Electron Dot Structure For Oxygen

Oxygen Electron Dot Structure A step by step explanation of how to draw the lewis dot structure for o (oxygen). i show you where oxygen is on the periodic table and how to determine how. A lewis electron dot diagram (or electron dot diagram, or a lewis diagram, or a lewis structure) is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. the number of dots equals the number of valence electrons in the atom. these dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ScreenShot2018-11-19at11.40.52PM-5bf3909a46e0fb00510dbd6d.png)
Electron Dot Structure For Oxygen We can illustrate the formation of a water molecule from two hydrogen atoms and an oxygen atom using lewis dot symbols: the structure on the right is the lewis electron structure, or lewis structure, for h 2 o. with two bonding pairs and two lone pairs, the oxygen atom has now completed its octet. Lewis structure, also known as lewis dot structure or electron dot structure, is a simple and straightforward way of representing the outermost electron shell in a chemical species like an atom, ion, or molecule. it shows how electrons are positioned around the atoms either as lone pairs or in a chemical bond, typically a covalent bond or a. Steps of drawing lewis diagram. find total valence electrons: it is two for each oxygen atom. find how many electrons are needed: it is four for one o2 molecule. look for the total number of bonds forming: double covalent bonds are forming in an o2 molecule. choose a central atom: both the atoms will be central. Final lewis structure for carbon dioxide: covalent bonds are indicated as dashes and lone pairs of electrons are shown as pairs of dots. in carbon dioxide, each oxygen atom has two lone pairs of electrons remaining; the covalent bonds between the oxygen and carbon atoms each use two electrons from the oxygen atom and two from the carbon.

Oxygen Valence Electrons O Oxygen Valency Electron Configuration Steps of drawing lewis diagram. find total valence electrons: it is two for each oxygen atom. find how many electrons are needed: it is four for one o2 molecule. look for the total number of bonds forming: double covalent bonds are forming in an o2 molecule. choose a central atom: both the atoms will be central. Final lewis structure for carbon dioxide: covalent bonds are indicated as dashes and lone pairs of electrons are shown as pairs of dots. in carbon dioxide, each oxygen atom has two lone pairs of electrons remaining; the covalent bonds between the oxygen and carbon atoms each use two electrons from the oxygen atom and two from the carbon. Lewis structure examples. the lewis electron dot structures of a few molecules are illustrated in this subsection. 1. lewis structure of co2. the central atom of this molecule is carbon. oxygen contains 6 valence electrons which form 2 lone pairs. since it is bonded to only one carbon atom, it must form a double bond. Lewis structure (electron dot diagram) for the oxygen molecule, o 2, or . there are 2 bonding pairs of electrons shared between the 2 oxygen atoms, and each oxygen atom also has 2 lone pairs (non bonding) pairs of electrons.

Electron Dot Structure For Oxygen Lewis structure examples. the lewis electron dot structures of a few molecules are illustrated in this subsection. 1. lewis structure of co2. the central atom of this molecule is carbon. oxygen contains 6 valence electrons which form 2 lone pairs. since it is bonded to only one carbon atom, it must form a double bond. Lewis structure (electron dot diagram) for the oxygen molecule, o 2, or . there are 2 bonding pairs of electrons shared between the 2 oxygen atoms, and each oxygen atom also has 2 lone pairs (non bonding) pairs of electrons.
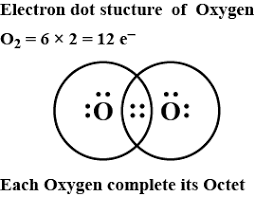
Oxygen Atom Lewis Structure

Comments are closed.