Download Accounting Basics Double Entry Accounting Debits And
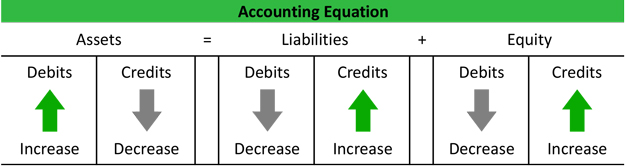
What Is Double Entry Accounting Bookkeeping Example Explanation Double entry system of accounting: definition. every business transaction has two effects or "changes" on an account. the system of bookkeeping under which both changes in a transaction are recorded together at an equal amount (one known as "credit" and the other as "debit") is known as the double entry system. concept of the double entry system. Debits and credits accounting formula. you can use debits and credits to figure out the net worth of your business. accounting applies the concepts of debits and credits to your assets, equity, and liabilities. a combination of these 3 items makes up the common sense formula for basic accounting: liabilities are what your business owes.
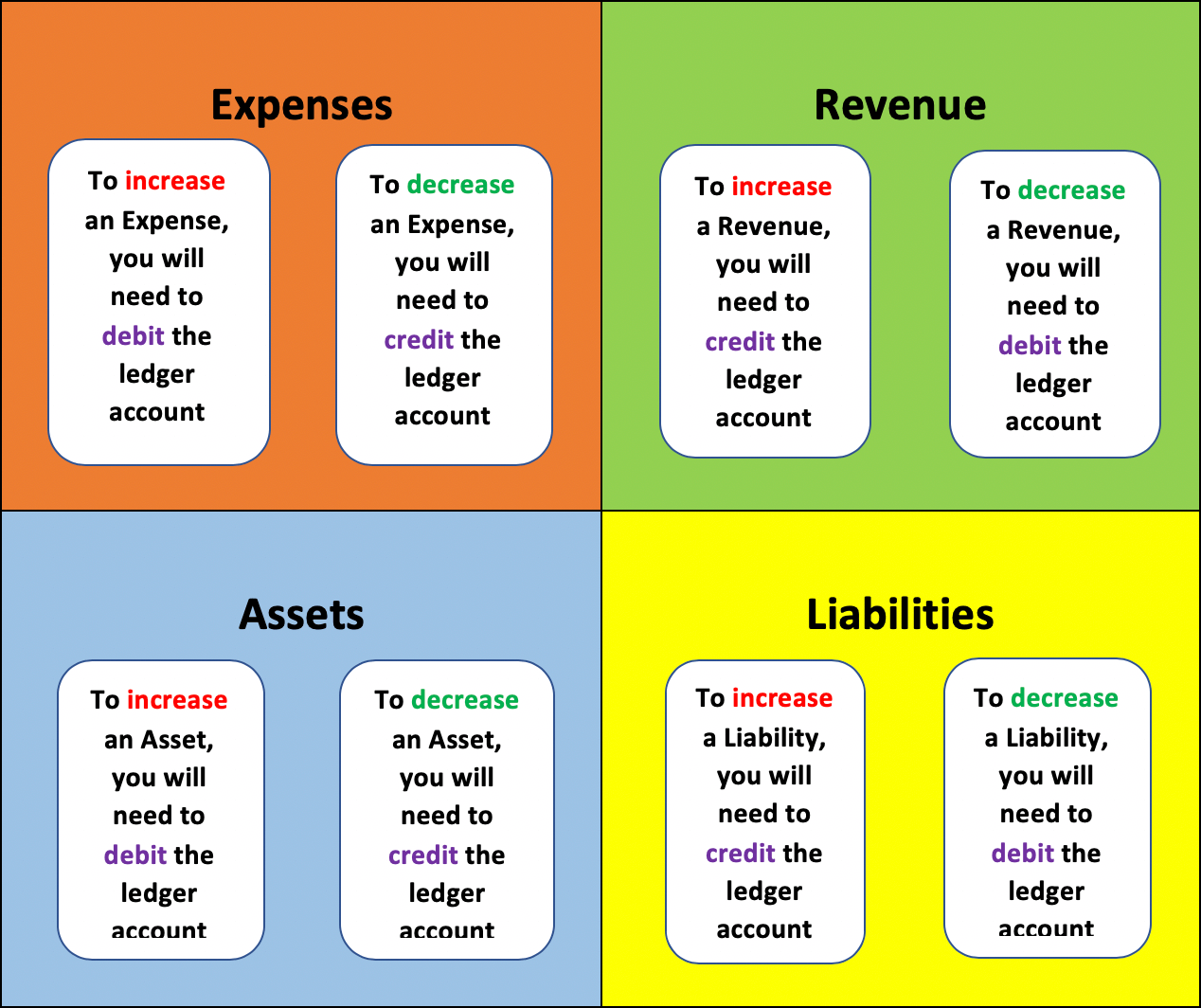
Double Entry Bookkeeping Explained Here are the meanings of those words: debit: an entry on the left side of an account. credit: an entry on the right side of an account. the debit and credit rule in double entry bookkeeping can be stated several ways: for each and every transaction, the total amount entered on the left side of an account (or accounts) must be equal to the total. Balance sheet – liabilities and stockholders' equity. part 5. statement of cash flows, double entry system, sample transaction #1. part 6. sample transactions #2 #3. part 7. sample transactions #4 #6. statement of cash flows. the third financial statement that joe needs to understand is the statement of cash flows. Accounting basics, part 1. what’s here in part 2 of this series, we pick up where this one ends. it illustrates and discusses the accounting cycle, adjusting entries, closing entries, trial balance and closing balance. in part 3, we illustrate and discuss the balance sheet, income statement and analyzing these financial reports. This method of recording is called double entry bookkeeping and provides a self balancing mechanism. therefore when recording a transaction it must be decided which accounts are debits and which are credits. this principle can be represented by the accounting equation as: a e = l oe r (debits) = (credits) where.
