Distributive Property Distributive Law
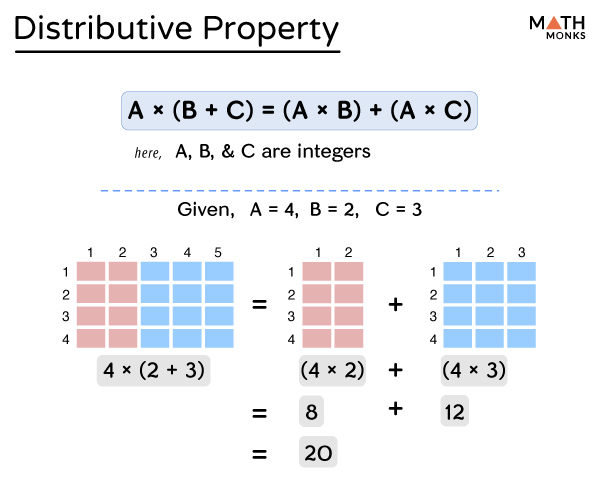
Distributive Property Law Definition Solved Examples Diagrams Distributive property of division. even though division is the inverse of multiplication, the distributive law holds true in the case of division but in a different way. we can show the division of larger numbers using the distributive property by breaking the dividend into two or more smaller factors to make the division problems easier to solve. The distributive property is a fundamental property that defines how multiplication operation is distributed over addition and subtraction. the distributive property is also called the distributive law of multiplication over addition and subtraction.
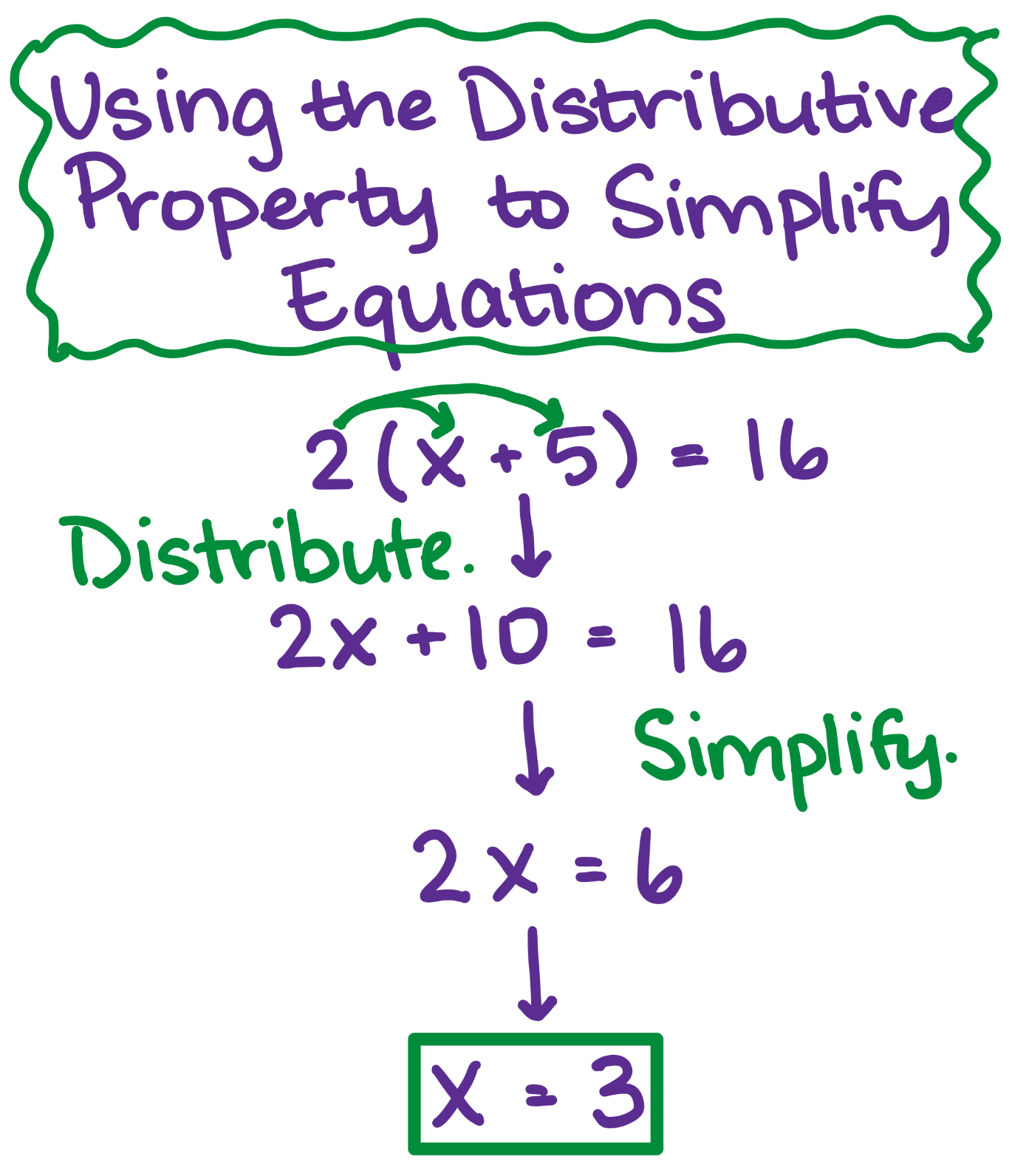
Simplify With Distributive Property Examples Practice Expii Distributive property. in mathematics, the distributive property of binary operations is a generalization of the distributive law, which asserts that the equality is always true in elementary algebra. for example, in elementary arithmetic, one has therefore, one would say that multiplication distributes over addition. The distributive law says that multiplying a number by a group of numbers added together is the same as doing each multiplication separately. example: 3 × (2 4) = 3×2 3×4. so the "3" can be "distributed" across the "2 4" into 3 times 2 and 3 times 4. commutative associative and distributive laws. The distributive property is also known as the distributive law of multiplication. this distributive property of multiplication is applicable over addition and subtraction. the formula for the