Covalent Bonding H2o
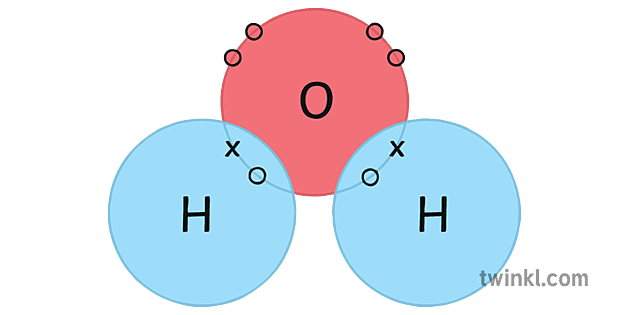
H2o Water Covalent Bonding Point Cross Diagram Science Ks4 Ammonia (mp –78, bp –33°c) is hydrogen bonded in the liquid and solid states. hydrogen bonding is responsible for ammonia 's remarkably high solubility in water. many organic (carboxylic) acids form hydrogen bonded dimers in the solid state. here the hydrogen bond acceptor is the π electron cloud of a benzene ring. Water is a simple molecule consisting of one oxygen atom bonded to two different hydrogen atoms. because of the higher electronegativity of the oxygen atom, the bonds are polar covalent (polar bonds). the oxygen atom attracts the shared electrons of the covalent bonds to a significantly greater extent than the hydrogen atoms.

Is H2o Ionic Or Covalent Techiescientist Covalent bond, in chemistry, the interatomic linkage that results from the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms. the binding arises from the electrostatic attraction of their nuclei for the same electrons. a bond forms when the bonded atoms have a lower total energy than that of widely separated atoms. Key takeaways. a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. the number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number of electrons it needs to reach octet. hydrogen is an exception to the octet rule. h forms only one bond because it needs only two electrons. Learn the basics about the covalent bonding of water, when learning about covalent bonding within properties of matter.water is made from one oxygen atom and. Chemical bonding of water. lewis structure of h 2 o indicating bond angle and bond length. water (h. 2o) is a simple triatomic bent molecule with c 2v molecular symmetry and bond angle of 104.5° between the central oxygen atom and the hydrogen atoms. despite being one of the simplest triatomic molecules, its chemical bonding scheme is.
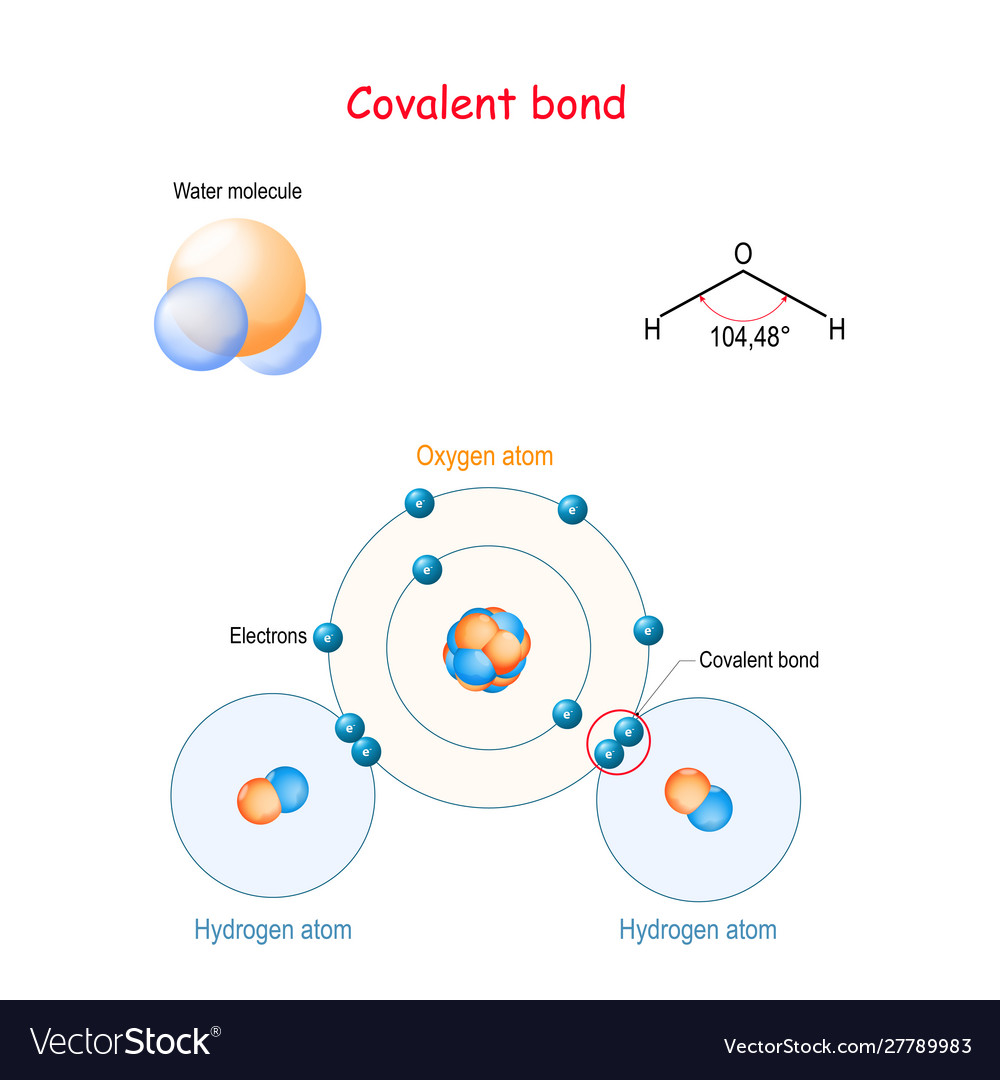
Covalent Bond For Example Water Molecule H2o Vector Image Learn the basics about the covalent bonding of water, when learning about covalent bonding within properties of matter.water is made from one oxygen atom and. Chemical bonding of water. lewis structure of h 2 o indicating bond angle and bond length. water (h. 2o) is a simple triatomic bent molecule with c 2v molecular symmetry and bond angle of 104.5° between the central oxygen atom and the hydrogen atoms. despite being one of the simplest triatomic molecules, its chemical bonding scheme is. Covalent bonds usually form between nonmetals. examples of covalent compounds include hydrogen (h 2), oxygen (o 2), carbon monoxide (co), ammonia (nh 3), water (h 2 o), and all organic compounds. there are compounds that contain both covalent and ionic bonds, such as potassium cyanide (kcn) and ammonium chloride (nh 4 cl). Each diagram shows the unsymmetrical shape of the water molecule. in (a) & (b), the polar covalent bonds are shown as lines. in part (c), the polar covalent bonds are shown as electron dots shared by the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. in part (d), the diagram shows the relative size of the atoms, and the bonds are represented by the touching of the.
