First Order Reaction Plot Vrogue Co

First Order Reaction Plot The differential equation describing first order kinetics is given below: rate = − d[a] dt = k[a]1 = k[a] the "rate" is the reaction rate (in units of molar time) and k is the reaction rate coefficient (in units of 1 time). however, the units of k vary for non first order reactions. these differential equations are separable, which simplifies. A plot of ln[no 2] versus t (part (b) in figure 14.4.1) shows us that the reaction is not first order in no 2 because a first order reaction would give a straight line. having eliminated zeroth order and first order behavior, we construct a plot of 1 [no 2] versus t (part (c) in figure 14.4.1).
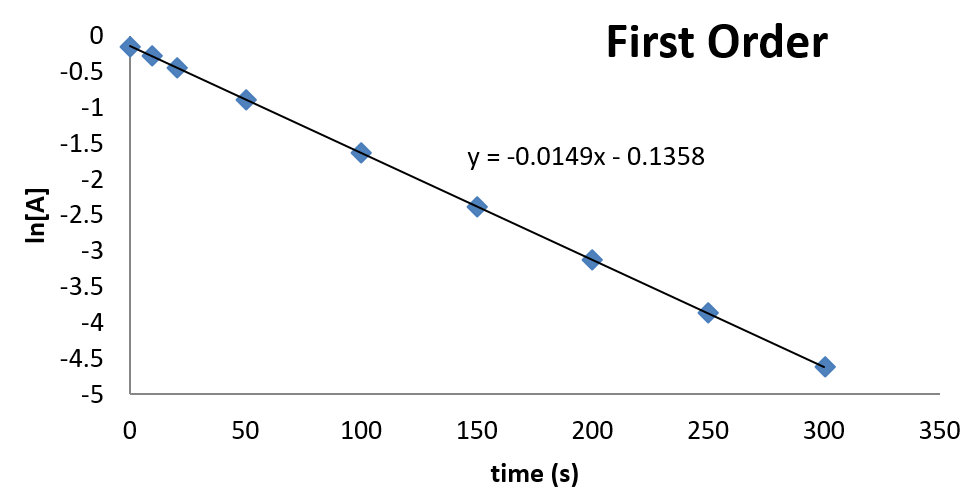
First Order Reaction Plot If a plot of reactant concentration versus time is not linear but a plot of the natural logarithm of reactant concentration versus time is linear, then the reaction is first order. the rate law and reaction order of the hydrolysis of cisplatin are determined from experimental data, such as those displayed in ta ble \(\pageindex{1}\). A → products. rate = k[a]n. where k is the rate constant and n is the reaction order. our objective is to determine the reaction order by calculating the n from a set of experiments. keep in mind that: if n = 0, the reaction is zero order, and the rate is independent of the concentration of a. if n = 1, the reaction is first order, and the. The concentration v s time graph for a first order reaction is provided below. for first order reactions, the equation ln [a] = kt ln [a] 0 is similar to that of a straight line (y = mx c) with slope k. this line can be graphically plotted as follows. thus, the graph for ln [a] v s t for a first order reaction is a straight line with. You can then plot 1 t as a measure of rate against the varying concentrations of the reactant you are investigating. if the reaction is first order with respect to that substance, then you would get a straight line. that's because in a first order reaction, the rate is proportional to the concentration. if you get a curve, then it isn't first.

First Order Reaction Plot The concentration v s time graph for a first order reaction is provided below. for first order reactions, the equation ln [a] = kt ln [a] 0 is similar to that of a straight line (y = mx c) with slope k. this line can be graphically plotted as follows. thus, the graph for ln [a] v s t for a first order reaction is a straight line with. You can then plot 1 t as a measure of rate against the varying concentrations of the reactant you are investigating. if the reaction is first order with respect to that substance, then you would get a straight line. that's because in a first order reaction, the rate is proportional to the concentration. if you get a curve, then it isn't first. If a set of rate data are plotted in this fashion but do not result in a straight line, the reaction is not first order in [latex]a[ latex]. figure 18.4.1. for a first order reaction, a plot of the natural log of the concentration of the reactant (a) versus time (t) results in a straight line. That means that that particular term disappears from the rate equation. the overall order of the reaction is found by adding up the individual orders. for example, if the reaction is first order with respect to both a and b (a = 1 and b = 1), the overall order is 2. we call this an overall second order reaction.

Comments are closed.