Factors Affecting Standard Reduction Potential Chemistry General
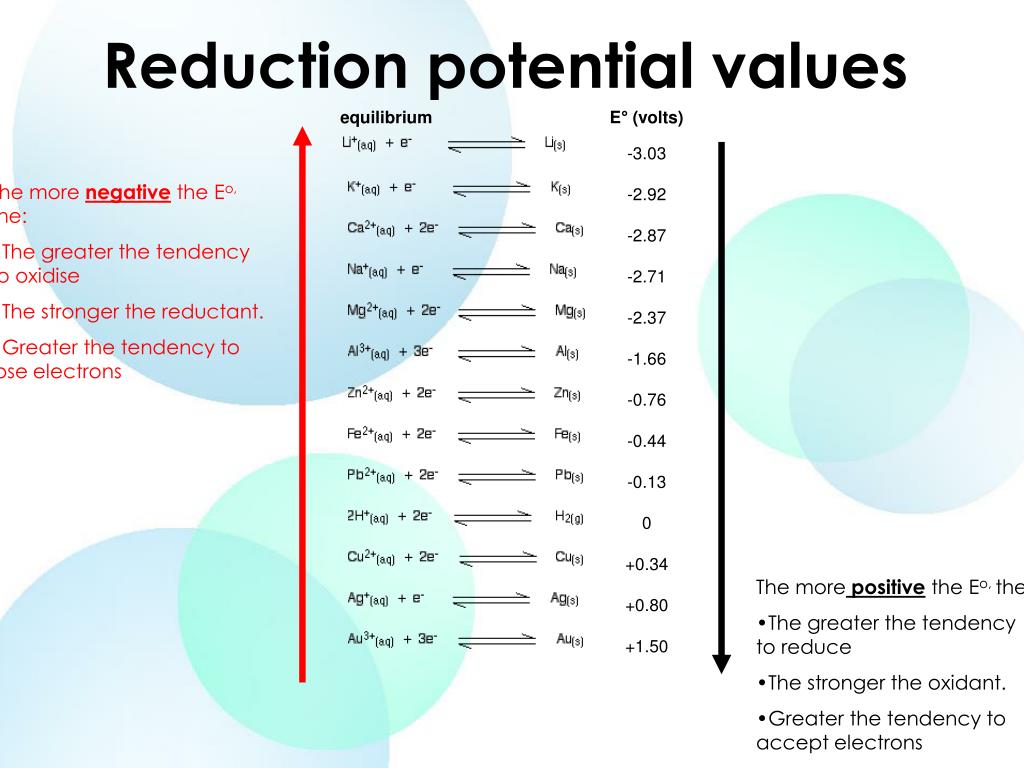
Ppt Standard Reduction Potential Powerpoint Presentation Free If the standard reduction potential of lithium is very negative, then the oxidation potential of lithium ion is very positive. if it is uphill to transfer an electron from hydrogen to lithium cation, it must be downhill to transfer an electron from a lithium atom to a proton. after all, hydrogen is more electronegative than any of the alkalis. It is written in the form of a reduction half reaction. an example can be seen below where "a" is a generic element and c is the charge. standard reduction potential. ac ce− → a (1) (1) a c c e − → a. for example, copper's standard reduction potential of eo = 0.340 v) e o = 0.340 v) is for this reaction: cu2 2e− → cu (2.

Factors Affecting Standard Reduction Potential Chemistry General The she consists of 1 atm of hydrogen gas bubbled through a 1 m hcl solution, usually at room temperature. platinum, which is chemically inert, is used as the electrode. the reduction half reaction chosen as the reference is. 2h (aq,1m) 2e− ⇌ h2(g,1 atm) e∘ = 0 v. e ° is the standard reduction potential. The reduction half reaction chosen as the reference is. 2h (aq,1 m) 2e − ⇌ h2(g, 1 atm) e ∘ = 0 v. e ° is the standard reduction potential. the superscript “°” on the e denotes standard conditions (1 bar or 1 atm for gases, 1 m for solutes). the voltage is defined as zero for all temperatures. figure 1. Since the definition of cell potential requires the half cells function as cathodes, these potentials are sometimes called standard reduction potentials. this approach to measuring electrode potentials is illustrated in figure 17.6 , which depicts a cell comprised of an she connected to a copper(ii) copper(0) half cell under standard state. Multiplying a constant into the stoichiometry of a half reaction does not affect the reduction potential. here, the silver half reaction is doubled, but cathode reduction potential is unchanged. the standard reduction potential represents a potential energy difference much like is experienced for a ball at the top of a hill as compared to the.