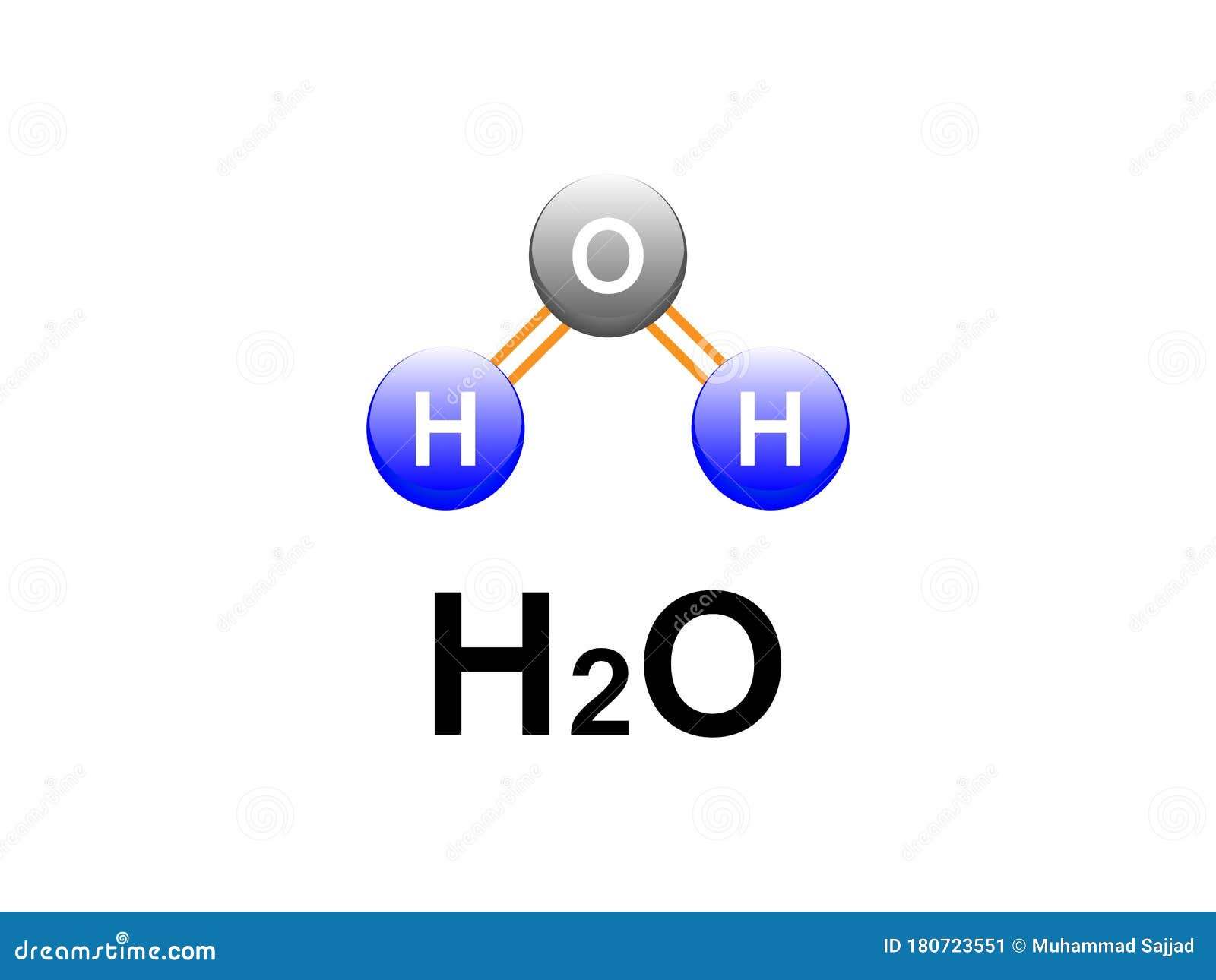
H2o Covalent Bonding Water Formula Diagram Design For Chemistry Labs Covalent bonds usually form between nonmetals. examples of covalent compounds include hydrogen (h 2), oxygen (o 2), carbon monoxide (co), ammonia (nh 3), water (h 2 o), and all organic compounds. there are compounds that contain both covalent and ionic bonds, such as potassium cyanide (kcn) and ammonium chloride (nh 4 cl). Each diagram shows the unsymmetrical shape of the water molecule. in (a) & (b), the polar covalent bonds are shown as lines. in part (c), the polar covalent bonds are shown as electron dots shared by the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. in part (d), the diagram shows the relative size of the atoms, and the bonds are represented by the touching of the.

Comments are closed.