Figure Schematic Representation Of Sodium Handling By The Kidney

Figure Schematic Representation Of Sodium Handling By The Kidney Schematic representation of sodium handling by the kidney, syndromes causing hypotension and hypertension, genetic factors influencing sodium reabsorption, and potential targeted therapeutic. The impact of renal sodium handling and the salt sensitivity of blood pressure in health and hypertension is a critical public health issue owing to the excess of dietary salt consumed globally and the significant percentage of the global population exhibiting salt sensitivity. this review highlights recent advances that have provided new.

Schematic Representation Of The Renal Handling Of Glucose And Sodium By Understanding renal sodium handling sodium, a vital electrolyte, serves as a key determinant of extracellular fluid volume and osmolality. the kidneys adeptly modulate sodium transport across various segments of the renal tubules to maintain sodium balance and regulate blood pressure. renal sodium handling primarily occurs in the proximal. The handling of sodium by the renal system is a key indicator of renal function. alterations in the corticomedullary distribution of sodium are considered important indicators of pathology in renal diseases. the derangement of sodium handling can be noninvasively imaged using sodium magnetic resonance imaging (23na mri), with data analysis allowing for the assessment of the corticomedullary. The renal handling of na( ) balance is a major determinant of the blood pressure (bp) level. the inability of the kidney to excrete the daily load of na( ) represents the primary cause of chronic. The hazard of excessive salt intake was elegantly discussed by mcgregor and de wardener more than 30 years ago in their essay “salt, diet and health: neptune’s poisoned chalice; the origins of high blood pressure.” 1 in this regard, chronic kidney disease (ckd) patients represent a particularly sensitive and vulnerable population, because the ability to regulate sodium and water.
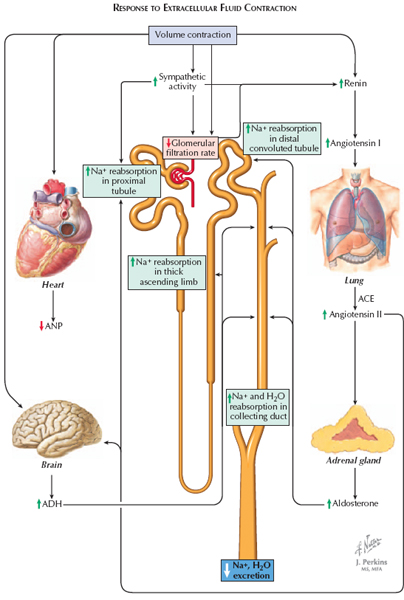
Renal Handling Of Sodium And Chloride Response To Extracellular Fluid The renal handling of na( ) balance is a major determinant of the blood pressure (bp) level. the inability of the kidney to excrete the daily load of na( ) represents the primary cause of chronic. The hazard of excessive salt intake was elegantly discussed by mcgregor and de wardener more than 30 years ago in their essay “salt, diet and health: neptune’s poisoned chalice; the origins of high blood pressure.” 1 in this regard, chronic kidney disease (ckd) patients represent a particularly sensitive and vulnerable population, because the ability to regulate sodium and water. Figure 1. schematic representation of sodium handling by the kidney, syndromes causing hypotension and hypertension, genetic factors influencing sodium reabsorption, and potential targeted therapeutic options. red denotes syndromes causing sodium retention. Understanding of renal k handling (figure 2) and ncc regulation (sect. iia, figure 3). b. renal k handling k is freely filtered by the glomerulus. with the assumption of a normal plasma k of ~4.5 mm and a normal glomer ular filtration rate (gfr) of ~180 l day, ~800 mmol of k is filtered by the kidneys each day. more than 90% of this.

Schematic Representation Of The Renal Handling Of Glucose And Sodium By Figure 1. schematic representation of sodium handling by the kidney, syndromes causing hypotension and hypertension, genetic factors influencing sodium reabsorption, and potential targeted therapeutic options. red denotes syndromes causing sodium retention. Understanding of renal k handling (figure 2) and ncc regulation (sect. iia, figure 3). b. renal k handling k is freely filtered by the glomerulus. with the assumption of a normal plasma k of ~4.5 mm and a normal glomer ular filtration rate (gfr) of ~180 l day, ~800 mmol of k is filtered by the kidneys each day. more than 90% of this.
Blood Pressure And Renal Handling Of Sodium

Comments are closed.