Cooling Curve Phase Diagram

Digging Into Phase Diagrams Cooling Curves Physical Chemistry A cooling curve for a sample that begins at the temperature and composition given by point a is shown in figure 8.10.1b 8.10. 1 b. figure 8.10.1 8.10. 1: (a) cooling of a two component system from liquid to solid. (b) cooresponding cooling curve for this process. as the sample cools from point a, the temperature will decrease at a rate. By removing the time axis from the curves and replacing it with composition, the cooling curves indicate the temperatures of the solidus and liquidus for a given composition. this allows the solidus and liquidus to be plotted to produce the phase diagram: this page titled 12.5: interpretation of cooling curves is shared under a cc by nc sa.

Heating And Cooling Curves Overview Examples Expii Interpretation of cooling curves. the melting temperature of any pure material (a one component system) at constant pressure is a single unique temperature. the liquid and solid phases exist together in equilibrium only at this temperature. when cooled, the temperature of the molten material will steadily decrease until the melting point is. Using the phase diagram. suppose you have a mixture of 67% lead and 33% tin. that's the mixture from the first cooling curve plotted above. suppose it is at a temperature of 300°c. that corresponds to a set of conditions in the area of the phase diagram labeled as molten tin and lead. now consider what happens if you cool that mixture. Heating and cooling curves are graphs. they plot a substance's temperature (y axis) against heat (x axis). for heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat energy. for cooling curves, we start with the gas phase and remove heat energy. cooling and heating curves have five segments. The phase diagram. constructing the phase diagram. you start from data obtained from the cooling curves. you draw a graph of the temperature at which freezing first starts against the proportion of tin and lead in the mixture. the only unusual thing is that you draw the temperature scale at each end of the diagram instead of only at the left.
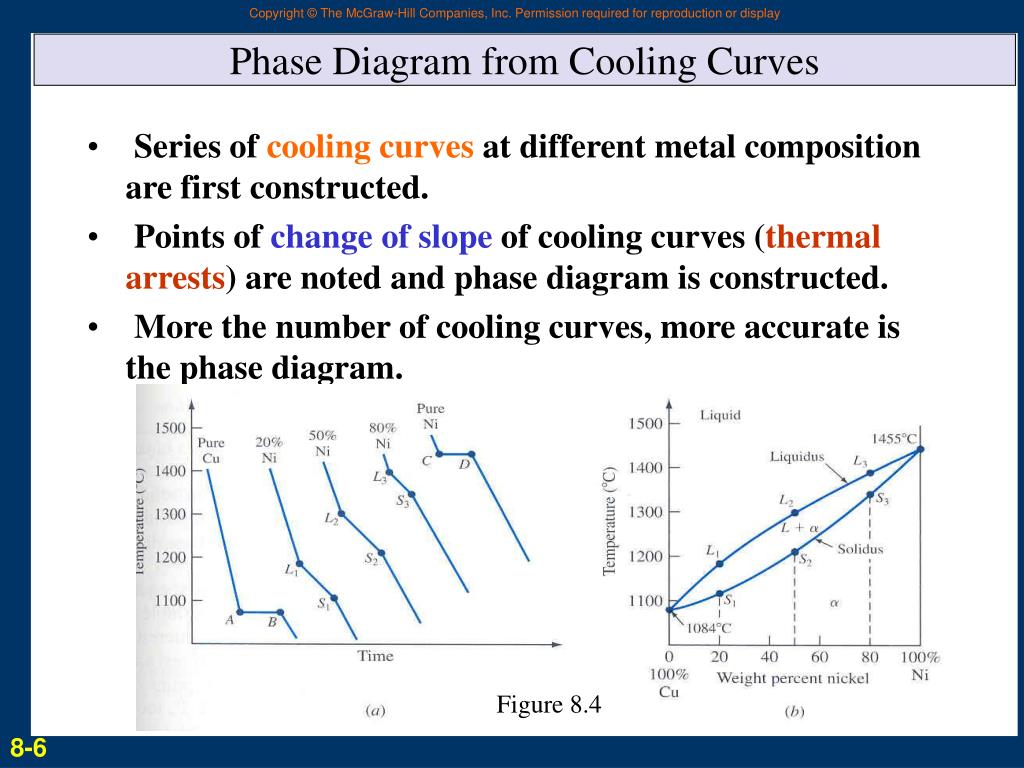
Cooling Curve Phase Diagram Heating and cooling curves are graphs. they plot a substance's temperature (y axis) against heat (x axis). for heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat energy. for cooling curves, we start with the gas phase and remove heat energy. cooling and heating curves have five segments. The phase diagram. constructing the phase diagram. you start from data obtained from the cooling curves. you draw a graph of the temperature at which freezing first starts against the proportion of tin and lead in the mixture. the only unusual thing is that you draw the temperature scale at each end of the diagram instead of only at the left. Phase diagram and “degrees of freedom”. phase diagrams is a type of graph used to show the equilibrium conditions between the thermodynamically distinct phases; or to show what phases are present in the material system at various t, p, and compositions. “equilibrium” is important: phase diagrams are determined by using slow cooling. A cooling curve is a line graph that represents the change of phase of matter, typically from a gas to a solid or a liquid to a solid. the independent variable (x axis) is time and the dependent variable (y axis) is temperature. [1] below is an example of a cooling curve used in castings. the initial point of the graph is the starting.

Heating And Cooling Curves Phase diagram and “degrees of freedom”. phase diagrams is a type of graph used to show the equilibrium conditions between the thermodynamically distinct phases; or to show what phases are present in the material system at various t, p, and compositions. “equilibrium” is important: phase diagrams are determined by using slow cooling. A cooling curve is a line graph that represents the change of phase of matter, typically from a gas to a solid or a liquid to a solid. the independent variable (x axis) is time and the dependent variable (y axis) is temperature. [1] below is an example of a cooling curve used in castings. the initial point of the graph is the starting.

Comments are closed.