Consumer Surplus Perfect Competition

Ppt Perfect Competition And Monopoly Powerpoint Presentation Free Note the creation of a deadweight loss that was formerly part of either consumer surplus or producer surplus when the market operated at the perfect competition equilibrium. this page titled 6.7: why perfect competition is desirable is shared under a cc by nc sa 3.0 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by anonymous via source. Perfect competition consumer surplus is an economic measurement of consumer benefits resulting from market competition. a consumer surplus happens when the price that consumers pay for a.
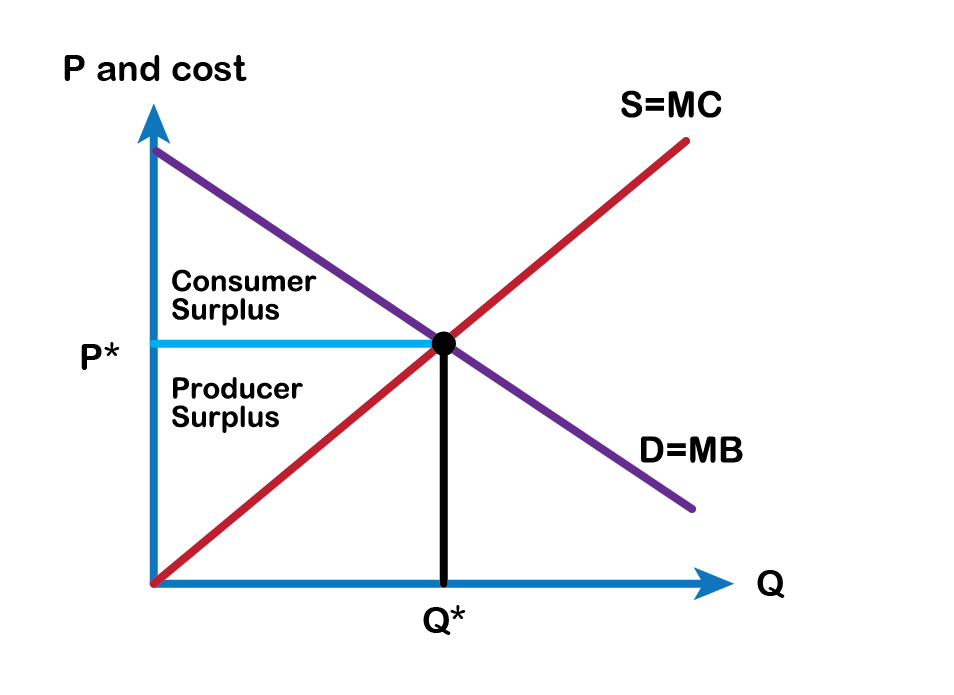
Perfect Competition Consumer Surplus Perfect competition and its significance, economic profit, output decisions, efficiency, and long run profit for firms in perfectly competitive markets. Perfect competition is an idealized market structure in which equal and identical products are sold. imperfect competition can be found in monopolies and real life examples. it involves companies. In the short run, we will assume that capital is fixed. to maximize short run profits, the firm selects a level of output where marginal revenue, mr, equals short run marginal cost. mr= p = mcs(q) “a competitive firm produces a quantity where price equals short run marginal cost, and marginal cost is rising.”. price. For a graph of the supply curve, the producer surplus corresponds to the area above the supply curve up to the horizontal line at the market price, again as shown in figure 6.11 "graph of market demand and market supply curves showing the consumer surplus and producer surplus when the market is in perfect competition equilibrium". consumer.

