Definition And Classification Of Lipids

1 Lipids Definition Classification Functions Lipid Chemistry 1 Lipids are oily or greasy nonpolar molecules, stored in the adipose tissue of the body. lipids are a heterogeneous group of compounds, mainly composed of hydrocarbon chains. lipids are energy rich organic molecules, which provide energy for different life processes. lipids are a class of compounds characterised by their solubility in nonpolar. Classification of lipids. lipids can be classified according to their hydrolysis products and according to similarities in their molecular structures. three major subclasses are recognized: 1. simple lipids (a) fats and oils which yield fatty acids and glycerol upon hydrolysis. (b) waxes, which yield fatty acids and long chain alcohols upon.
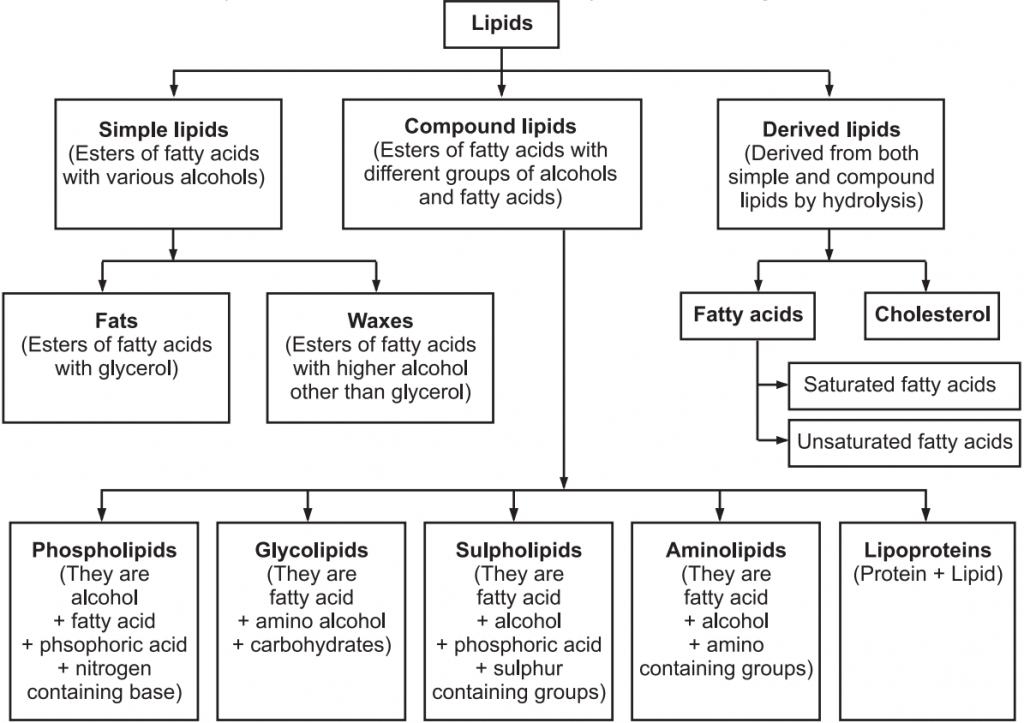
Functions Of Lipids Definition Classification Examples A lipid is any of various organic compounds that are insoluble in water. they include fats, waxes, oils, hormones, and certain components of and function as energy storage molecules and chemical messengers. together with proteins carbohydrates, lipids are one of the principal structural components of living . Lipids formed from fatty acids. fatty acids are carboxylic acids with 12 22 carbon atoms connected in a long, unbranched chain. as shown in the diagram above, most lipids are classified as esters or amides of fatty acids. waxes are esters formed from long chain fatty acids and long chain alcohols. most natural waxes are mixtures of such esters. Although the term "lipid" is sometimes used as a synonym for fats, fats are a subgroup of lipids called triglycerides. lipids also encompass molecules such as fatty acids and their derivatives (including tri , di , monoglycerides, and phospholipids), as well as other sterol containing metabolites such as cholesterol. [6]. This classification system has been the foundation for the lipid maps structure database (lmsd) [], which is discussed in more detail below.the most convenient way of viewing the classification hierarchy is through the lipid maps nature lipidomic gateway [] where one may conveniently browse examples of categories, classes and subclasses stored in the lmsd.
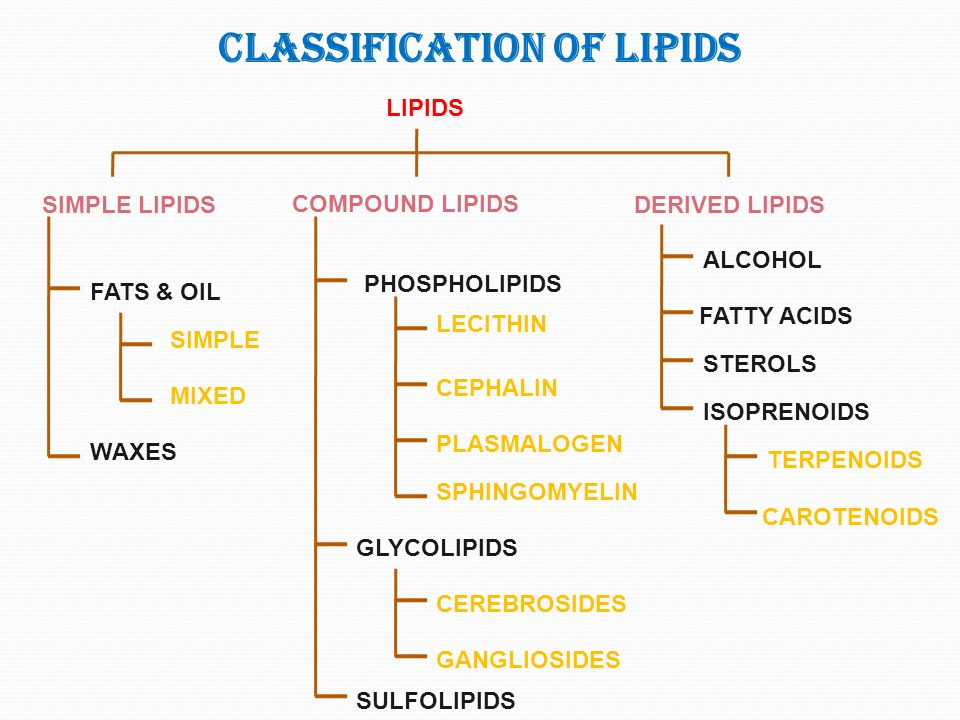
Functions Of Lipids Definition Classification Examples Although the term "lipid" is sometimes used as a synonym for fats, fats are a subgroup of lipids called triglycerides. lipids also encompass molecules such as fatty acids and their derivatives (including tri , di , monoglycerides, and phospholipids), as well as other sterol containing metabolites such as cholesterol. [6]. This classification system has been the foundation for the lipid maps structure database (lmsd) [], which is discussed in more detail below.the most convenient way of viewing the classification hierarchy is through the lipid maps nature lipidomic gateway [] where one may conveniently browse examples of categories, classes and subclasses stored in the lmsd. Classification of lipids. lipids, given their diverse nature and crucial role in various biological processes, have been extensively studied and classified. their classification primarily arises from their structural and functional characteristics. herein is a detailed breakdown of the lipid classification:. These lipids have enormous structural variability given the large number of different fatty acids (both saturated and unsaturated) and head groups that can be attached to a phosphate attached to the carbon 3 of glycerol. the structures of the most common glycerophospholipids are shown in figure 10.1.16 10.1. 16.

