Formation Of Double Bond In Oxygen Molecule

Formation Of Double Bond In Oxygen Molecule Youtube A double covalent bond is where two pairs of electrons are shared between the atoms rather than just one pair. some simple molecules containing double bonds. oxygen, o2. two oxygen atoms can both achieve stable structures by sharing two pairs of electrons as in the diagram. the double bond is shown conventionally by two lines joining the atoms. Das academy of science ap state board 10th class chemical bond formation of double bond in oxygen molecule.

Draw The Atomic Orbit Structure Diagram For Formation Of Knowledgeboat An oxygen atom has 6 electrons in its outer shell. oxygen is in group 6 of the periodic table. two oxygen atoms will each share two electrons to form two covalent bonds and make an oxygen molecule (o 2). this is a picture of an oxygen molecule. by sharing the four electrons where the shells touch each oxygen atom can count 8 electrons in its. Thus, we have the effective formation of a c=o “double bond.” notice that the pi bond in the c=o “double bond” appears distorted, indicating higher electron density around the oxygen than around the carbon. this is because the c=o bond is polar. the more electronegative oxygen atom attracts bonding electrons towards itself more strongly. Steps of drawing lewis diagram. find total valence electrons: it is two for each oxygen atom. find how many electrons are needed: it is four for one o2 molecule. look for the total number of bonds forming: double covalent bonds are forming in an o2 molecule. choose a central atom: both the atoms will be central. Carbon and members of the oxygen family of elements (the chalcogens) participate in double bonds. examples of double bonds are o 2 (oxygen, o=o), co 2 (carbon dioxide, o=c=o), and c 2 h 2 (ethylene, h c=c h). the double bond consists of one sigma (σ) bond and one pi (π) bond. a pi bond forms by sideways overlapping of p orbitals. triple bond.
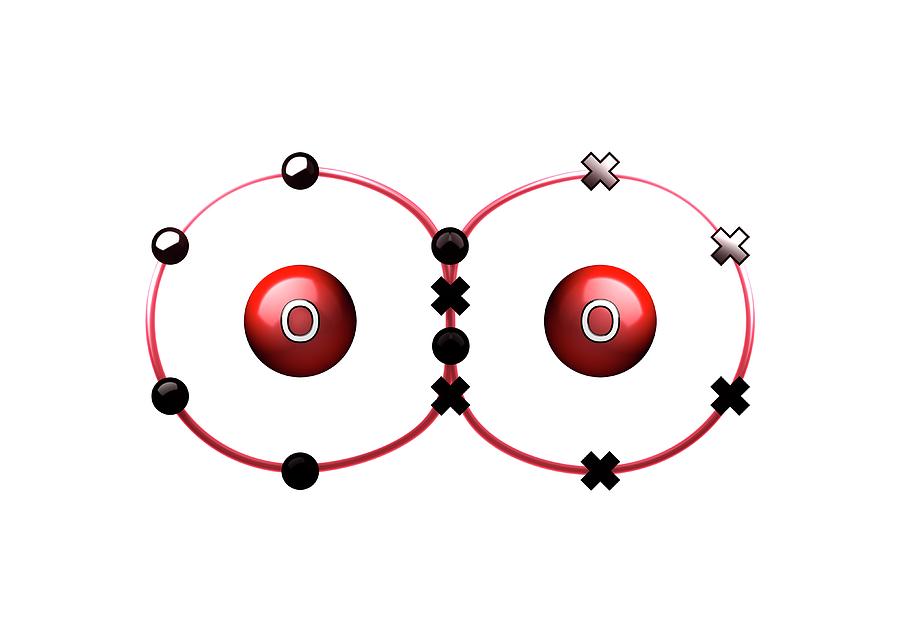
Bond Formation In Oxygen Molecule Photograph By Animate4 Science Steps of drawing lewis diagram. find total valence electrons: it is two for each oxygen atom. find how many electrons are needed: it is four for one o2 molecule. look for the total number of bonds forming: double covalent bonds are forming in an o2 molecule. choose a central atom: both the atoms will be central. Carbon and members of the oxygen family of elements (the chalcogens) participate in double bonds. examples of double bonds are o 2 (oxygen, o=o), co 2 (carbon dioxide, o=c=o), and c 2 h 2 (ethylene, h c=c h). the double bond consists of one sigma (σ) bond and one pi (π) bond. a pi bond forms by sideways overlapping of p orbitals. triple bond. Figure 8.5.13 8.5. 13: the molecular orbital energy diagram for o 2 predicts two unpaired electrons. we calculate the bond order as. o2 = (8 − 4) 2 = 2 o 2 = (8 − 4) 2 = 2. oxygen's paramagnetism is explained by the presence of two unpaired electrons in the (π 2py, π 2pz)* molecular orbitals. Double bonds. for example, consider the homonuclear diatomic covalent molecule named molecular oxygen, whose chemical formula is o 2 recall that for a covalent molecule, the information represented in its chemical formula must be a direct reflection of its lewis structure.

Comments are closed.