Ppt Ec 100 Week 10 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 2009854 In the short run, we will assume that capital is fixed. to maximize short run profits, the firm selects a level of output where marginal revenue, mr, equals short run marginal cost. mr= p = mcs(q) “a competitive firm produces a quantity where price equals short run marginal cost, and marginal cost is rising.”. price. For a graph of the supply curve, the producer surplus corresponds to the area above the supply curve up to the horizontal line at the market price, again as shown in figure 6.11 "graph of market demand and market supply curves showing the consumer surplus and producer surplus when the market is in perfect competition equilibrium". consumer. Consumer surplus, understood as the sum of all individual consumer surpluses, corresponds to area a a’ a’’ b b’ c. when we repeat this process with a far greater number of buyers, we get a nice, straight demand curve. now, let’s say the price for a given good is set at p 0. in that case, consumer surplus is area cs. A price ceiling is imposed at $400, so firms in the market now produce only a quantity of 15,000. as a result, the new consumer surplus is t v, while the new producer surplus is x. (b) the original equilibrium is $8 at a quantity of 1,800. consumer surplus is g h j, and producer surplus is i k.
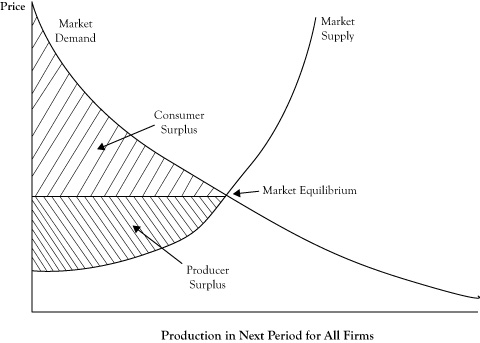
Market Equilibrium And The Perfect Competition Model Consumer surplus, understood as the sum of all individual consumer surpluses, corresponds to area a a’ a’’ b b’ c. when we repeat this process with a far greater number of buyers, we get a nice, straight demand curve. now, let’s say the price for a given good is set at p 0. in that case, consumer surplus is area cs. A price ceiling is imposed at $400, so firms in the market now produce only a quantity of 15,000. as a result, the new consumer surplus is t v, while the new producer surplus is x. (b) the original equilibrium is $8 at a quantity of 1,800. consumer surplus is g h j, and producer surplus is i k.
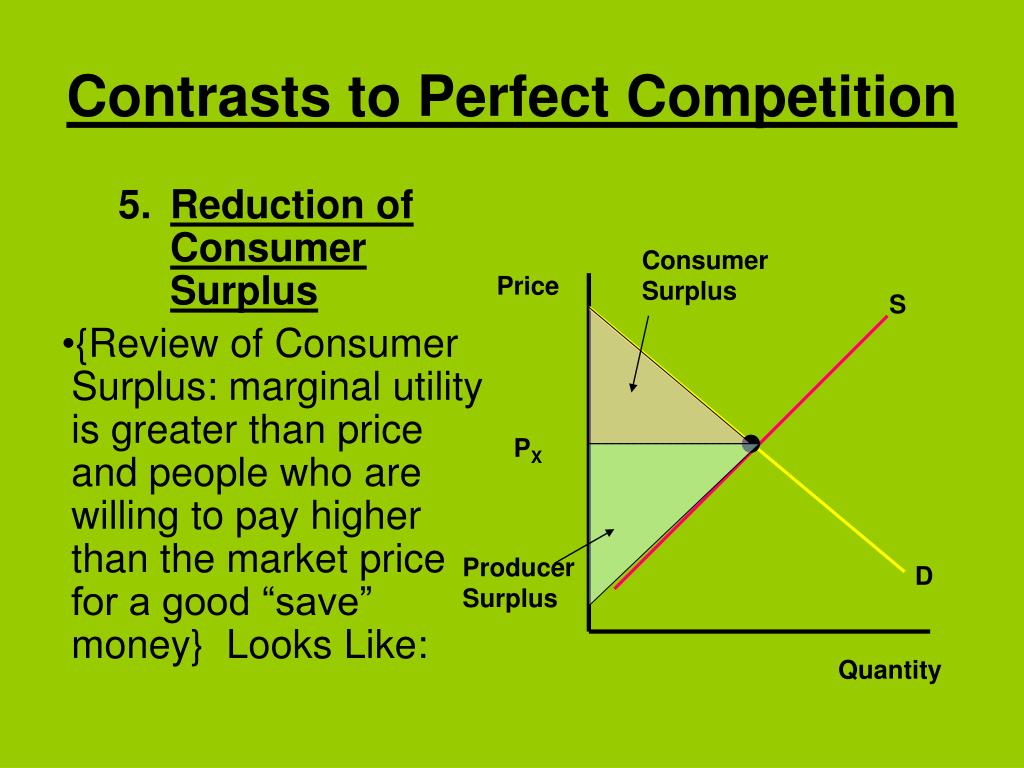
Ppt Ap Microeconomics Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5767208

Comments are closed.