Eyeglasses Lens Thickness Whats The Difference Clearlycontacts Ca

Choosing The Right Lenses For Your Glasses In this video we explain the differences in thickness and weight between standard eyeglasses lenses and high index eyeglasses lenses.you can order designer g. 2. choose your lens usage. look for an option that suits your lifestyle. common options include: standard lenses ; multifocal lenses ; lenses with blue light protection ; sunglasses lenses ; transitions® lenses ; 3. choose your lens index. select a lens based on the thickness, features, and price that best fits your prescription and budget.

Eyeglasses Lens Thickness What S The Difference Clearlycontacts Ca Here’s the meaning behind each of these letters and numbers on your glasses prescription: 1. od “oculus dexter” indicates your right eye’s parameters. 2. os “oculus sinister” shows your left eye’s parameters. 3. sph “sphere” indicates the amount of lens power prescribed for nearsighted or farsighted vision. Entire frame: measure horizontally – start inside frame width. put the edge of your ruler over your frame and measure from the left hinge to the right hinge. 2. bridge and lenses: measure the width of the bridge and subtract that measurement from the frame width. this will give you the measurement for the frames alone. 1.67 vs 1.74 high index lenses explained. so, what’s the difference between all the different lens index options shown in the table above? let’s take a look and give you a better idea. starting with 1.61 vs 1.67 high index lenses — the 1.67 lens is extremely thin whereas despite still being stylish, the 1.61 lens is extra thin. The main difference between 1.57 and 1.61 index lenses is the thickness of the lens material. an individual’s prescription lens power may also influence which type of lens to use for eyewear. for example, if the lens power is approximately 2.00, it may be more suitable to opt for 1.56 index lenses. the thickness is around 3mm.

Eyeglass Lens Thickness Chart 1.67 vs 1.74 high index lenses explained. so, what’s the difference between all the different lens index options shown in the table above? let’s take a look and give you a better idea. starting with 1.61 vs 1.67 high index lenses — the 1.67 lens is extremely thin whereas despite still being stylish, the 1.61 lens is extra thin. The main difference between 1.57 and 1.61 index lenses is the thickness of the lens material. an individual’s prescription lens power may also influence which type of lens to use for eyewear. for example, if the lens power is approximately 2.00, it may be more suitable to opt for 1.56 index lenses. the thickness is around 3mm. Extra thin 1.74 lenses. super thin glasses that are suitable for corrections above ± 6. please note that the maximum values are ± 10 and ± 4 for the cylinder. even the most beautiful frame will not be comfortable when you choose the wrong lens thickness. our guide will help you to choose the right lens. Strong prescriptions result in a thicker lens than with high index lenses. see related: plastic vs. polycarbonate lenses: advantages & disadvantages overview of high index lenses. high index lenses are thin, lightweight lenses made from a special type of plastic. to be considered high index, a lens must have a refractive index of at least 1.60.

1 To 20 Glasses Thickness Comparison Youtube Extra thin 1.74 lenses. super thin glasses that are suitable for corrections above ± 6. please note that the maximum values are ± 10 and ± 4 for the cylinder. even the most beautiful frame will not be comfortable when you choose the wrong lens thickness. our guide will help you to choose the right lens. Strong prescriptions result in a thicker lens than with high index lenses. see related: plastic vs. polycarbonate lenses: advantages & disadvantages overview of high index lenses. high index lenses are thin, lightweight lenses made from a special type of plastic. to be considered high index, a lens must have a refractive index of at least 1.60.

Lens Thickness Guide
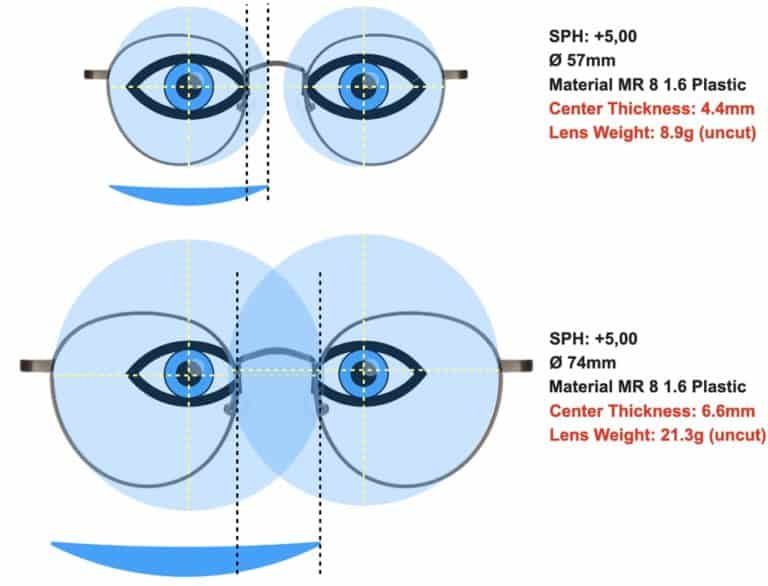
Different Lens Thickness Shown For How Big Your Eyes Look Progressive

Comments are closed.