Food Chain Examples With Labels At Andrew Brown Blog

Horizontal Food Chain At Crystal Chambliss Blog Definition of food chain. a food chain shows energy pathways in ecosystems. each ecosystem on the planet has food chains of organisms ranging from producers to consumers. the producers are on the lowest level of the food chain, while the consumers that eat those producers are called primary consumers. higher level consumers who eat those. Typically, a food chain is represented by a diagram where arrows show the direction of energy and nutrients flow. many herbivores eat grass, and deer can eat other plants besides grass. even a tiger can eat many types of animals and plants. thus, each animal is part of multiple food chains. all interconnected to make a food web.
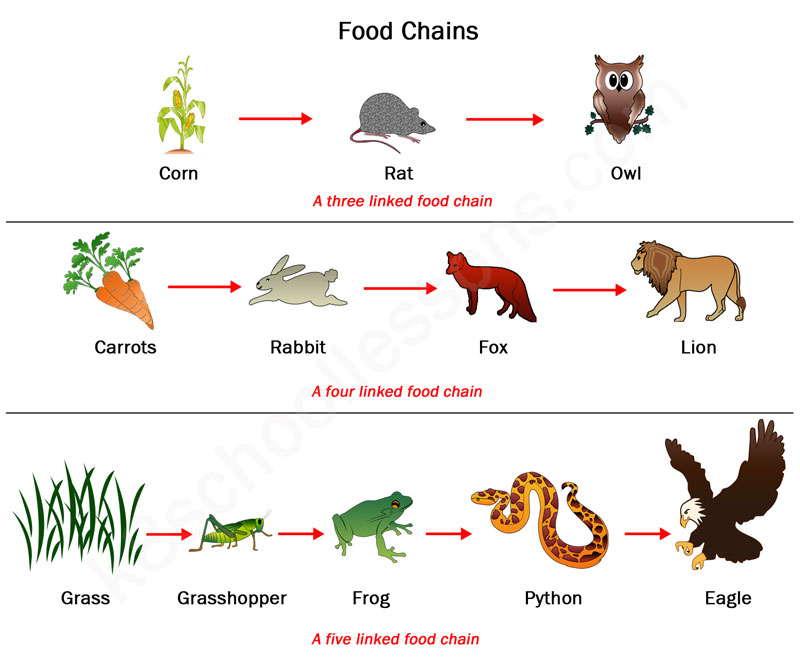
Simple Food Chain Examples At Lillie Hilbert Blog Maybe you’ve studied a little ecology and come across the terms “food chain” and “food web.” both help ecologists explain the ways that energy from food travels through an ecosystem. in this post, we will dive into the differences between food chains and food webs, and look at some examples of both!. The food chain is a series of creatures that begins with producer organisms, having consumers at various levels in between, and ends with decomposer species. a food web connects numerous food chains. the food chain takes a single path, whereas the food web takes several paths. the food chain teaches us about the relationships between creatures. Food chain examples. different ecosystems will have different food chains. let’s look at some examples of the food chain: food chain in a forest. in a forest ecosystem, plants and trees are the ones that make things. a deer eats plants, while a carnivore like a tiger eats a deer. plants —> deer —> tiger. food chain in a grassland. Example: foxes preying on rabbits. tertiary consumption: tertiary consumers, often apex predators, eat secondary consumers, occupying the top of the food chain. example: eagles feeding on foxes. decomposition: decomposers like bacteria and fungi break down dead organisms, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
