Consumer Surplus With Price Ceiling
Solved Pri Use The Graph To Answer The Following Questions Calculate Learn how consumer surplus is the difference between the maximum price a consumer is willing to pay and the actual price they do pay. see how price changes affect consumer surplus and the demand curve. Learn how price ceilings can reduce consumer surplus and create deadweight loss in a market. see how the demand and supply diagrams illustrate the efficiency and redistribution effects of price ceilings.

Solved Use The Graph Below To Answer The Following Chegg Learn how a price ceiling reduces consumer surplus and creates deadweight loss in a market. see examples, graphs, and calculations of consumer surplus and price ceiling. Consumer surplus is t u, and producer surplus is v w x. a price ceiling is imposed at $400, so firms in the market now produce only a quantity of 15,000. as a result, the new consumer surplus is t v, while the new producer surplus is x. (b) the original equilibrium is $8 at a quantity of 1,800. This video shows (using equations and graphs) how to find consumer surplus, producer surplus, and deadweight loss from a price ceiling. two extensions are gi. Learn what a price ceiling is, how it affects consumers and producers, and how to graph it. a price ceiling is a limit on the price of a good or service set by the government to protect consumers, but it can also create deadweight loss and quantity shortage.

Solved What Is The Effect Of A Price Ceiling Set Above Chegg This video shows (using equations and graphs) how to find consumer surplus, producer surplus, and deadweight loss from a price ceiling. two extensions are gi. Learn what a price ceiling is, how it affects consumers and producers, and how to graph it. a price ceiling is a limit on the price of a good or service set by the government to protect consumers, but it can also create deadweight loss and quantity shortage. A price ceiling is a type of price control that's usually government mandated and sets the maximum amount a seller can charge for a good or service. price ceilings are typically imposed on. Learn how price floors and ceilings affect the market equilibrium, consumer surplus, producer surplus, and social surplus. see examples of price floors and ceilings in the real world and how they create deadweight loss and redistribute surplus.
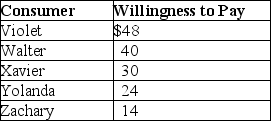
Economic Efficiency Government Price Setting And Taxes Flashcards Quiz A price ceiling is a type of price control that's usually government mandated and sets the maximum amount a seller can charge for a good or service. price ceilings are typically imposed on. Learn how price floors and ceilings affect the market equilibrium, consumer surplus, producer surplus, and social surplus. see examples of price floors and ceilings in the real world and how they create deadweight loss and redistribute surplus.

Producer Surplus Price Floor At Robert Henley Blog

Comments are closed.