Figure 10 27 Continuous Cooling Transformation Diagram Engineering Callister
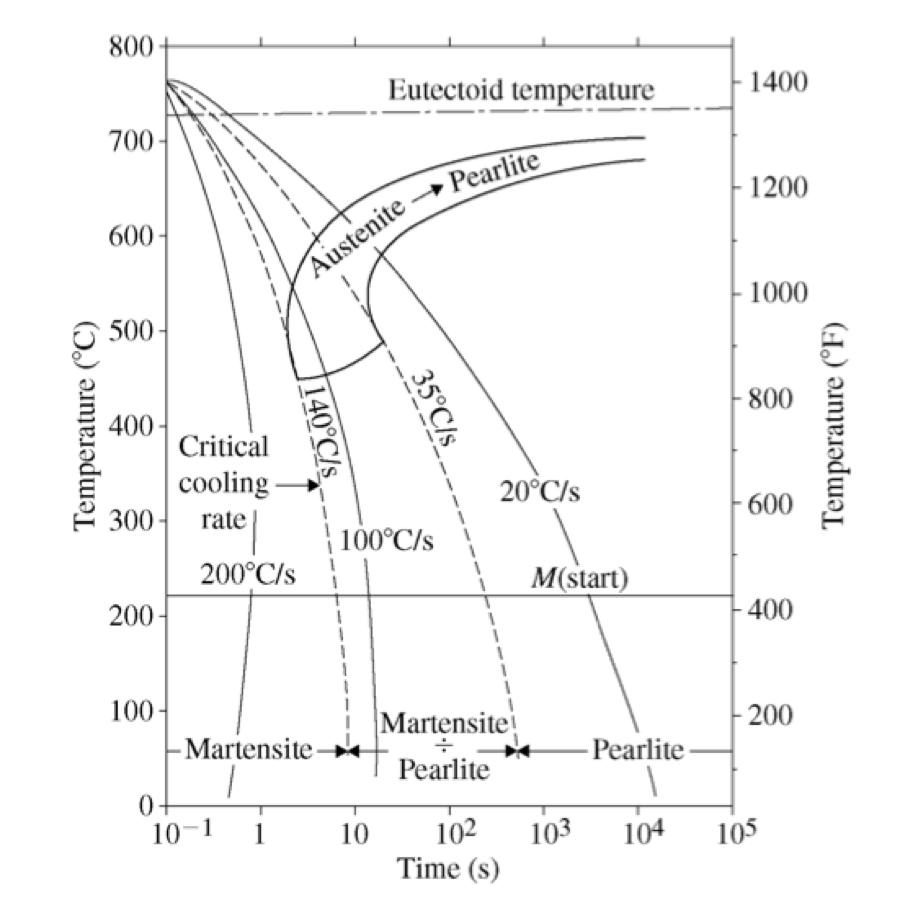
Continuous Cooling Transformation Diagram 10.24 figure 10.40 shows the continuous cooling transformation diagram for a 0.35 wt% c iron—carbon alloy. make a copy of this figure and then sketch and label continuous cooling questions and problems 355 alloy of eutectoid composition. 10.27 name the microstructural products of 4340 alloy steel specimens that are first com. Mechanical engineering expert. figure below (from callister & rethwisch) shows the continuous cooling transformation diagram for a 1.13 wt% c iron carbon alloy. make a copy of this figure and then sketch and label continuous cooling curves to yield the following microstructures: (a) fine pearlite and proeutectoid cementite (b) martensite (c.
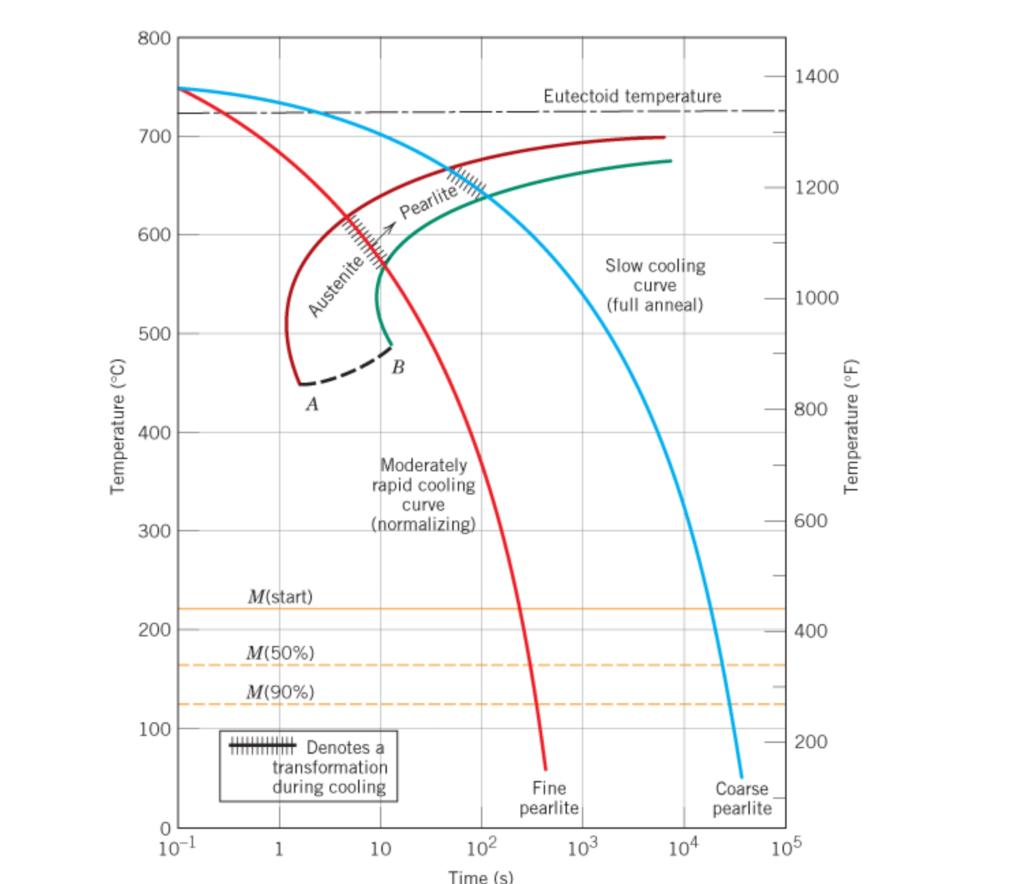
Continuous Cooling Transformation Diagram Definition: stability of phases during continuous cooling of austenite. there are two types of cct diagrams. i) plot of (for each type of transformation) transformation start, specific fraction of transformation and transformation finish temperature against transformation time on each cooling curve. 10.14,callister 7e. (fig. 10.14 adapted from h. boyer (ed.) atlas of isothermal transformation and cooling transformation diagrams, american society for metals, 1997, p. 28.) effect of cooling history in fe c system 400 500 600 700 0 % p e a r l i t e 1 0 5 austenite (stable) t e (727°c) austenite (unstable) pearlite t(°c) 110102 103 104 105. Chemical engineering 378 continuous cooling transformation diagram. cooling curve. fig. 10.26, figure 10.40, callister & rethwisch 10e. Figure $10.40$ shows the continuous cooling transformation diagram for a $1.13 \mathrm{wt} \%$ c iron carbon alloy. make a copy of this figure and then sketch and label continuous cooling curves to yield the following microstructures: (a) fine pearlite and proeutectoid cementite (b) martensite (c) martensite and proeutectoid cementite.
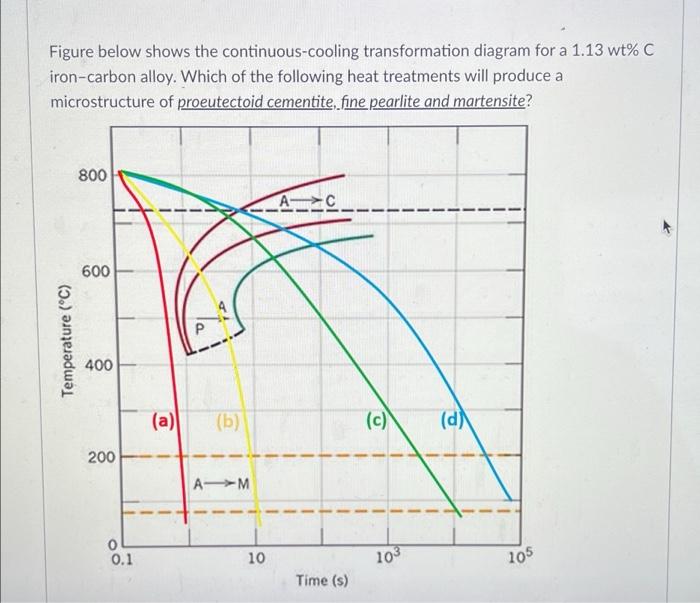
