Example Of Secondary Consumer

Tropical Rainforest Secondary Consumers Learn what a secondary consumer is and see examples of aquatic and terrestrial secondary consumers. find out how they function in the food chain and why they are important for the ecosystem. Secondary consumers can be defined as a group of living organisms that mainly feed on primary consumers or herbivores to get energy. they are placed on the third trophic level in a food chain. some secondary consumers also feed on both producers and primary consumers. so, secondary consumers range from carnivores that consume meat to omnivores.

Food Chain With 3 Trophic Levels Learn what a secondary consumer is, how it differs from a primary consumer, and what functions it performs in a food chain. see examples of aquatic and terrestrial secondary consumers, and how they can switch between trophic levels depending on the environment. Learn what a secondary consumer is and how it fits into the ecological pyramid. see examples of secondary consumers, such as bears, wolves, and lions, and how they get their energy from primary consumers. Secondary consumers: a lion preying on a gazelle, a spider catching flies, or a bear that eats fish are examples of secondary consumers. ecological impact: primary consumers: they directly affect the population and health of primary producers and are crucial for sustaining many primary producers through processes like seed dispersal. Learn how secondary consumers regulate populations of primary consumers and influence ecosystem stability and biodiversity. explore the different types of secondary consumers, such as carnivores, omnivores, and insectivores, and see examples of each.
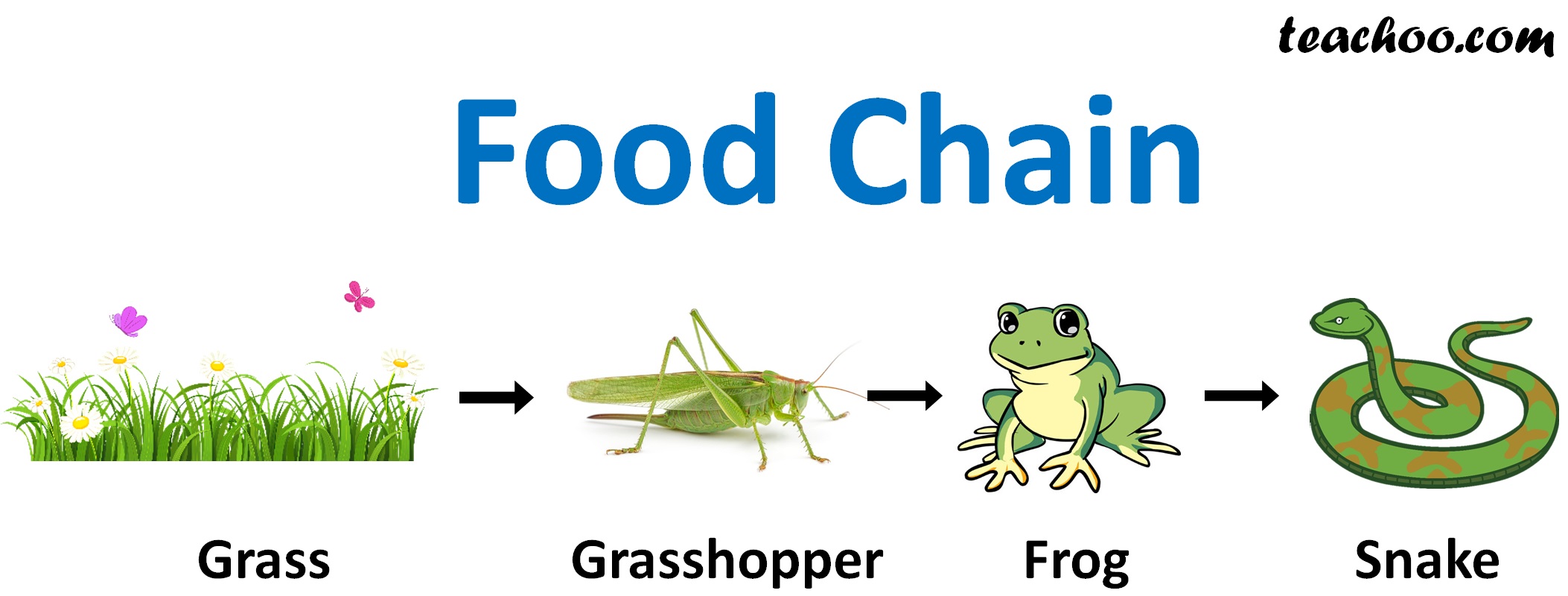
Food Chain With 4 Trophic Levels Secondary consumers: a lion preying on a gazelle, a spider catching flies, or a bear that eats fish are examples of secondary consumers. ecological impact: primary consumers: they directly affect the population and health of primary producers and are crucial for sustaining many primary producers through processes like seed dispersal. Learn how secondary consumers regulate populations of primary consumers and influence ecosystem stability and biodiversity. explore the different types of secondary consumers, such as carnivores, omnivores, and insectivores, and see examples of each. Secondary consumers are organisms that feed on primary consumers, which are plants or herbivores. they are either carnivores or omnivores, and have different adaptations to suit their habitats and prey. learn more about secondary consumers and their roles in the food chain. Primary consumer examples include cows, insects that eat sap, or sea creatures like plankton or krill – and the birds, fish, coyotes and humans that eat them are secondary consumers. secondary consumers can be either carnivores or omnivores, and their position on an energy pyramid can change depending on what they eat or choose to eat.

Comments are closed.