Female Pelvic Anatomy Laparoscopic
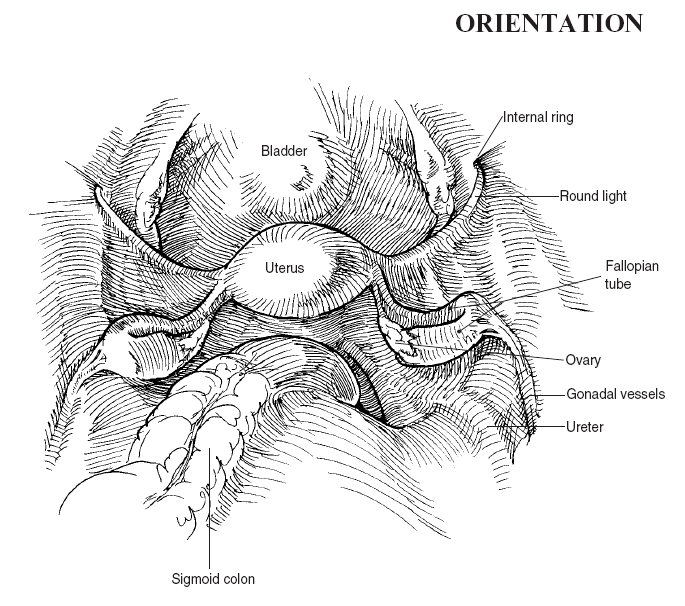
Laparoscopic Surgery Of The Female Pelvis Basicmedical Key The anatomy of the female genital tract and lower urinary and gastrointestinal tracts relevant to the surgeon performing laparotomy or laparoscopy, with an emphasis on clinical relevance and avoiding potential complications, is reviewed here. surgical pelvic anatomy from a vaginal approach and the surgical anatomy of the anterior abdominal wall. Figure 2 female pelvis: uterus, ovary, rectouterine pouch female. anatomical parts. ampulla of uterine tube. arteries of lower limb. base of sacrum. colon. female internal genitalia. fundus of bladder. infundibulum of uterine tube.
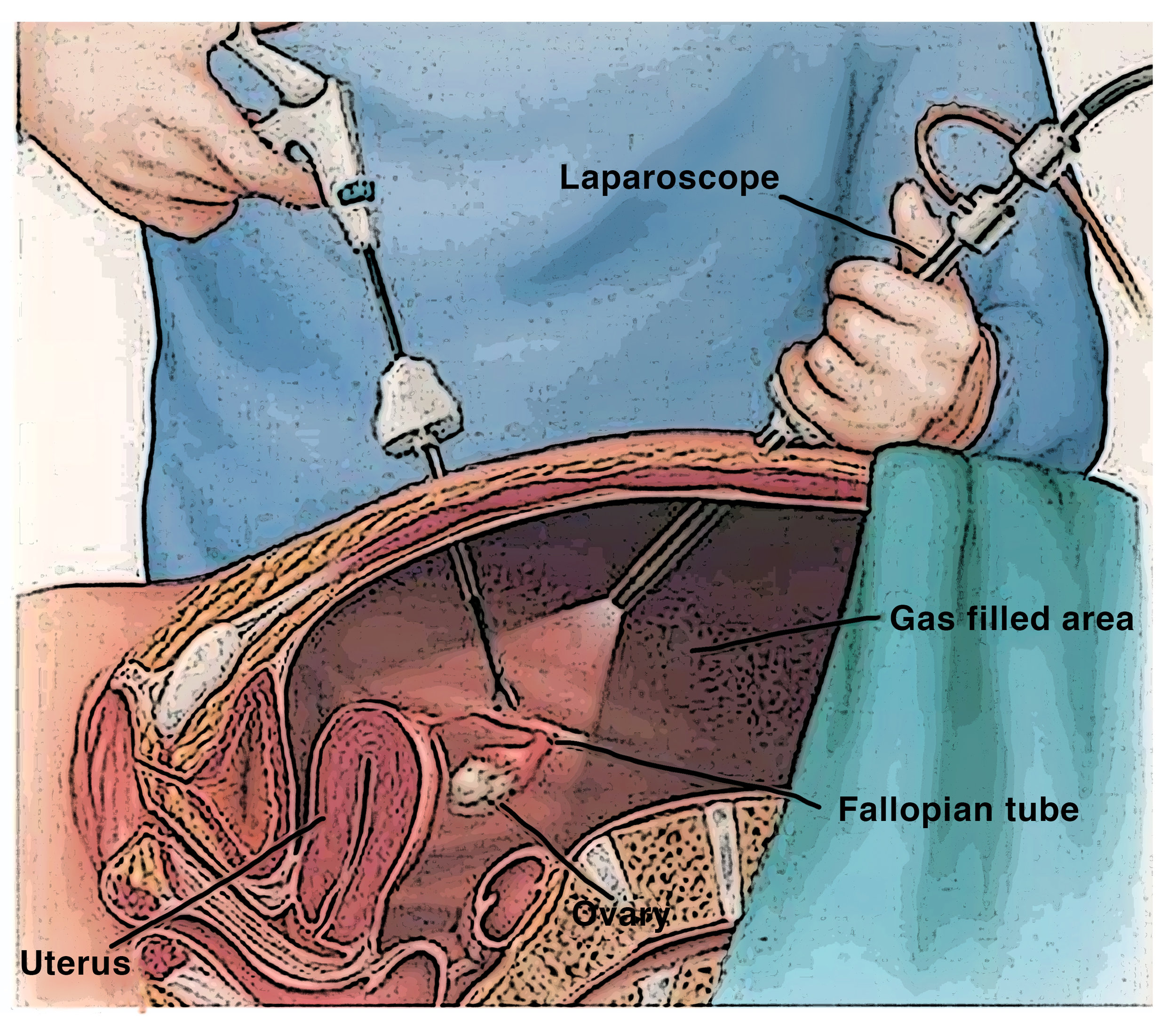
Laparoscopic Surgery For Endometriosis Statesboro Ga Statesboro Norman rosenblum, phd ’75, md ’78, facog, facs, professor and director of the division of gynecologic oncology in the sidney kimmel medical college at thomas. The pelvic cavity is a bowl like structure that sits below the abdominal cavity. the true pelvis, or lesser pelvis, lies below the pelvic brim (figure 1). this landmark begins at the level of the sacral promontory posteriorly and the pubic symphysis anteriorly. the space below contains the bladder, rectum, and part of the descending colon. in females, the pelvis also houses the uterus. The surgical landmarks of the bony pelvis are the ischial spine, pubic arch, pectineal line, obturator foramen and coccyx. the female upper genital tract consists of the cervix, uterine corpus, fallopian tubes and ovaries. a sagittal