Formation Of Water Molecule Water H2o Formation Water Molecule H2o Covalentbond Short

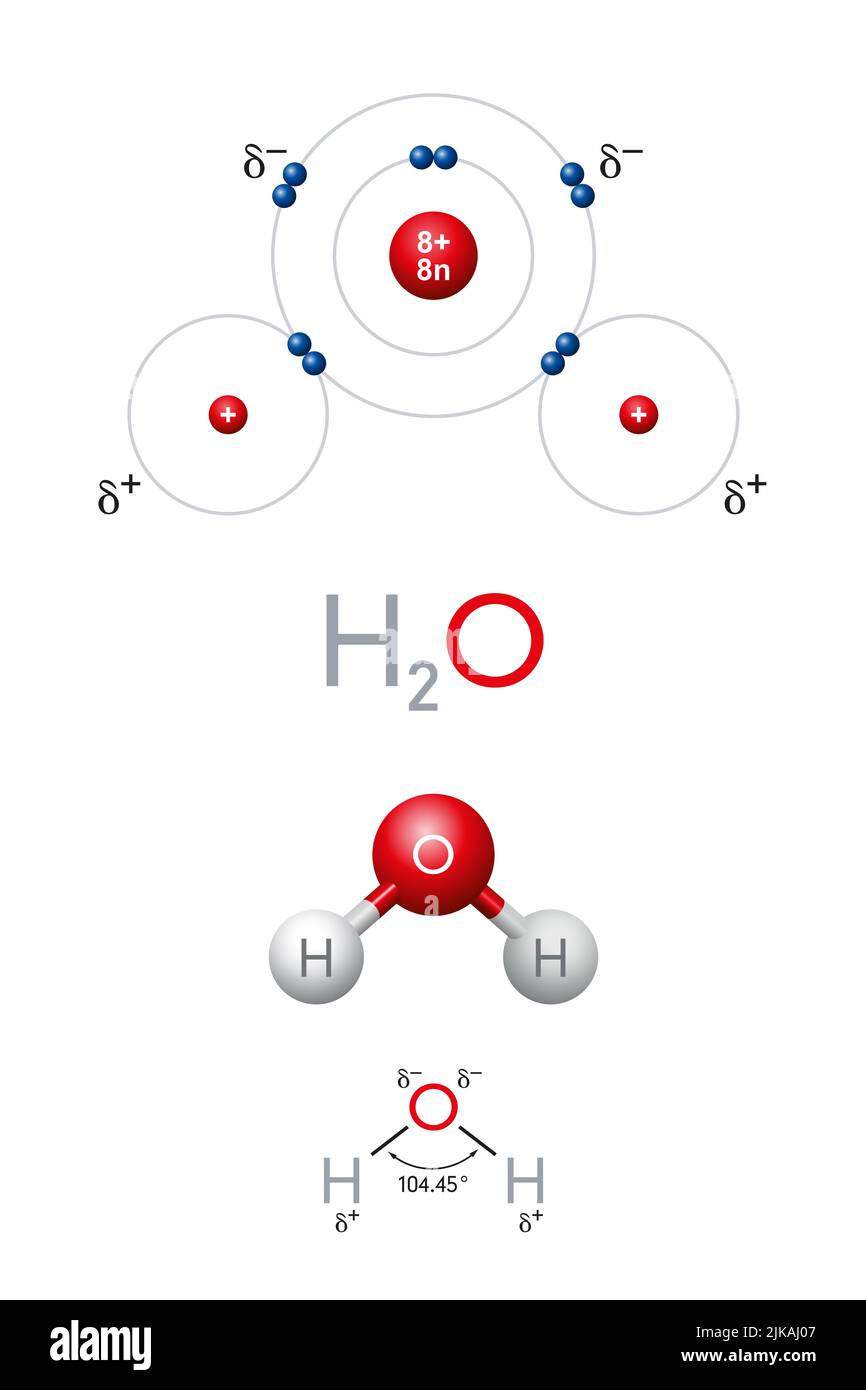
Bond Formation In Water Molecule Stock Image C028 6476 Science Water is a simple molecule consisting of one oxygen atom bonded to two different hydrogen atoms. because of the higher electronegativity of the oxygen atom, the bonds are polar covalent (polar bonds). the oxygen atom attracts the shared electrons of the covalent bonds to a significantly greater extent than the hydrogen atoms. The bent shape of the water molecule is critical because the polar o h bonds do not cancel one another and the molecule as a whole is polar. figure 2 below illustrates the net polarity of the water molecule. the oxygen is the negative end of the molecule, while the area between the hydrogen atoms is the positive end of the molecule.
