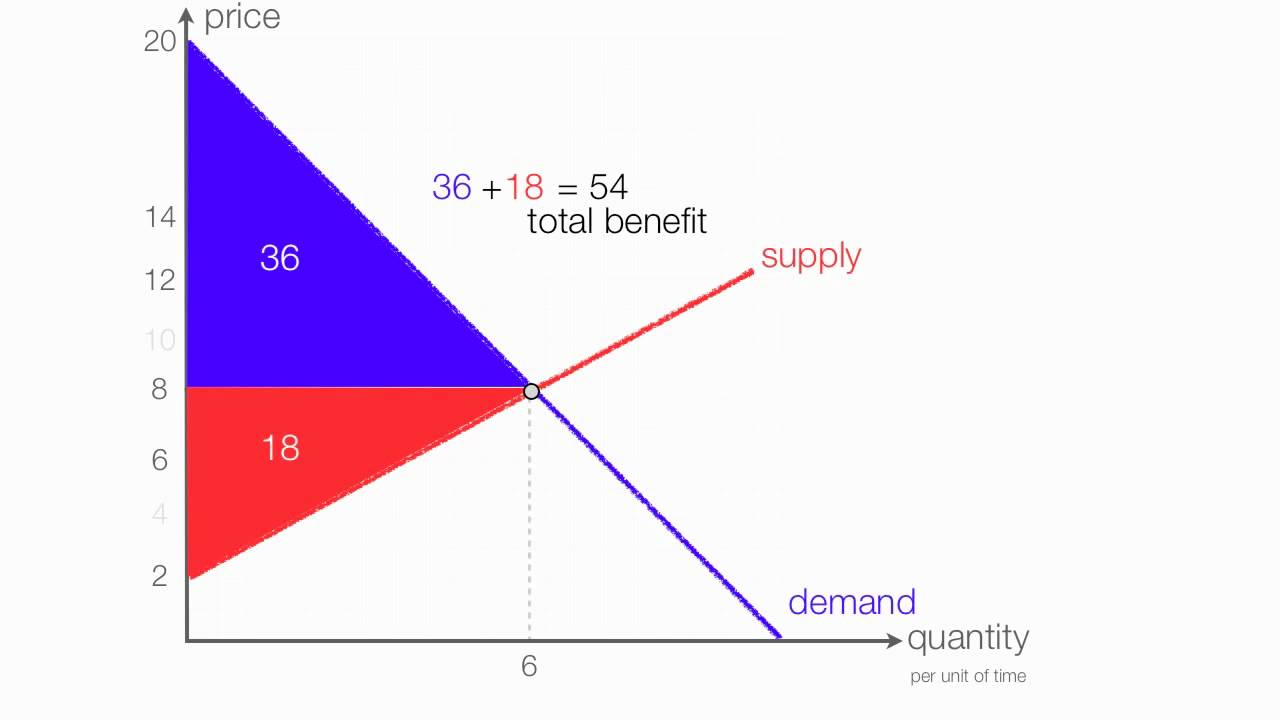
How To Calculate Consumer Surplus And Producer Surplus With A Price The amount that a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s actual cost is called producer surplus. in figure 1, producer surplus is the area labeled g—that is, the area between the market price and the segment of the supply curve below the equilibrium. to summarize, producers created and sold 28 tablets to consumers. The amount that a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s actual cost is called producer surplus. in figure 1, producer surplus is the area labeled g—that is, the area between the market price and the segment of the supply curve below the equilibrium. to summarize, producers created and sold 28 tablets to consumers.

Comments are closed.