Consumer Surplus Microeconomics

Consumer Surplus Diagram Examples How To Calculate Course: ap®︎ college microeconomics > unit 2. lesson 6: market equilibrium and consumer and producer surplus. market equilibrium. market equilibrium. demand curve as marginal benefit curve. consumer surplus introduction. total consumer surplus as area. producer surplus. equilibrium, allocative efficiency and total surplus. Consumer surplus is the benefit or good feeling of getting a good deal. for example, let’s say that you bought an airline ticket for a flight to disney world during school vacation week for $100.
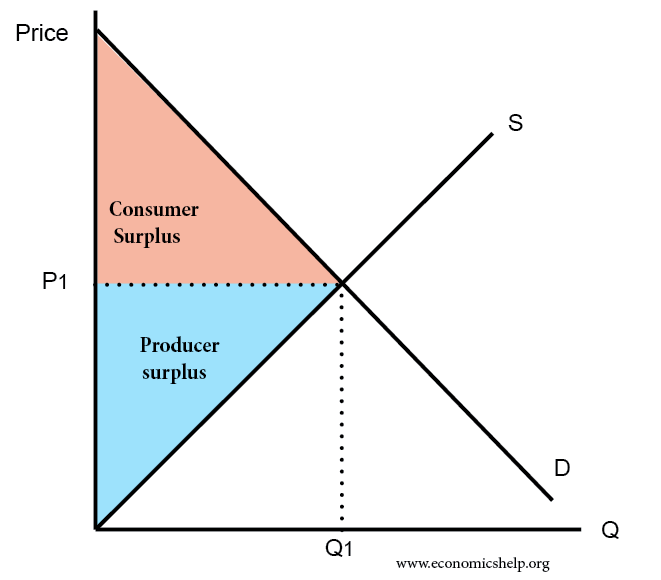
Definition Of Consumer Surplus Economics Help Consumer surplus is the difference between the price that consumers pay and the price that they are willing to pay. on a supply and demand curve, it is the area between the equilibrium price and the demand curve. for example, if you would pay 76p for a cup of tea, but can buy it for 50p – your consumer surplus is 26p. Learn how to calculate and illustrate consumer surplus, producer surplus, and social surplus using demand and supply curves. see how efficiency and allocative efficiency are related to surplus concepts. Consumer surplus always decreases when a binding price floor is instituted in a market above the equilibrium price. the total economic surplus equals the sum of the consumer and producer surpluses. price helps define consumer surplus, but overall surplus is maximized when the price is pareto optimal, or at equilibrium. Description. this lecture covers supply and demand curves, consumer surplus, and producer surplus. see handout 9 for relevant graphs for this lecture instructor: prof. jonathan gruber.

Explaining Consumer Surplus Tutor2u Economics Consumer surplus always decreases when a binding price floor is instituted in a market above the equilibrium price. the total economic surplus equals the sum of the consumer and producer surpluses. price helps define consumer surplus, but overall surplus is maximized when the price is pareto optimal, or at equilibrium. Description. this lecture covers supply and demand curves, consumer surplus, and producer surplus. see handout 9 for relevant graphs for this lecture instructor: prof. jonathan gruber. A price ceiling is imposed at $400, so firms in the market now produce only a quantity of 15,000. as a result, the new consumer surplus is t v, while the new producer surplus is x. (b) the original equilibrium is $8 at a quantity of 1,800. consumer surplus is g h j, and producer surplus is i k. Economic efficiency (article) | khan academy. microeconomics. course: microeconomics > unit 4. lesson 2: market interventions and deadweight loss. rent control and deadweight loss. minimum wage and price floors. how price controls reallocate surplus. price ceilings and price floors.

Comments are closed.