Covalent Bonding Ammonia (mp –78, bp –33°c) is hydrogen bonded in the liquid and solid states. hydrogen bonding is responsible for ammonia 's remarkably high solubility in water. many organic (carboxylic) acids form hydrogen bonded dimers in the solid state. here the hydrogen bond acceptor is the π electron cloud of a benzene ring. Water is made up of two hydrogens and one oxygen atom, arranged in a tetrahedral shape. oxygen is highly electronegative, which creates a partial negative charge on one end of the molecule, and a partial positive charge on the other. so, water molecules are able to form hydrogen bonds with one another, giving water many of its unique properties. Chemical bonding of water. lewis structure of h 2 o indicating bond angle and bond length. water (h. 2o) is a simple triatomic bent molecule with c 2v molecular symmetry and bond angle of 104.5° between the central oxygen atom and the hydrogen atoms. despite being one of the simplest triatomic molecules, its chemical bonding scheme is. Water is a tiny bent molecule with the molecular formula h 2 o, consisting of two light hydrogen atoms attached to each 16 fold heavier oxygen atom. each molecule is electrically neutral but polar, with the center of positive and negative charges located in different places. each hydrogen atom has a nucleus consisting of a single positively.

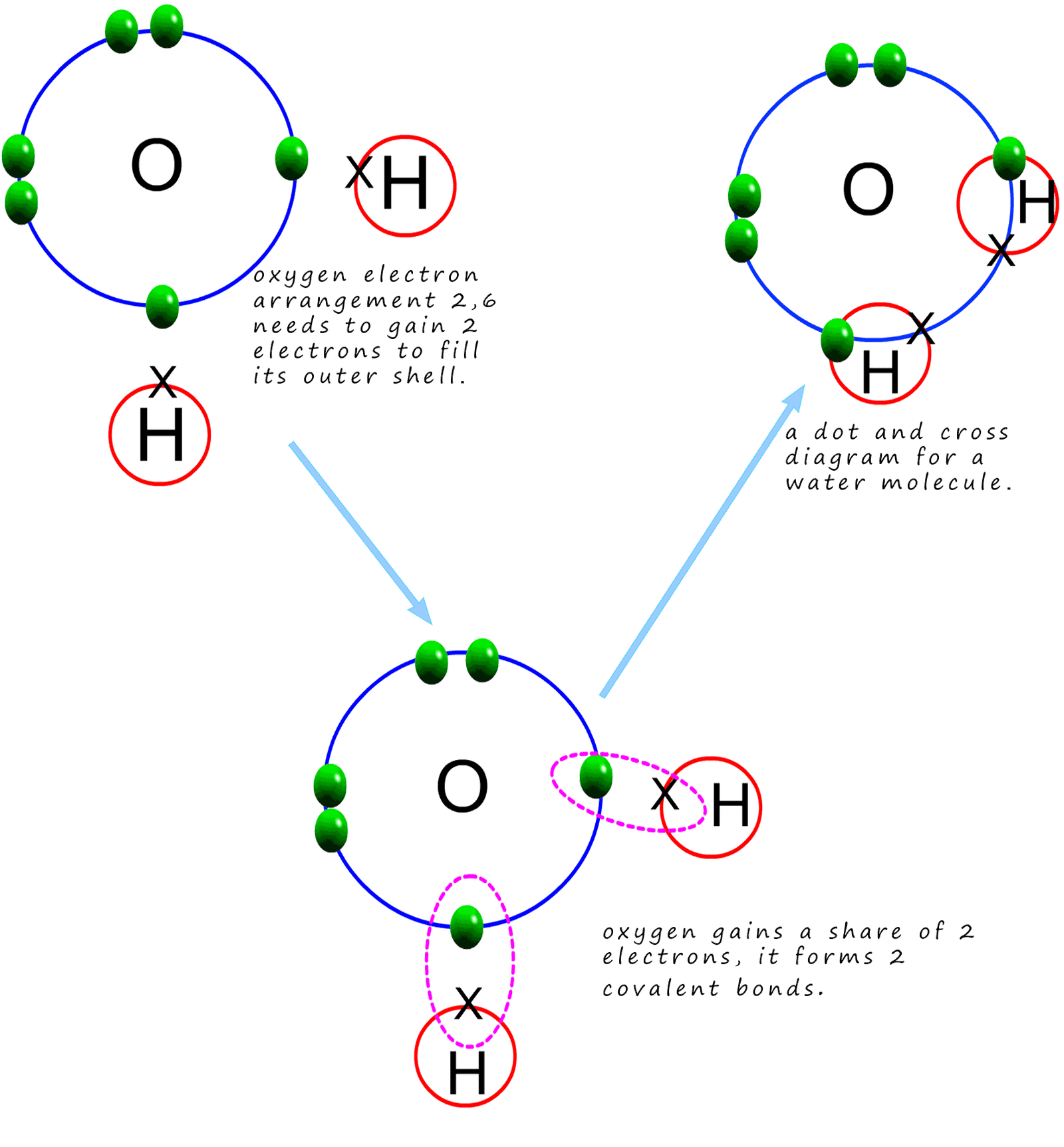
Water Definition Chemical Formula Structure Molecule Facts Chemical bonding of water. lewis structure of h 2 o indicating bond angle and bond length. water (h. 2o) is a simple triatomic bent molecule with c 2v molecular symmetry and bond angle of 104.5° between the central oxygen atom and the hydrogen atoms. despite being one of the simplest triatomic molecules, its chemical bonding