Solved Figure Below Shows The Continuous Cooling Chegg Chemical engineering 378 continuous cooling transformation diagram. cooling curve. fig. 10.26, figure 10.40, callister & rethwisch 10e. Figure $10.40$ shows the continuous cooling transformation diagram for a $1.13 \mathrm{wt} \%$ c iron carbon alloy. make a copy of this figure and then sketch and label continuous cooling curves to yield the following microstructures: (a) fine pearlite and proeutectoid cementite (b) martensite (c) martensite and proeutectoid cementite. Question: figure below (from callister \& rethwisch) shows the continuous cooling transformation diagram for a 1.13wt%c iron carbon alloy. make a copy of this figure and then sketch and label continuous cooling curves to yield the following microstructures: (a) fine pearlite and cementite (b) martensite (c) martensite and cementite (d) coarse pearlite and cementite. Figure 10.40 shows the continuous cooling transformation diagram for a 0.35 wt\% $\mathrm{c}$ iron carbon alloy. make a copy of this figure and then sketch and label continuous cooling curves to yield the following microstructures: (a) fine pearlite and proeutectoid ferrite (b) martensite (c) martensite and proeutectoid ferrite.

Schematic Illustration Of Continuous Cooling Transformation C C T Question: figure below (from callister \& rethwisch) shows the continuous cooling transformation diagram for a 1.13wt%c iron carbon alloy. make a copy of this figure and then sketch and label continuous cooling curves to yield the following microstructures: (a) fine pearlite and cementite (b) martensite (c) martensite and cementite (d) coarse pearlite and cementite. Figure 10.40 shows the continuous cooling transformation diagram for a 0.35 wt\% $\mathrm{c}$ iron carbon alloy. make a copy of this figure and then sketch and label continuous cooling curves to yield the following microstructures: (a) fine pearlite and proeutectoid ferrite (b) martensite (c) martensite and proeutectoid ferrite.

Continuous Cooling Transformation Diagrams Chapter 10 Continuous Cooling

Comments are closed.