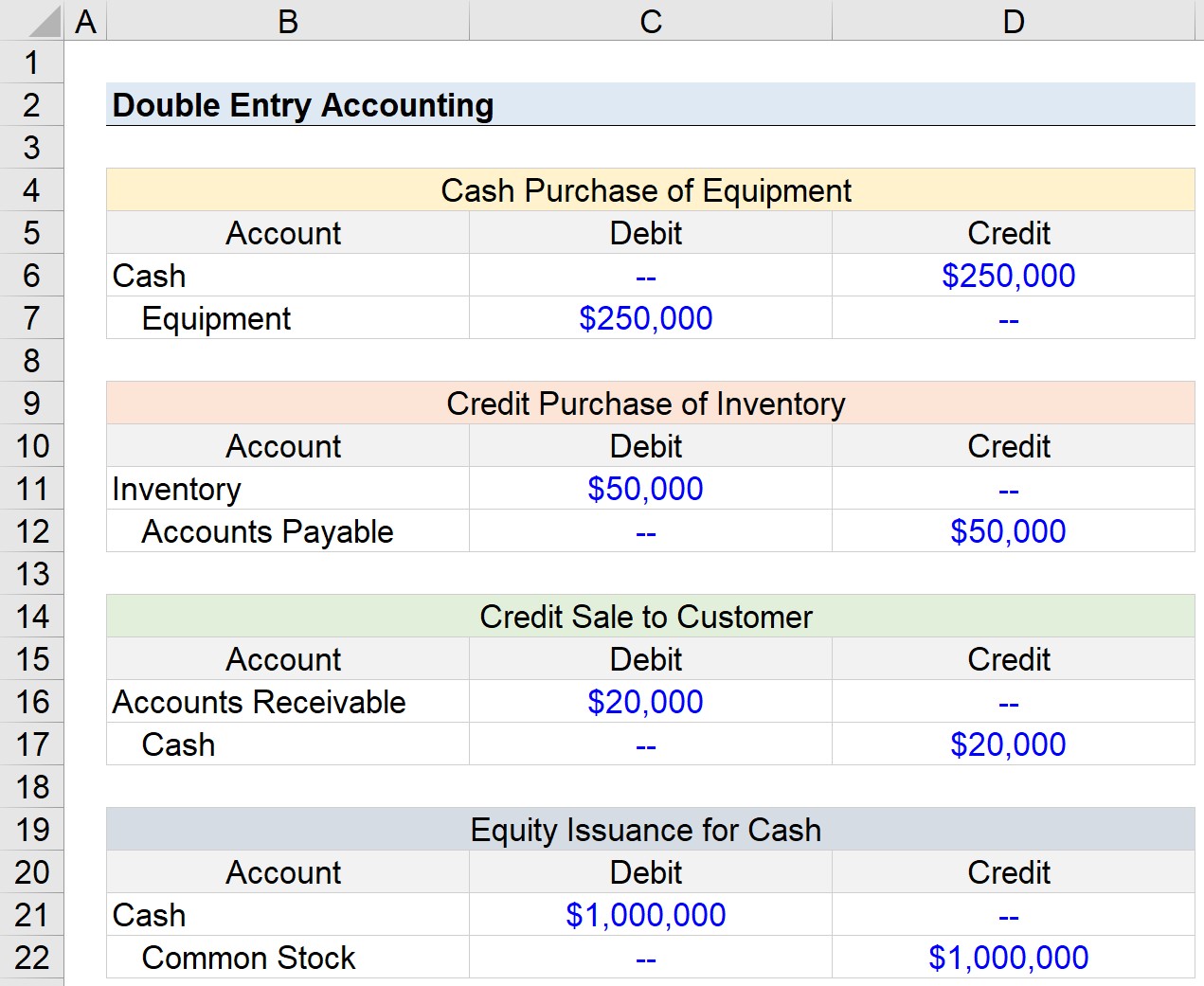
Double Entry Accounting 2022 Accounting basics, part 1. what’s here in part 2 of this series, we pick up where this one ends. it illustrates and discusses the accounting cycle, adjusting entries, closing entries, trial balance and closing balance. in part 3, we illustrate and discuss the balance sheet, income statement and analyzing these financial reports. This method of recording is called double entry bookkeeping and provides a self balancing mechanism. therefore when recording a transaction it must be decided which accounts are debits and which are credits. this principle can be represented by the accounting equation as: a e = l oe r (debits) = (credits) where. Double entry bookkeeping uses the terms debit and credit. they refer to entries made in accounts to reflect the transactions of a business. the terms are often abbreviated to dr which originates from the latin ‘debere’ meaning to owe and cr from the latin ‘credere’ meaning to believe. do not try to read anything more into the terms. Double entry accounting is a method of bookkeeping that tracks where your money comes from and where it’s going. every financial transaction gets two entries, a “debit” and a “credit” to describe whether money is being transferred to or from an account, respectively. each accounting entry affects two different accounts: for example.

Download Accounting Basics Double Entry Accounting Debits And Double entry bookkeeping uses the terms debit and credit. they refer to entries made in accounts to reflect the transactions of a business. the terms are often abbreviated to dr which originates from the latin ‘debere’ meaning to owe and cr from the latin ‘credere’ meaning to believe. do not try to read anything more into the terms. Double entry accounting is a method of bookkeeping that tracks where your money comes from and where it’s going. every financial transaction gets two entries, a “debit” and a “credit” to describe whether money is being transferred to or from an account, respectively. each accounting entry affects two different accounts: for example.

Comments are closed.