Food Chain Of Grass
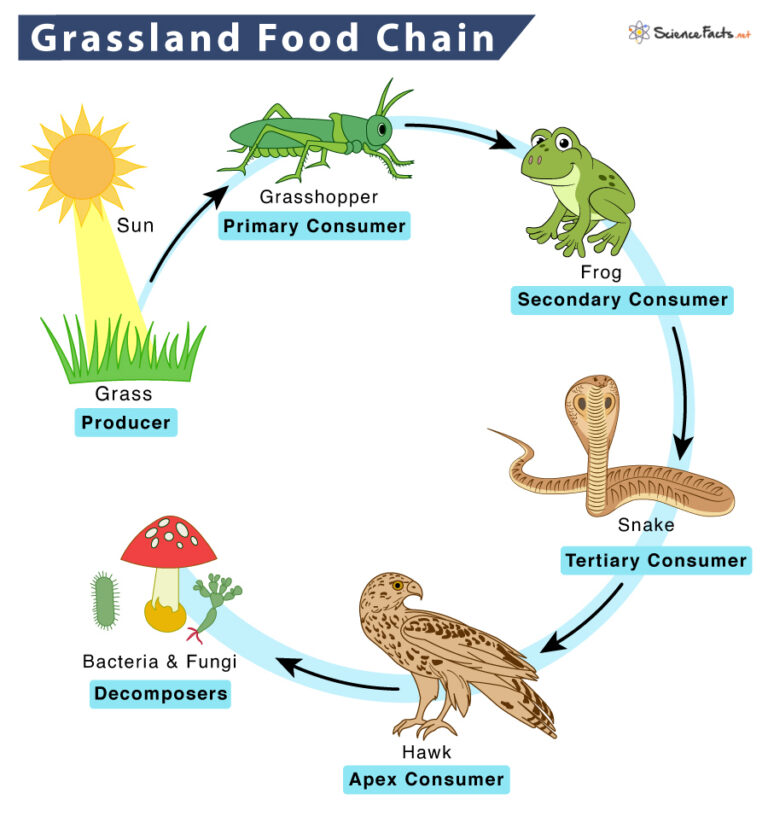
Grassland Food Chain Examples And Diagram In a grassland food chain, the grass is the producer. it produces food using the sun’s energy. the primary consumers follow the producers. insects like grasshoppers are primary grasslands consumers as they depend on the green plant for their food (herbivores). occasionally, primary consumers are omnivores as well, such as aardvarks. Food webs better represent the complexity of ecosystems, where most organisms consume multiple types of food and are preyed upon by various predators. for example: food chain example: grass → grasshopper → frog → snake → hawk. food web example: in a forest ecosystem, grasshoppers may be eaten by frogs, birds, and spiders, while snakes.

Food Chain Of Grass A grassland food chain. the first step of the food chain (sometimes referred to as the bottom of the food chain) is usually made up of producers organisms that can make their own food. in a. Grassland food webs consist of interconnected food chains within an ecosystem, illustrating the flow of energy between organisms. these food webs typically start with producers, such as plants, that create their own food through photosynthesis. herbivores consume plants, carnivores eat other animals, and omnivores consume both plants and animals. A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and. A food chain shows how plants and animals get their energy. here is an example of a simple food chain: grass → cow → human. the grass is the producer. the cow and human are consumers.

40 Grassland Food Web Diagram Wiring Diagrams Manual A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and. A food chain shows how plants and animals get their energy. here is an example of a simple food chain: grass → cow → human. the grass is the producer. the cow and human are consumers. The food chain describes who eats whom in the wild. every living thing—from one celled algae to giant blue whales (balaenoptera musculus)—needs food to survive. each food chain is a possible pathway that energy and nutrients can follow through the ecosystem. for example, grass produces its own food from sunlight. a rabbit eats the grass. In a detrital food chain, dead organic matter of plants and animals is broken down by decomposers, e.g., bacteria and fungi, and moves to detritivores and then carnivores.

Comments are closed.