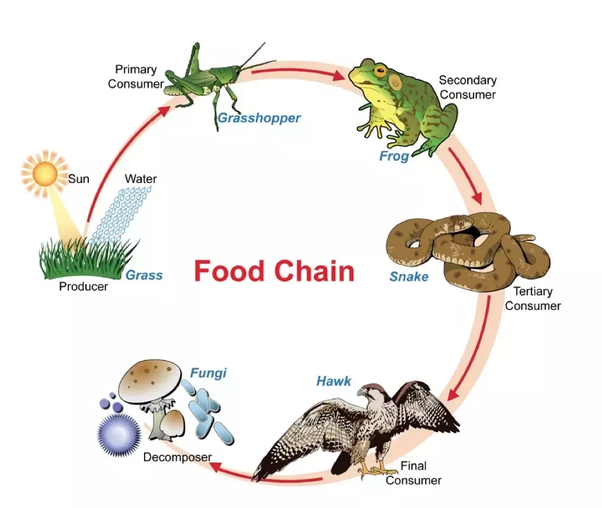
Food Chain Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary Food chain examples. different ecosystems will have different food chains. let’s look at some examples of the food chain: food chain in a forest. in a forest ecosystem, plants and trees are the ones that make things. a deer eats plants, while a carnivore like a tiger eats a deer. plants —> deer —> tiger. food chain in a grassland. Example: foxes preying on rabbits. tertiary consumption: tertiary consumers, often apex predators, eat secondary consumers, occupying the top of the food chain. example: eagles feeding on foxes. decomposition: decomposers like bacteria and fungi break down dead organisms, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem. Food chains. a food chain represents a single pathway by which energy and matter flow through an ecosystem. an example is shown in figure below. food chains are generally simpler than what really happens in nature. most organisms consume—and are consumed by—more than one species. this food chain includes producers and consumers. A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another. each organism in a food chain occupies a specific trophic level (energy level), its position in the food chain. the first trophic level in the food chain is the producers.
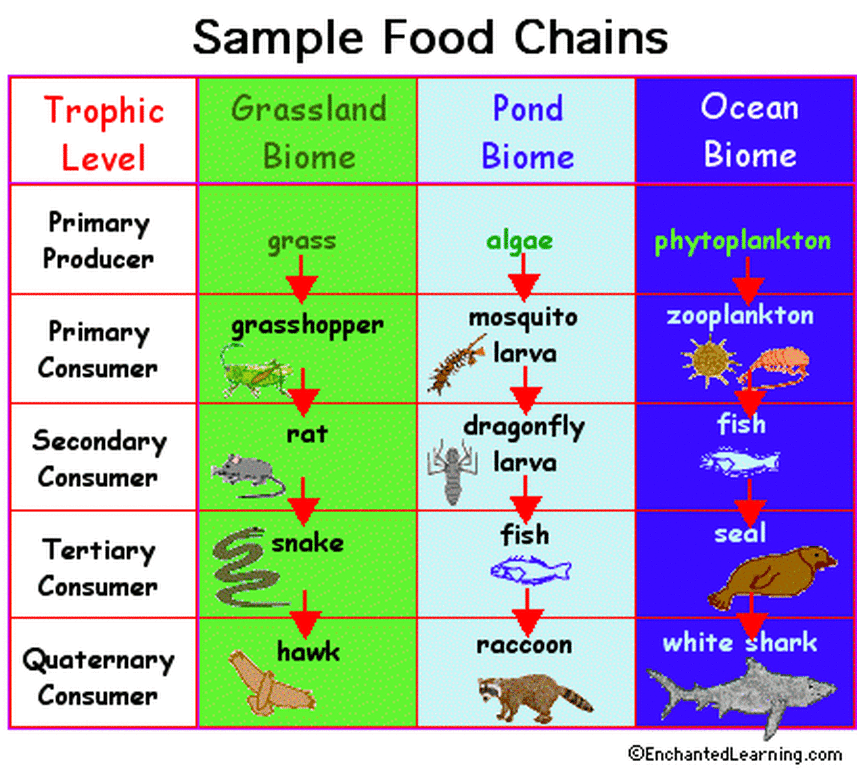
Food Chain Examples With 5 Organisms At Cameron Gasaway Blog Food chains. a food chain represents a single pathway by which energy and matter flow through an ecosystem. an example is shown in figure below. food chains are generally simpler than what really happens in nature. most organisms consume—and are consumed by—more than one species. this food chain includes producers and consumers. A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another. each organism in a food chain occupies a specific trophic level (energy level), its position in the food chain. the first trophic level in the food chain is the producers.

Comments are closed.