Easiest Way To Draw Vulva Female Reproductive Organs External

How To Draw Female Reproductive System Easily Step By Step Youtube The external female genitalia are a part of the female reproductive system, and include the: mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibule, hymen, vestibular bulb and vestibular glands. the components of the external female genitalia occupy a large part of the female perineum and collectively form what's known as the vulva. The vulva and its structures form the external genitalia. the internal genitalia include a three part system of ducts: the uterine tubes, the uterus, and the vagina. this system of ducts connects to the ovaries, the primary reproductive organs. the ovaries produce egg cells and release them for fertilization. fertilized eggs develop inside the.
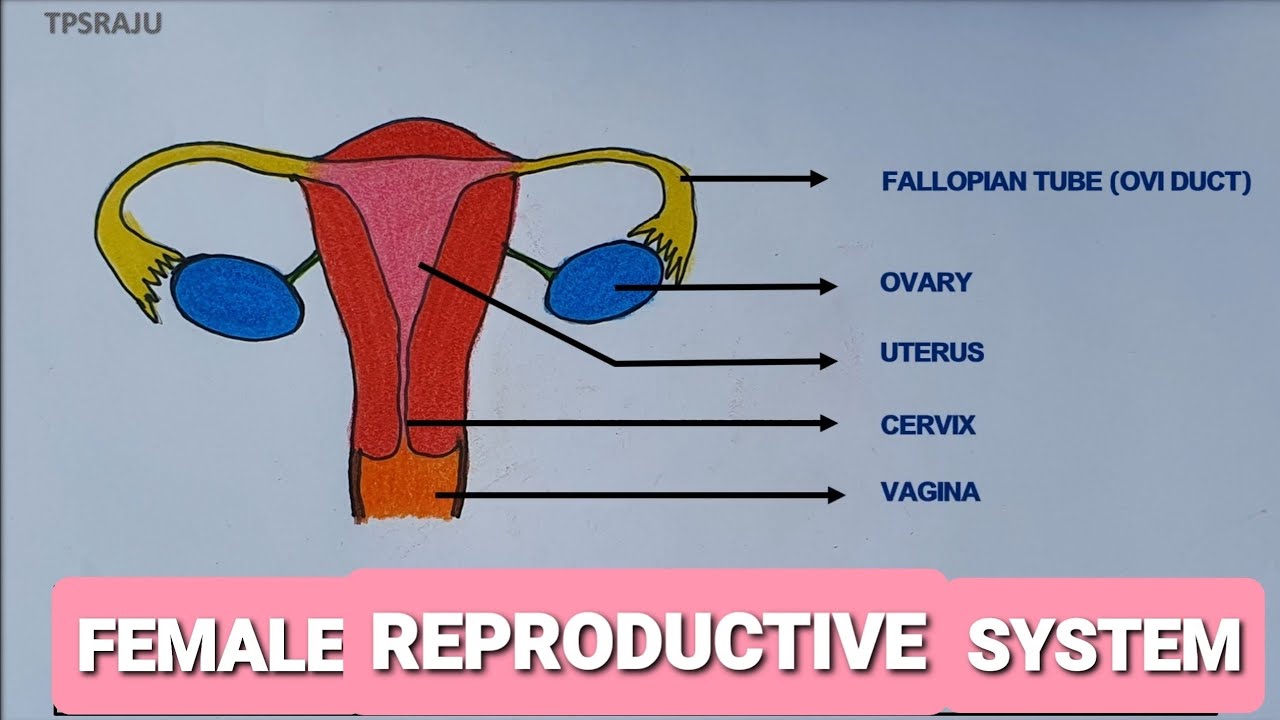
How To Draw Female Reproductive System Easily The Structure Of Female Female anatomy includes the internal and external structures, including those responsible for hormones, reproduction, and sexual activity. the female reproductive system is essential for hormone regulation, sexual pleasure, pregnancy, breastfeeding, and more. the main parts of the female anatomy can be broken up into external and internal parts. The external female reproductive structures are referred to collectively as the vulva (figure 2 and 3). the mons pubis is a pad of fat that is located at the anterior, over the pubic bone. after puberty, it becomes covered in pubic hair. the labia majora (labia = “lips”; majora = “larger”) are folds of hair covered skin that begin just. The external female reproductive structures are referred to collectively as the vulva (figure 23.1.2 23.1. 2). the mons pubis is a pad of fat that is located at the anterior, over the pubic bone. after puberty, it becomes covered in pubic hair. the labia majora (labia = “lips”; majora = “larger”) are folds of hair covered skin that. Figure 23.3.6 23.3. 6: ovaries, uterine tubes, and uterus. this anterior view shows the relationship of the ovaries, uterine tubes (oviducts), and uterus. sperm enter through the vagina, and fertilization of an ovulated oocyte usually occurs in the distal uterine tube. from left to right, lm × 400, lm × 20.

How To Draw Female Reproductive System Diagram Functions Anatomy The external female reproductive structures are referred to collectively as the vulva (figure 23.1.2 23.1. 2). the mons pubis is a pad of fat that is located at the anterior, over the pubic bone. after puberty, it becomes covered in pubic hair. the labia majora (labia = “lips”; majora = “larger”) are folds of hair covered skin that. Figure 23.3.6 23.3. 6: ovaries, uterine tubes, and uterus. this anterior view shows the relationship of the ovaries, uterine tubes (oviducts), and uterus. sperm enter through the vagina, and fertilization of an ovulated oocyte usually occurs in the distal uterine tube. from left to right, lm × 400, lm × 20. The components of the vulva are the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibule, hymen, bulb of vestibule and vestibular glands. the vulva is important in many aspects like reproduction and sexual pleasure, parturition and the protection of the internal genital organs. terminology. english: vulva latin: vulva, pudendum femininum. The female reproductive system is made up of internal and external organs that function to produce haploid gametes called eggs (or oocytes), secrete sex hormones (such as estrogen), and carry and give birth to a fetus. as shown in figure 11.6.2 11.6. 2, the internal reproductive organs include the vagina, uterus, fallopian (uterine) tubes, and.

Comments are closed.