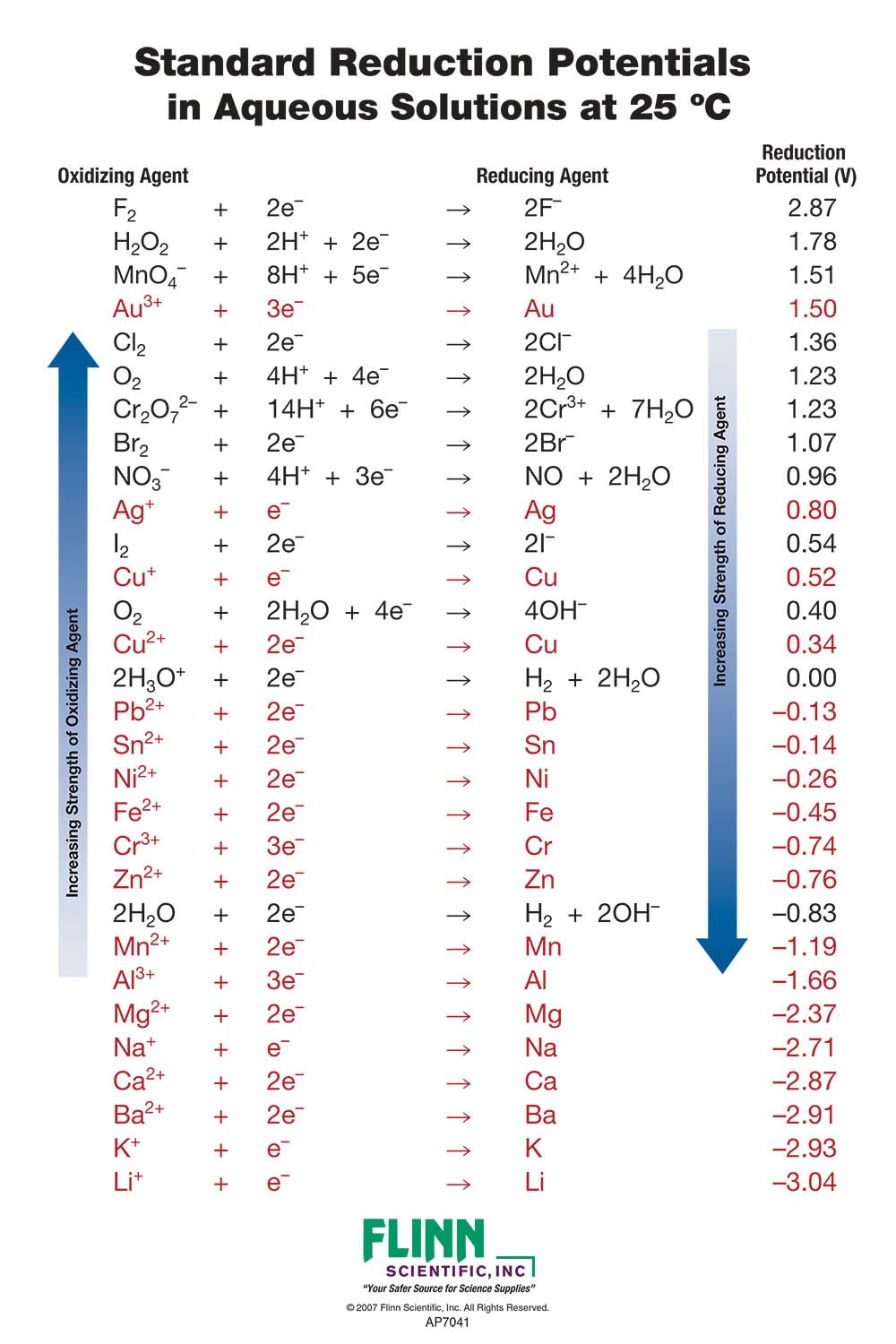
Standard Reduction Potential Charts For Chemistry Since the definition of cell potential requires the half cells function as cathodes, these potentials are sometimes called standard reduction potentials. this approach to measuring electrode potentials is illustrated in figure 17.6 , which depicts a cell comprised of an she connected to a copper(ii) copper(0) half cell under standard state. Multiplying a constant into the stoichiometry of a half reaction does not affect the reduction potential. here, the silver half reaction is doubled, but cathode reduction potential is unchanged. the standard reduction potential represents a potential energy difference much like is experienced for a ball at the top of a hill as compared to the. The standard reduction potential can be determined by subtracting the standard reduction potential for the reaction occurring at the anode from the standard reduction potential for the reaction occurring at the cathode. the minus sign is necessary because oxidation is the reverse of reduction. e∘ cell = e∘ cathode − e∘ anode e cell ∘. The reduction potentials in the table are, indirectly, an index of differences in electronic energy levels. the electron on gold is at a higher energy level than if it were on fluoride. it is thus motivated to spontaneously transfer to the fluorine atom, generating a potential in the circuit of 1.04v.