What Are Lipids Function Structure Definition Of Lipids Classification of lipids. lipids, given their diverse nature and crucial role in various biological processes, have been extensively studied and classified. their classification primarily arises from their structural and functional characteristics. herein is a detailed breakdown of the lipid classification:. These lipids have enormous structural variability given the large number of different fatty acids (both saturated and unsaturated) and head groups that can be attached to a phosphate attached to the carbon 3 of glycerol. the structures of the most common glycerophospholipids are shown in figure 10.1.16 10.1. 16.
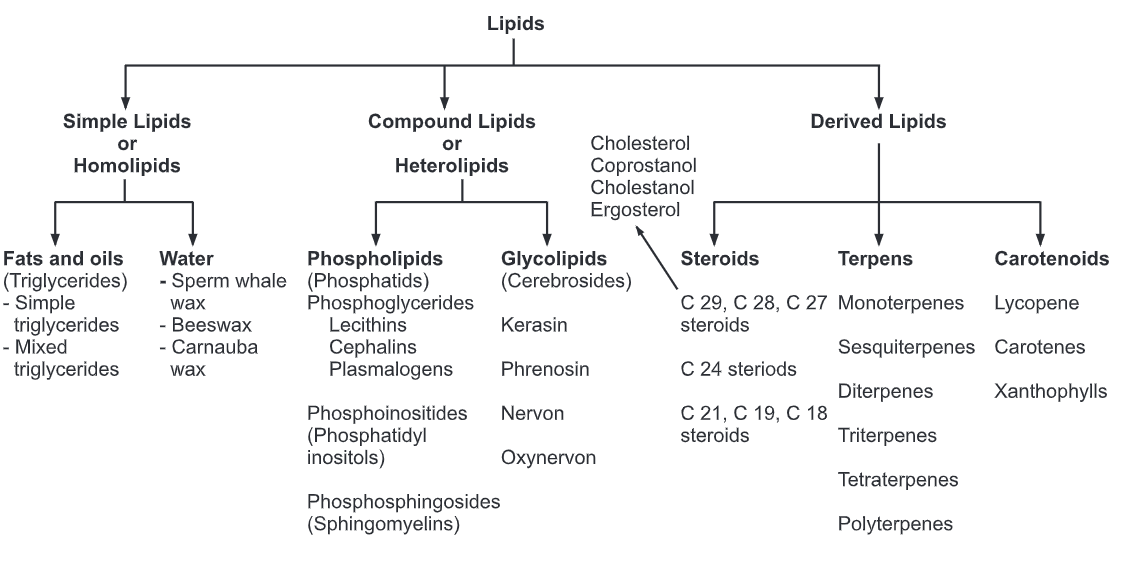
Classification Of Lipids Biology Ease

Lipids Introduction And Classification A Level Biology Revision Notes

Comments are closed.