Egr Exhaust Gas Recirculation

Exhaust Gas Recirculation Egr Complete Guide Architectures X Exhaust gas recirculation. in internal combustion engines, exhaust gas recirculation (egr) is a nitrogen oxide (no x) emissions reduction technique used in petrol gasoline, diesel engines and some hydrogen engines. [1] egr works by recirculating a portion of an engine's exhaust gas back to the engine cylinders. The exhaust gas recirculation or egr system is one of several vehicle emission control systems. it helps reduce the amount of the nitrogen oxides (nox) in the exhaust gases. nitrogen oxides are normally formed in the process of combustion in the engine cylinders. egr system.

Exhaust Gas Recirculation Egr Complete Guide Components X Exhaust gas recirculation is a method by which a portion of an engine’s exhaust gas is returned to its combustion chambers via the inlet system. a basic conceptual schematic of an exhaust gas recirculation system is shown in figure 1. figure 1. schematic representation of egr system. Learn what egr is, how it works, and why it is used to reduce nox emissions from diesel engines. find out the types, components, and control of egr systems, and the effects of egr on engine performance and emissions. Exhaust gas recirculation (egr) complete guide – components. exhaust gas recirculation (egr) systems are widely used in diesel engines with the purpose of reducing the formation of nitrogen oxides (no x), by lowering the combustion temperature and the amount of oxygen into the cylinders. depending on whether the exhaust gas is recirculated. Exhaust gas recirculation (egr) is the most common technology to reduce nitrogen oxides (nox) emissions on diesel internal combustion engines (ice). egr takes exhaust gases from the exhaust manifold and reintroduces them into the intake manifold, mixing them with fresh air.

Exhaust Gas Recirculation Egr Complete Guide Architectures X Exhaust gas recirculation (egr) complete guide – components. exhaust gas recirculation (egr) systems are widely used in diesel engines with the purpose of reducing the formation of nitrogen oxides (no x), by lowering the combustion temperature and the amount of oxygen into the cylinders. depending on whether the exhaust gas is recirculated. Exhaust gas recirculation (egr) is the most common technology to reduce nitrogen oxides (nox) emissions on diesel internal combustion engines (ice). egr takes exhaust gases from the exhaust manifold and reintroduces them into the intake manifold, mixing them with fresh air. Egr stands for exhaust gas recirculation, a vehicle emissions control concept used in both gasoline and diesel engines. the egr valve — which works differently depending on how old the car is. Egr works by routing, cooling and feeding a controlled amount of exhaust gas created during combustion back into an engine’s intake air system. this process dilutes the air and fuel mixture that enters the combustion chambers, which reduces the engine's peak combustion temperature. the lower temperature means less nox is formed during.
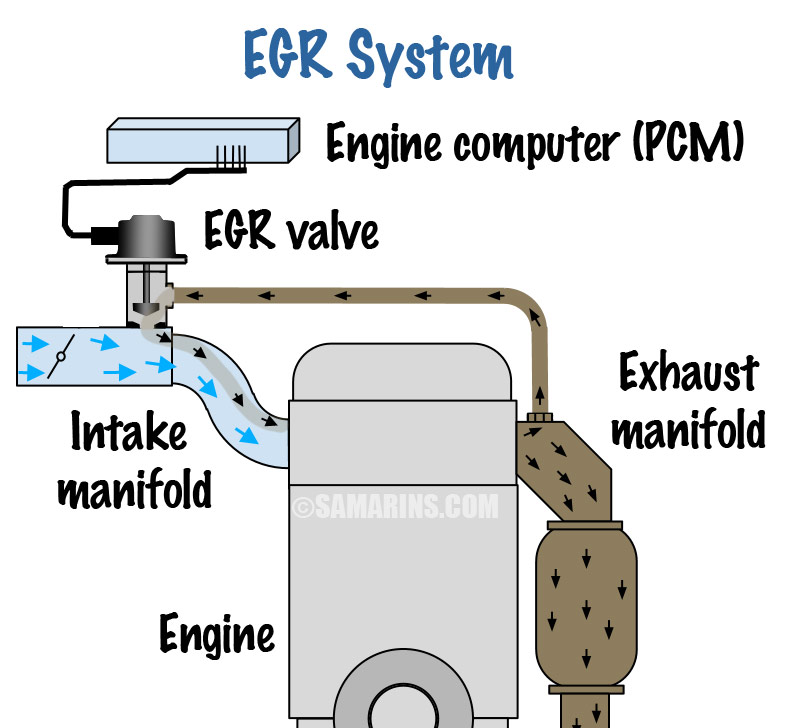
How Exhaust Gas Recirculation Egr System Works Egr stands for exhaust gas recirculation, a vehicle emissions control concept used in both gasoline and diesel engines. the egr valve — which works differently depending on how old the car is. Egr works by routing, cooling and feeding a controlled amount of exhaust gas created during combustion back into an engine’s intake air system. this process dilutes the air and fuel mixture that enters the combustion chambers, which reduces the engine's peak combustion temperature. the lower temperature means less nox is formed during.

Principle Of Exhaust Gas Re Circulation Egr Youtube

Exhaust Gas Recirculation Egr System Working Principle Design And

Comments are closed.