Electrochemistry The Standard Reduction Potential Youtube The standard reduction potential can be determined by subtracting the standard reduction potential for the reaction occurring at the anode from the standard reduction potential for the reaction occurring at the cathode. the minus sign is necessary because oxidation is the reverse of reduction. e∘ cell = e∘ cathode − e∘ anode e cell ∘. The reduction potentials in the table are, indirectly, an index of differences in electronic energy levels. the electron on gold is at a higher energy level than if it were on fluoride. it is thus motivated to spontaneously transfer to the fluorine atom, generating a potential in the circuit of 1.04v.
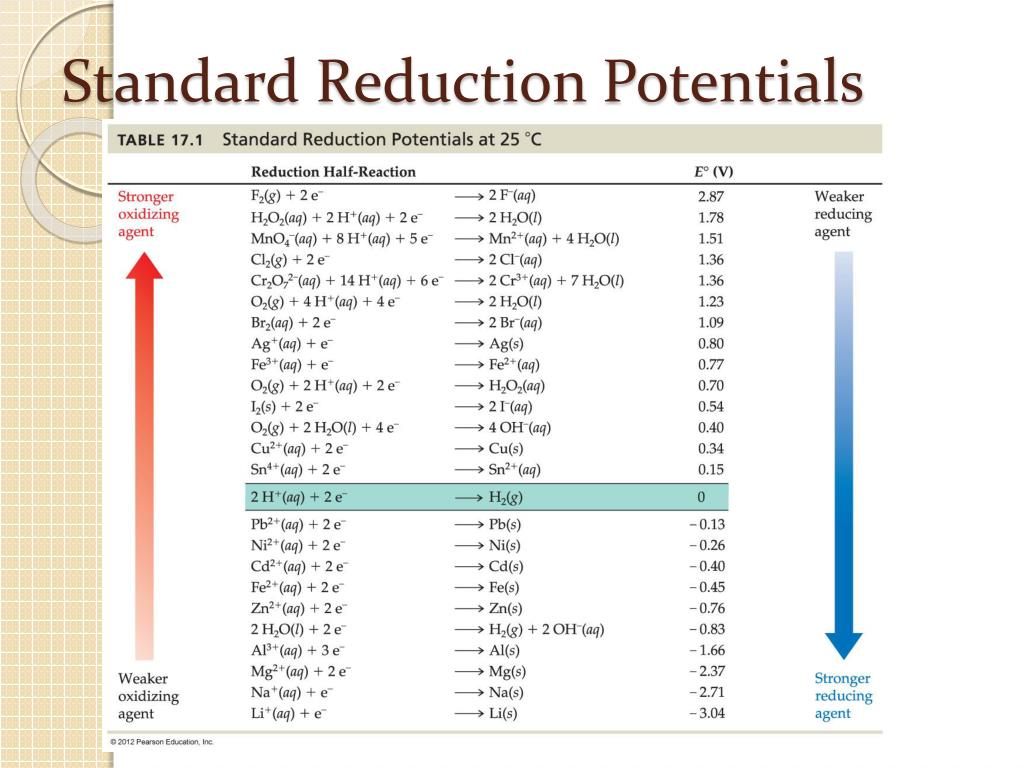
Ppt Chapter 17 Electrochemistry Powerpoint Presentation Free

Comments are closed.