view of the female pelvis is shown in fig. 1. This learning module is a visual guide to the anatomy of the female pelvis, focusing on the anatomical features and relationships essential to open and laparoscopic pelvic surgery. learning outcomes after completing this module, the learner will:.

Normal Anatomy Of The Female Pelvis A B Axial A And Sagittal B The surgical landmarks of the bony pelvis are the ischial spine, pubic arch, pectineal line, obturator foramen and coccyx. the female upper genital tract consists of the cervix, uterine corpus, fallopian tubes and ovaries. a sagittal view of the female pelvis is shown in fig. 1. This learning module is a visual guide to the anatomy of the female pelvis, focusing on the anatomical features and relationships essential to open and laparoscopic pelvic surgery. learning outcomes after completing this module, the learner will:. Also included is a discussion of the contemporary understanding of female pelvic organ support, with an emphasis on the functional and surgical anatomy of the vagina, urethra, and pelvic floor. the anatomy of the female genital tract and lower urinary and gastrointestinal tracts relevant to the surgeon performing laparotomy or laparoscopy is. 1 surgical anatomy of the female pelvis; 2 female genital tract trauma: evaluation and management; 3 bleeding disorders and anticoagulation; 4 healthcare of lesbian, bisexual, and transgender patients; section 2 gynecologic surgery; section 3 infertility; section 4 urogynecology and pelvic floor dysfunction; section 5 gynecologic oncology.

Comments are closed.