scheme is. Water is a tiny bent molecule with the molecular formula h 2 o, consisting of two light hydrogen atoms attached to each 16 fold heavier oxygen atom. each molecule is electrically neutral but polar, with the center of positive and negative charges located in different places. each hydrogen atom has a nucleus consisting of a single positively. Polar water molecule. lesson 5.1 interactive. first frame of the animation: electrons are shared between atoms in a covalent bond. remind students how the shared electrons in a water molecule are attracted to the protons in both the oxygen and the hydrogen atoms. these attractions hold the atoms together. An oxygen atom has 6 electrons in its outer shell. oxygen is in group 6 of the periodic table. a hydrogen atom has 1 electron in its outer shell. hydrogen can only form 1 bond. two hydrogen atoms each share their 1 electron with oxygen to form two covalent bonds and make a water molecule (h 2 o). this is a picture of a water molecule.

Bond Formation In Water Molecule Stock Image C028 6477 Science Polar water molecule. lesson 5.1 interactive. first frame of the animation: electrons are shared between atoms in a covalent bond. remind students how the shared electrons in a water molecule are attracted to the protons in both the oxygen and the hydrogen atoms. these attractions hold the atoms together. An oxygen atom has 6 electrons in its outer shell. oxygen is in group 6 of the periodic table. a hydrogen atom has 1 electron in its outer shell. hydrogen can only form 1 bond. two hydrogen atoms each share their 1 electron with oxygen to form two covalent bonds and make a water molecule (h 2 o). this is a picture of a water molecule.
H2o Hydrogen Bonds Hi Res Stock Photography And Images Alamy

Comments are closed.