distributive property is expressed as, a × (b c) = (a × b) (a × c). The distributive property, also referred to as the distributive law, is a property of real numbers that states that multiplication distributes over addition. this means that multiplying by a group of numbers being added together is the same as multiplying each of the numbers in the group separately, then adding the products together.
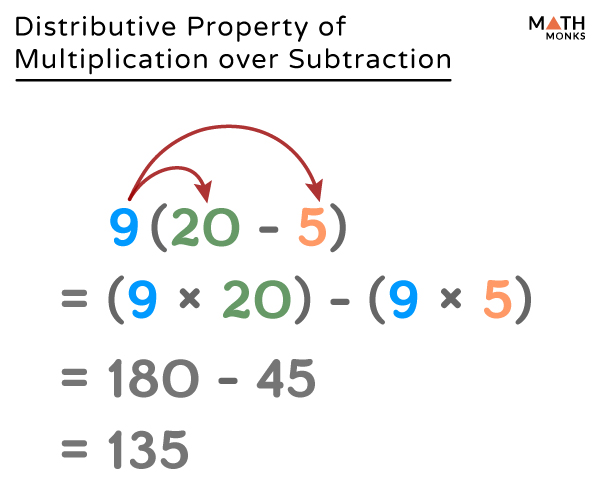
Distributive Property Law Definition Solved Examples Diagrams The distributive property is also known as the distributive law of multiplication. this distributive property of multiplication is applicable over addition and subtraction. the formula for the distributive property is expressed as, a × (b c) = (a × b) (a × c). The distributive property, also referred to as the distributive law, is a property of real numbers that states that multiplication distributes over addition. this means that multiplying by a group of numbers being added together is the same as multiplying each of the numbers in the group separately, then adding the products together. Distributive law. the "distributive law" is the best one of all, but needs careful attention. this is what it lets us do: 3 lots of (2 4) is the same as 3 lots of 2 plus 3 lots of 4. so, the 3× can be "distributed" across the 2 4, into 3×2 and 3×4. and we write it like this:. The distributive property is the rule that relates addition and multiplication.specifically, it states that \( a(b c) = ab ac \) \( (a b)c = ac bc .\) it is a useful tool for expanding expressions, evaluating expressions, and simplifying expressions.

Comments are closed.